Kodak 2007 Annual Report Download - page 69
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 69 of the 2007 Kodak annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
68
NOTE 13: FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
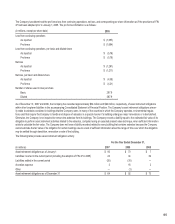
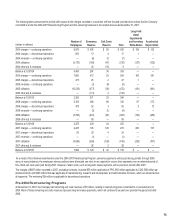
The following table presents the carrying amounts of the assets (liabilities) and the estimated fair values of financial instruments:
(in millions)
As of December 31,
2007 2006
Carrying Amount Fair Value Carrying Amount Fair Value
Marketable securities:
Current $ 29 $ 29 $ 18 $ 18
Long-term — — 4 4
Long-term borrowings (1,289) (1,285) (2,714) (2,740)
Foreign currency forwards (22) (22) (18) (18)
Silver forwards 3 3 — —
Marketable securities are valued at quoted market prices. The fair values of long-term borrowings are determined by reference to quoted market prices.
The fair values for the remaining financial instruments in the above table are determined by reference to quoted market prices and reflect the estimated
amounts the Company would pay or receive to terminate the contracts. The carrying values of cash and cash equivalents, trade receivables, short-term
borrowings and payables approximate their fair values.
The Company, as a result of its global operating and financing activities, is exposed to changes in foreign currency exchange rates, commodity prices and
interest rates, which may adversely affect its results of operations and financial position. The Company manages such exposures, in part, with derivative
financial instruments. The fair values of these derivative contracts are reported in other current assets or accounts payable and other current liabilities in
the accompanying Consolidated Statement of Financial Position.
Foreign currency forward contracts are used to hedge existing foreign currency denominated assets and liabilities, especially those of the Company’s
International Treasury Center, as well as forecasted foreign currency denominated intercompany sales. Silver forward contracts are used to mitigate the
Company’s risk to fluctuating silver prices. The Company’s exposure to changes in interest rates results from its investing and borrowing activities used to
meet its liquidity needs. Long-term debt is generally used to finance long-term investments, while short-term debt is used to meet working capital require-
ments. The Company does not utilize financial instruments for trading or other speculative purposes.
The Company may enter into foreign currency forward contracts that are designated as cash flow hedges of exchange rate risk related to forecasted
foreign currency denominated intercompany sales. Hedge gains and losses are reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) into
cost of goods sold as the inventory transferred in connection with the intercompany sales is sold to third parties. As of December 31, 2007 and 2006, the
Company had no open foreign currency cash flow hedges. During 2007 and 2006, there were no foreign currency cash flow hedges and nothing was
reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) to cost of goods sold. During 2005, gains of $11 million (pre-tax) were reclassified from
accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) to cost of goods sold.
The Company does not apply hedge accounting to the foreign currency forward contracts used to offset currency-related changes in the fair value of
foreign currency denominated assets and liabilities. These contracts are marked to market through net earnings (loss) at the same time that the exposed
assets and liabilities are remeasured through net earnings (loss) (both in other income (charges), net). The majority of the contracts of this type held by the
Company are denominated in euros. As of December 31, 2007, the fair value of these open contracts was an unrealized loss of $22 million (pre-tax). The
effects of foreign currency transactions, including related hedging activities, were gains of $2 million and losses of $1 million and $32 million in the years
2007, 2006, and 2005, respectively, and are included in other income (charges), net in the accompanying Consolidated Statement of Operations.
The Company has entered into silver forward contracts that are designated as cash flow hedges of price risk related to forecasted worldwide silver
purchases. The fair values of silver forward contracts are reported in other current assets and/or accounts payable and current liabilities, and the effective
portion of the gain or loss on the derivative is recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). Hedge gains and losses are reclassified into
cost of goods sold as the related silver-containing products are sold to third parties. These gains (losses) transferred to cost of goods sold are generally
offset by increased (decreased) costs of silver purchased in the open market. As of December 31, 2007, the fair value of open silver forward contracts was
an unrealized gain of $3 million, which is included in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). If this amount were to be realized, all of it would be
reclassified into cost of goods sold during the next twelve months. Additionally, realized gains of $7 million (pre-tax), related to closed silver contracts, have
been deferred in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). These gains will be reclassified into cost of goods sold as the related silver-containing
products are sold, all within the next twelve months. During 2007, realized gains of $1 million (pre-tax) were reclassified from accumulated other compre-
hensive income (loss) to cost of goods sold. Hedge ineffectiveness was insignificant.
The Company’s financial instrument counterparties are high-quality investment or commercial banks with significant experience with such instruments. The
Company manages exposure to counterparty credit risk by requiring specific minimum credit standards and diversification of counterparties. The Company
has procedures to monitor the credit exposure amounts. The maximum credit exposure at December 31, 2007 was not significant to the Company.