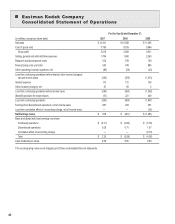
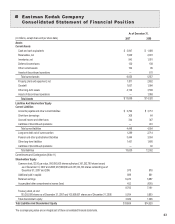
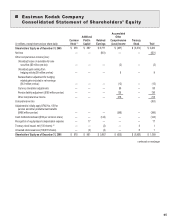
Kodak 2007 Annual Report Download - page 52
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 52 of the 2007 Kodak annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.51
Revenue
The Company’s revenue transactions include sales of the following: products; equipment; software; services; equipment bundled with products and/or ser-
vices and/or software; integrated solutions; and intellectual property licensing. The Company recognizes revenue when realized or realizable and earned,
which is when the following criteria are met: persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; delivery has occurred; the sales price is fixed or determinable;
and collectibility is reasonably assured. At the time revenue is recognized, the Company provides for the estimated costs of customer incentive programs,
warranties and estimated returns and reduces revenue accordingly.
For product sales, the recognition criteria are generally met when title and risk of loss have transferred from the Company to the buyer, which may be upon
shipment or upon delivery to the customer site, based on contract terms or legal requirements in certain jurisdictions. Service revenues are recognized as
such services are rendered.
For equipment sales, the recognition criteria are generally met when the equipment is delivered and installed at the customer site. Revenue is recognized
for equipment upon delivery as opposed to upon installation when there is objective and reliable evidence of fair value for the installation, and the amount
of revenue allocable to the equipment is not legally contingent upon the completion of the installation. In instances in which the agreement with the
customer contains a customer acceptance clause, revenue is deferred until customer acceptance is obtained, provided the customer acceptance clause
is considered to be substantive. For certain agreements, the Company does not consider these customer acceptance clauses to be substantive because
the Company can and does replicate the customer acceptance test environment and performs the agreed upon product testing prior to shipment. In these
instances, revenue is recognized upon installation of the equipment.
Revenue for the sale of software licenses is recognized when: (1) the Company enters into a legally binding arrangement with a customer for the license
of software; (2) the Company delivers the software; (3) customer payment is deemed fixed or determinable and free of contingencies or significant
uncertainties; and (4) collection from the customer is reasonably assured. If the Company determines that collection of a fee is not reasonably assured,
the fee is deferred and revenue is recognized at the time collection becomes reasonably assured, which is generally upon receipt of payment. Software
maintenance and support revenue is recognized ratably over the term of the related maintenance period.
The Company’s transactions may involve the sale of equipment, software, and related services under multiple element arrangements. The Company
allocates revenue to the various elements based on their fair value. Revenue allocated to an individual element is recognized when all other revenue
recognition criteria are met for that element.
The timing and the amount of revenue recognized from the licensing of intellectual property depend upon a variety of factors, including the specific terms
of each agreement and the nature of the deliverables and obligations. When the Company has continuing obligations related to a licensing arrangement,
revenue related to the ongoing arrangement is recognized over the period of the obligation. Revenue is only recognized after all of the following criteria are
met: (1) the Company enters into a legally binding arrangement with a licensee of Kodak’s intellectual property, (2) the Company delivers the technology or
intellectual property rights, (3) licensee payment is deemed fixed or determinable and free of contingencies or significant uncertainties, and (4) collection
from the licensee is reasonably assured.
At the time revenue is recognized, the Company also records reductions to revenue for customer incentive programs in accordance with the provisions
of Emerging Issues Task Force (EITF) Issue No. 01-09, “Accounting for Consideration Given from a Vendor to a Customer (Including a Reseller of the
Vendor’s Products).” Such incentive programs include cash and volume discounts, price protection, promotional, cooperative and other advertising allow-
ances, and coupons. For those incentives that require the estimation of sales volumes or redemption rates, such as for volume rebates or coupons, the
Company uses historical experience and internal and customer data to estimate the sales incentive at the time revenue is recognized.
In instances where the Company provides slotting fees or similar arrangements, this incentive is recognized as a reduction in revenue when payment is
made to the customer (or at the time the Company has incurred the obligation, if earlier) unless the Company receives a benefit over a period of time, in
which case the incentive is recorded as an asset and is amortized as a reduction of revenue over the term of the arrangement. Arrangements in which the
Company receives an identifiable benefit include arrangements that have enforceable exclusivity provisions and those that provide a clawback provision
entitling the Company to a pro rata reimbursement if the customer does not fulfill its obligations under the contract.
The Company may offer customer financing to assist customers in their acquisition of Kodak’s products. At the time a financing transaction is consummat-
ed, which qualifies as a sales-type lease, the Company records equipment revenue equal to the total lease receivable net of unearned income. Unearned
income is recognized as finance income using the effective interest method over the term of the lease. Leases not qualifying as sales-type leases are
accounted for as operating leases. The Company recognizes revenue from operating leases on an accrual basis as the rental payments become due.
The Company’s sales of tangible products are the only class of revenues that exceeds 10% of total consolidated net sales. All other sales classes are
individually less than 10%, and therefore, have been combined with the sales of tangible products on the same line in accordance with Regulation S-X.
Incremental direct costs (i.e. costs that vary with and are directly related to the acquisition of a contract which would not have been incurred but for the
acquisition of the contract) of a customer contract in a transaction that results in the deferral of revenue are deferred and netted against revenue in
proportion to the related revenue recognized in each period if: (1) an enforceable contract for the remaining deliverable items exists; and (2) delivery of
the remaining items in the arrangement is expected to generate positive margins allowing realization of the deferred costs. Otherwise, these costs are
expensed as incurred and included in cost of goods sold in the accompanying Consolidated Statement of Operations.