Rogers 2012 Annual Report Download - page 83
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 83 of the 2012 Rogers annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
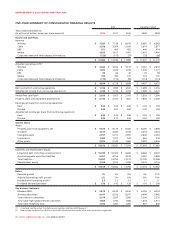
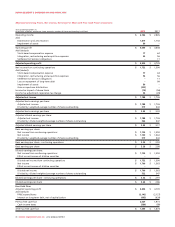
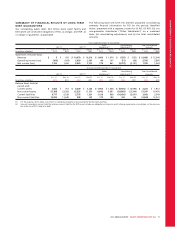
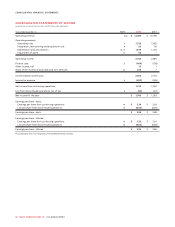
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
• Ethernet: A local area data communications network protocol that
accepts transmissions from computers and terminals and delivers
transmissions over shielded coaxial cable or over shielded twisted
pair telephone wire.
• EV-DO (Evolution Data Optimized): Full name CDMA 2000 EV-DO,
Evolution Data Optimized is part of the CDMA2000 family of standards
and is a wireless radio broadband protocol that delivers download
data rates of up to 3.1 Mbps in its commonly deployed Revision A
specification. CDMA is a generally North America specific standard.
• Facilities-Based Service, Network or Provider: telecom services
company that largely owns the network upon which they sell
services to their customers.
• Fibre-Optics: A method for the transmission of information (voice,
video or data) in which light is modulated and transmitted over
hair-thin filaments of glass called fibre-optic cables. The bandwidth
capacity of fibre-optic cable is much greater than that of copper
wire and light can travel relatively long distances through glass
without the need for amplification. In many cases, fibre-optic
connections must be converted to electrical connections to be
interconnected with networking equipment.
• Frame relay: A standardized WAN technology used for voice and
data transfer between LANs.
• FTTF (Fibre-to-the-Feeder): A term typically used to describe CATV
Fibre to the Node (FTTN) networks. Coaxial cables are normally used
for the terminal network segment (from the node to the end-user).
• Gigabyte (GB): A measure of computer storage capacity. One
gigabyte equals one thousand megabytes.
• Gigahertz (GHz): A measure of frequency. One gigahertz equals
one thousand megahertz.
• GSM (Global System for Mobile): GSM is a TDMA-based technology
and a member of the so-called “second generation” (2G) family of
mobile protocols. GSM is deployed widely across North America,
Europe and around the world, especially at the 850, 900, 1800 and
1900 MHz frequency bands. When delivered in the 1800/1900 MHz
frequency band, GSM is sometimes referred to as PCS (Personal
Communications Services).
• HD (high definition): A resolution that is substantially higher than
that of standard-definition television.
• HFC (Hybrid Fibre Coax): An advanced cable network architecture
that enables a cable television network to carry two-way, digital
traffic for extremely fast Internet access, cable telephony (i.e.,
home phone service) and hundreds of channels of digital television.
• Hotspot: The WiFi wireless access point in a public place such as a
café, train station, airport, commercial office property or
conference centre.
• HSPA+ (High Speed Packet Access): An IP-based packet-data
enhancement to WCDMA technology that provides high-speed
broadband packet data services over 3G networks.
• ILEC (Incumbent Local Exchange Carrier): Typically the traditional
phone company and original local exchange carrier in a given market.
• IP (Internet Protocol): The packet-based computer network
protocol that all machines on the Internet must know so that they
can communicate with one another. IP is basically a set of data
switching and routing rules that specify how information is cut up
into packets and how they are addressed for delivery between
computers.
• LAN (Local Area Network): A private data communications network
linking a variety of data devices, such as personal computers,
servers and printers so that they can share files, all housed in a
defined building or geographic area.
• LTE (Long-Term Evolution): A fourth generation cellular wireless
technology (also known as 4G). Compared to HSPA/UMTS LTE
improves spectral efficiency, lowers costs, improves services and,
most importantly, allows for higher data rates. LTE technology is
being deployed and is designed to deliver at speeds up to 150Mbps
with further increases over time.
• M2M (machine-to-machine): a technology that connects people,
devices, networks and everyday objects while communicating and
interpreting data that can be acted upon in a timely manner. The
underlying technology that enables solutions at the enterprise level
and enables a growing number of connected solutions in the
consumer world.
• Megahertz (MHz): Millions of hertz. A measure of frequency, with
one megahertz equal to one thousand kilohertz.
• MLSE: Maple Leaf Sports and Entertainment, which owns and
operates the Toronto Maple Leafs, the Toronto Raptors, the
Toronto FC and the Toronto Marlies.
• Mobile commerce: The buying and selling of goods and services
through wireless handheld devices such as cellular telephones and
personal digital assistants.
• MPEG (Moving Pictures Experts Group): The group that has defined
the standards for multimedia transmission, including music and
video files. The term can also refer to the file compression/
decompression format itself such as MPEG-2, MPEG-3 or MPEG-4.
• Near-field-communication: A form of contactless communication
between devices like smartphones or tablets.
• Near-net: Buildings that are geographically close to our existing
facilities-based network.
• Off-net: Buildings that are serviced by other facilities-based
network providers.
• On-net: Buildings that are serviced by our facilities-based network.
• Optical wave connectivity: A point-to-point private line service that
is delivered over an optical network using Wavelength Division
Multiplexing technology.
• PCS (Personal Communications Service): A lower powered, higher
frequency competitive wireless technology to first generation
cellular networks. Whereas cellular typically operates in the 800-
900 MHz range, PCS operates in the 1.8-1.9 GHz range, which
typically requires that cells be smaller and closer together.
• POPs (Percentage of Population): A wireless industry term referring
to the percentage of population residing in a market covered by a
wireless network.
• Postpaid: A conventional method of payment for wireless service
where a subscriber pays a fixed monthly fee for a significant
portion of services and the usage is billed in arrears, subsequent to
consuming the services. Usually arranged on a term contract basis.
• PPV (Pay per View): Pay television programming for which cable
subscribers pay a separate fee for each program viewed.
• Prepaid: A method of payment for wireless service that allows a
subscriber to prepay for a set amount of airtime in advance of
actual usage. Generally, a subscriber’s prepaid account is debited at
the time of usage so that actual usage cannot exceed the prepaid
amount until an additional prepayment is made.
2012 ANNUAL REPORT ROGERS COMMUNICATIONS INC. 79