Sallie Mae 2014 Annual Report Download - page 119
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 119 of the 2014 Sallie Mae annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.SLM CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
(Dollars in thousands, unless otherwise noted)
10. Borrowed Funds
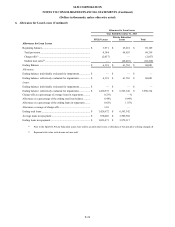
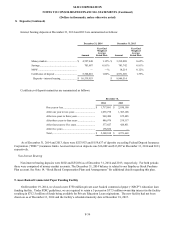
We maintain discretionary uncommitted Federal Funds lines of credit with various correspondent banks, which totaled
$100,000 at December 31, 2014. The interest rate charged to the Company on these lines of credit is priced at Fed Funds plus a
spread at the time of borrowing, and is payable daily. We did not utilize these lines of credit in 2014, 2013 and 2012.
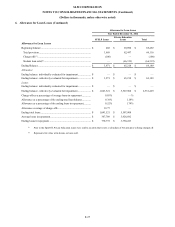
We established an account at the FRB to meet eligibility requirements for access to the Primary Credit borrowing facility
at the FRB’s Discount Window (“Window”). All borrowings at the Window must be fully collateralized. We pledged asset-
backed and mortgage-backed securities, as well as FFELP Loans and Private Education Loans to the FRB as collateral for
borrowings at the Window. Generally, collateral value is assigned based on the estimated fair value of the pledged assets. At
December 31, 2014 and 2013, the lendable value of our collateral at the FRB totaled $1,398,286 and $900,217, respectively.
The interest rate charged to us is the discount rate set by the FRB. We did not utilize this facility in 2014 and 2013.
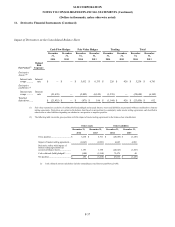
11. Derivative Financial Instruments
Risk Management Strategy
We maintain an overall interest rate risk management strategy that incorporates the use of derivative instruments to
minimize the economic effect of interest rate changes. Our goal is to manage interest rate sensitivity by modifying the repricing
frequency and underlying index characteristics of certain balance sheet liabilities so the net interest margin is not, on a material
basis, adversely affected by movements in interest rates. As a result of interest rate fluctuations, hedged liabilities will
appreciate or depreciate in market value or create variability in cash flows. Income or loss on the derivative instruments that are
linked to the hedged item will generally offset the effect of this unrealized appreciation or depreciation or volatility in cash
flows for the period the item is being hedged. We view this strategy as a prudent management of interest rate risk.
Although we use derivatives to offset (or minimize) the risk of interest rate changes, the use of derivatives does expose us
to both market and credit risk. Market risk is the chance of financial loss resulting from changes in interest rates and market
liquidity. Credit risk is the risk that a counterparty will not perform its obligations under a contract and it is limited to the loss of
the fair value gain in a derivative that the counterparty owes us less collateral held or plus collateral posted. When the fair value
of a derivative contract less collateral held or plus collateral posted is negative, we owe the counterparty and, therefore, we have
no credit risk exposure to the counterparty; however, the counterparty has exposure to us. We minimize the credit risk in
derivative instruments by entering into transactions with highly rated counterparties that are reviewed regularly by our Credit
Department. We also maintain a policy of requiring that all derivative contracts be governed by an International Swaps and
Derivative Association Master Agreement. Depending on the nature of the derivative transaction, bilateral collateral
arrangements generally are required as well. When we have more than one outstanding derivative transaction with the
counterparty, and there exists legally enforceable netting provisions with the counterparty (i.e., a legal right to offset receivable
and payable derivative contracts), the “net” mark-to-market exposure, less collateral held or plus collateral posted, represents
exposure with the counterparty. When there is a net negative exposure, we consider our exposure to the counterparty to be zero.
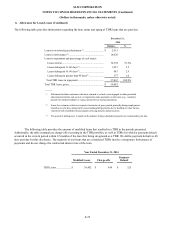
At December 31, 2014 and 2013, we had a net positive exposure (derivative gain positions to us less collateral which has been
posted by counterparties to us) related to derivatives of $60,784 and $3,517, respectively.
Accounting for Derivative Instruments
Derivative instruments that are used as part of our interest rate risk management strategy are interest rate swaps. The
accounting for derivative instruments requires that every derivative instrument, including certain derivative instruments
embedded in other contracts, be recorded on the balance sheet as either an asset or liability measured at fair value. Our
derivative instruments are classified and accounted for by us as fair value hedges and cash flow hedges.
Fair Value Hedges
Fair value hedges are generally used by us to hedge the exposure to changes in fair value of a recognized fixed-rate
liability. We enter into interest rate swaps to economically convert fixed-rate debt into variable rate debt. For fair value hedges,
F-35