ICICI Bank 2009 Annual Report Download - page 176
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 176 of the 2009 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F102
Identification and assessment
Operational risks and controls across the Bank are documented and updated regularly. ORMG facilitates the
business and operation groups for carrying out self assessment on a periodic basis. Risk mitigation plans are
monitored to ensure timely mitigation of risks. Internal controls are tested by Internal Audit and the teams
administering compliance of Sarbanes Oxley Act in the Bank. The testing results are incorporated in the
operational risk assessment. The new product and process approval framework facilitates detailed review of
risks in the products/processes prior to the launch.
Measurement, monitoring, mitigation and reporting
Transactions resulting in operational losses are recorded in a separate operational risk account and are regularly
reported. The Bank has initiated steps to measure bank-wide operational value-at-risk that would facilitate
migration to the Advanced Measurement Approach. Root cause analysis is carried out for the significant
operational risk incidents reported and corrective actions are incorporated back into respective processes.
Operational risk exposures and risk mitigation plans are monitored by ORMC. Operational risk management
status is updated to the Board on a half-yearly basis. Bank-wide operational risk profile is monitored by the
Board on a periodic basis. Operational risk profiles are presented to the business and operations management
on a periodic basis.
For facilitating comprehensive operational risk management, the Bank is in the process of implementing
operational risk management application software during the year ending March 31, 2010.
Operational risk management in international locations
ORMG is responsible for design, development and continuous enhancement of the operational risk management
framework across the Bank including overseas banking subsidiaries and overseas branches. While the common
framework is adopted, suitable modifications in the processes are carried out depending upon the requirements
of the local regulatory guidelines, if any.
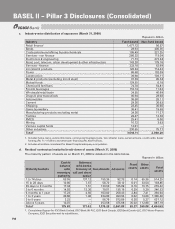
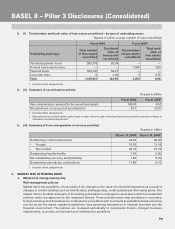
b. Capital requirement for operational risk (March 31, 2009)
As per the mandate from RBI, the Bank had adopted Basic Indicator Approach for computing capital charge
for operational risk. Based on the timelines given by RBI for adopting advanced approaches, the Bank has
taken up quantitative and qualitative steps to migrate to advanced approaches.
Rupees in billion
Amount1
Capital required for operational risk as per Basic Indicator Approach 21.14
1. Includes all entities considered for Basel II capital adequacy computation.
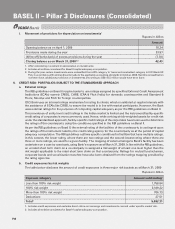
11. INTEREST RATE RISK IN THE BANKING BOOK (IRRBB)
a. Risk Management Framework for IRRBB
Interest rate risk is the risk of potential variability in earnings and capital value resulting from changes in market
interest rates. Interest rate risk in the banking book refers to the risk associated with interest rate sensitive
instruments that are not held in the trading book of the Bank. The Bank holds assets, liabilities and off balance
sheet items across various markets with different maturity or re-pricing dates and linked to different benchmark
rates, thus creating exposure to unexpected changes in the level of interest rates in such markets.
Organizational set-up
Asset Liability Management Committee (ALCO) is a Committee of the Board of Directors with responsibility of
management of the balance sheet of the Bank with a view to manage the market risk exposure assumed by
the Bank within the risk parameters laid down by the Board of Directors/Risk Committee. Structural Rate Risk
Management Group (SRRMG) manages the risk in domestic operations whereas the Asset Liability Management
(ALM) groups in overseas branches are responsible for the risk at their respective branches, under direction
of the Bank’s ALM team for overseas branches. The Board of Directors/Risk Committee/ALCO have oversight
on the functioning of the other entities in the group, including with respect to management of IRRBB. The
treasuries at these entities manage the IRRBB within the parameters approved by respective Boards.
BASEL II – Pillar 3 Disclosures (Consolidated)