Burger King 2011 Annual Report Download - page 53
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 53 of the 2011 Burger King annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
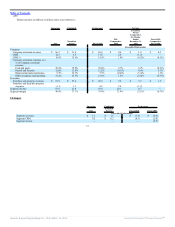
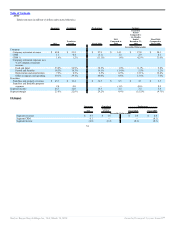
Key Business Metrics
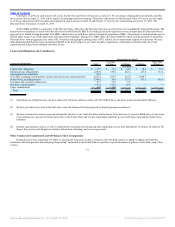
Successor Combined Predecessor
2011
Transition
Period Fiscal 2010 Fiscal 2009
Systemwide sales growth 13.5% 18.6% 4.8% 8.5%
Comparable sales growth
Company 4.3% (3.1)% (4.1)% (3.2)%
Franchise 8.1% 6.8% (1.1)% 2.3%
System 7.9% 6.2% (1.3)% 1.9%
NRG
Company 1 2 5 8
Franchise 81 33 55 68
System 82 35 60 76
Net Refranchisings (trailing twelve months) — — — —
Restaurant counts at period end
Company 97 96 97 92
Franchise 1,125 1,044 1,041 986
System 1,222 1,140 1,138 1,078
2011 compared to 2010
Company restaurants
Company restaurant revenues increased primarily due to positive Company comparable sales growth and slightly favorable FX impact.
CRM % increased primarily as a result of the leveraging effect of positive comparable sales growth on our fixed labor and occupancy and other operating
costs, favorability in food margins primarily driven by a new supplier contract and benefits realized from an adjustment to a previous estimate of occupancy and
other operating costs. These factors were partially offset by a shift in product mix driven by promotions of lower margin menu items, the impact of acquisition
accounting and higher labor costs associated with food delivery and kiosks.
Franchise and Property
Franchise and property revenues increased due to franchise NRG, franchise comparable sales growth, the recognition of cumulative royalties previously
deferred and an increase in initial franchise fees driven by an increase in franchise NRG. Franchise and property expenses decreased due to the recovery of
previously reserved receivables. FX impact was not significant.
Segment income and segment margin
Segment income and margin increased due to an increase in CRM and CRM %, an increase in net franchise and property income and a decrease in
Management G&A.
Transition Period compared to the Six Months Ended December 31, 2009
Company restaurants
Company restaurant revenues increased due to favorable FX impact, partially offset by the effects of negative Company comparable sales growth.
52
Source: Burger King Holdings Inc, 10-K, March 14, 2012 Powered by Morningstar® Document Research℠