Rogers 2012 Annual Report Download - page 84
Download and view the complete annual report
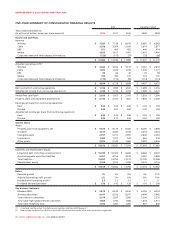
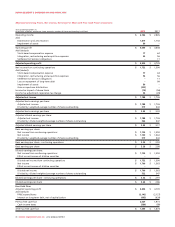
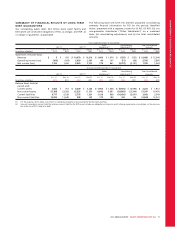
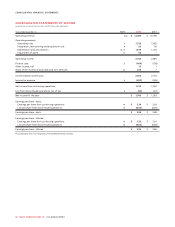
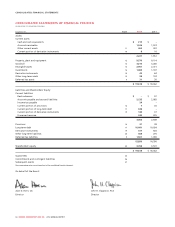
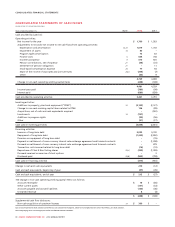
Please find page 84 of the 2012 Rogers annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
• PVR (Personal Video Recorder): A consumer electronics device or
application software that records video in a digital format to a disk
drive, USB flash drive, SD memory card or other local or networked
mass storage device. The term includes set-top boxes with direct to
disk recording facility, portable media players with recording,
recorders such as camcorders that record onto secure digital
memory cards and software for personal computers which enables
video capture and playback to and from a hard disk.
• SAP: A provider of enterprise application software.
• Set-top box: A stand-alone analog or digital device that receives
and decodes programming so that it may be displayed on a
television. Set-top boxes may be used to receive broadcast, cable
and satellite programming.
• SIP (Session Initiation Protocol): A protocol typically used to set up
telephone calls and other real-time communications between users
over the Internet and to and from the PSTN.
• Smartphone: An advanced wireless mobile device or personal
digital assistant (PDA) that provides text messaging, e-mail,
Internet access, multimedia downloads and social networking
functionality in addition to voice.
• Spectrum: A term generally applied to electromagnetic radio
frequencies used in the transmission of sound, data and video.
Various portions of spectrum are designated for cellular service,
television, FM radio, satellite transmissions, etc.
• Streaming media: The process that allows audio or video content to
start playing on your computer screen before the entire file is
downloaded to your machine. Prior to streaming media, users
needed the entire audio or video file on their computer in order to
play.
• SVOD (Subscription Video on Demand): Offers, for a monthly
charge, access to specific programming with unlimited viewing on
an on-demand basis.
• Switched digital video: A cable network technology that enables
the carrier to make all channels available to all subscribers while
not having to physically broadcast every available channel. As only
a percentage of homes on a network node are actively watching a
given channel at a given time, rarely are all channels being
accessed. With switched video, the unwatched channels do not
need to be sent. Instead, a subscribers’ digital box sends a channel
request signal back to the distribution hub and if a channel is not
currently being transmitted on the coaxial line, the distribution
hub allocates a new channel and transmits the requested channel
to the coaxial cable via the fibre-optic node. By sending the digital
video in this more efficient manner, additional uses may be made
of the freed up bandwidth.
• VOD (Video on Demand): A cable service that allows a customer to
select and order movies and shows at any time from a library of
thousands of titles. The content, which is stored on large servers
connected to the cable network, is then delivered via a dedicated
stream to the viewer set up by the network upon request. Viewers
can then pause, fast forward or rewind the content. VOD enables a
cable operator to offer significantly more content than if it had to
broadcast every show in its library separately to all subscribers.
• VoIP (Voice over IP): The technology used to transmit real time
voice conversations in data packets over a data network using
Internet Protocol. Such data networks include telephone company
networks, cable TV networks, wireless networks, corporate
intranets and the Internet.
• VPN (Virtual Private Network): A private data network in which
some of the links between nodes are carried on an open or shared
network (such as the Internet) instead of by dedicated circuits. VPN
traffic over the open or shared network is typically encapsulated
and encrypted (sometimes referred to as “tunnelled”) to ensure
privacy and security is maintained.
• WAN (Wide Area Network): A data network extending/
interconnecting multiple local area network LANs using wireline or
wireless telecommunications.
• WiFi (802.11): WiFi is the commercial name for a networking
technology standard for wireless LANs. Wireless LANs essentially
provide the same service as wired networks, but at lower speeds.
WiFi allows any user with a WiFi enabled device to connect to a
wireless access point at multi-megabit speeds, typically between
11 Mbps and 50 Mbps depending upon the type of technology
chosen and how many users are using the network at a given time.
80 ROGERS COMMUNICATIONS INC. 2012 ANNUAL REPORT