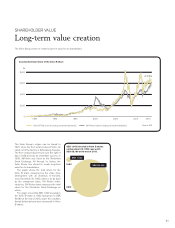
Volvo 2013 Annual Report Download - page 90
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 90 of the 2013 Volvo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
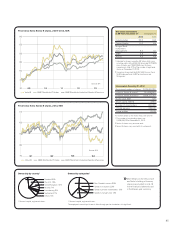
Currencies Interest rates in Sweden, Europe and the U.S.
1005 06 07 08 090403 11 12 13
8.0 7.3 7.5 7.4 6.8 7.8 7.2 6.7 6.9 6.5 6.4
9.1 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.3 10.9 10.4 9.0 8.9 8.6 8.9
6.7 6.5 6.7 5.8 5.8 8.6 7.7 8.3 9.0 7.5 6.1
Source: Reuters
SEK/100 JPY
SEK/USD
SEK/EUR
07
4.3
4.3
4.0
08
2.4
2.9
2.2
03
4.6
4.1
4.0
04
4.4
4.0
4.2
05
3.4
3.4
4.3
06
3.7
3.8
4.8
Source: Reuters
Government bonds, 10 year benchmarks
10
3.3
3.0
3.3
11
1.6
1.8
1.9
12
1.5
1.3
1.8
13
2.5
1.9
3.0
09
3.4
3.4
3.8
%
Sweden
Europe
The U.S.
RISKS AND UNCERTAINTIES
Managed risk-taking
All business operations involve risk – managed risk-taking is a
condition of maintaining a sustained favorable profi tability.
Risk may be due to events in the world and can
affect a given industry or market. Risk can be
specifi c to a single company. At the Volvo Group
work is carried out daily to identify, measure and
manage risk – in some cases the Group can
infl uence the likelihood that a risk-related event
will occur. In cases in which such events are
beyond the Group’s control, the Group strives to
minimize the consequences.
AB Volvo has, for more than fi ve years, worked
with enterprise risk management (ERM), which is
a systematic and structured process to identify,
understand, aggregate, report and mitigate the
risks that might threaten Group strategic objec-
tives. The aim of ERM is to improve business
performance and optimize the costs of manag-
ing risk; i.e. protecting and enhancing the Volvo
Group’s enterprise value. ERM contributes to
meeting the high standards of corporate gov-
ernance expected from the Group’s stakehold-
ers and is looked upon as an integral part of
good corporate governance as refl ected in the
Swedish Corporate Governance Code.
The risks to which the Volvo Group are
exposed are classifi ed into three main categories:
• External-related risks – such as the cyclical
nature of the commercial vehicles business,
intense competition, changes in prices for
commercial vehicles and government regula-
tions.
• Financial risks – such as currency fl uctua-
tions, interest level fl uctuations, market value
of shares or similar instruments, credit risk
and liquidity risk.
• Operational risks – such as market recep-
tion of new products, reliance on suppliers,
protection of intangible assets, complaints
and legal actions by customers and other third
parties and risk related to human capital.
EXTERNAL-RELATED RISK
The commercial vehicles industry
is cyclical
The Volvo Group’s markets undergo signifi cant
changes in demand as the general economic en -
vironment fl uctuates. Investments in infrastruc-
ture, major industrial projects, mining and hous-
ing construction all impact the Group’s opera-
tions as its products are central to these sectors.
Adverse changes in the economic conditions for
the Volvo Group’s customers may also impact ex -
isting order books through cancellations of pre-
viously placed orders. The cyclical demand for the
Group’s products makes the fi nancial result of
the operations dependable on the Group’s ability
to react quickly to changes in demand, in particu-
lar to the ability to adapt production levels and
production and operating expenses.
Intense competition
Continued consolidation in the industry is
expected to create fewer but stronger competi-
tors. Our major competitors are Daimler, Iveco,
MAN, Navistar, Paccar, Scania, Sinotruk, Bruns-
wick, Caterpillar, CNH, Cummins, Deere, Hitachi,
Komatsu and Terex. In recent years, new com-
petitors have emerged in Asia, particularly in
China. These new competitors are mainly active
in their domestic markets, but are expected to
increase their presence in other parts of the world.
Prices may change
The prices of commercial vehicles have, at
times, changed considerably in certain markets
over a short period. This instability is caused by
several factors, such as short-term variations in
demand, shortages of certain component prod-
ucts, uncertainty regarding underlying eco-
nomic conditions, changes in import regulations,
excess inventory and increased competition.
Overcapacity within the industry can occur if
there is a lack of demand, potentially leading to
increased price pressure.
Extensive government regulation
Regulations regarding exhaust emission levels,
noise, safety and levels of pollutants from pro-
duction plants are extensive within the industry.
Most of the regulatory challenges regarding
products relate to reduced engine emissions.
The Volvo Group is a signifi cant player in the
commercial vehicle industry and one of the
world’s largest producers of heavy-duty diesel
engines. The product development capacity with-
in the Volvo Group is well consolidated to be able
to focus resources for research and develop-
ment to meet tougher emission regulations.
Future product regulations are well known, and
the product development strategy is well tuned
to the introduction of new regulations.
FINANCIAL RISK
In its operations, the Volvo Group is exposed to
various types of fi nancial risks. Group-wide
policies, which are updated and decided upon
annually, form the basis of each Group company’s
management of these risks. The objectives of
the Group’s policies for management of fi nan-
cial risks are to optimize the Group’s capital
costs by utilizing economies of scale, to mini-
mize negative effects on income as a result of
changes in currency or interest rates, to opti-
mize risk exposure and to clarify areas of
re sponsibility. Monitoring and control that
established policies are adhered to is continu-
ously conducted. Information about key aspects
of the Group’s system for internal controls and
risk management in conjunction with the fi nan-
cial reporting is provided in the Corporate
Governance Report on page 104–106 in the
printed version. Most of the Volvo Group’s fi nan-
cial transactions are carried out through the
in-house bank, Volvo Treasury, that conducts its
operations within established risk mandates
and limits. Customer credit risks are mainly
managed by the different business areas.
The nature of the various fi nancial risks and
objectives and the policies for the management
of these risks are described in detail in notes 4
and 30. Various aspects of fi nancial risk are
BOARD OF DIRECTORS’ REPORT 2013 GROUP PERFORMANCE
86