Vodafone 2007 Annual Report Download - page 21
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 21 of the 2007 Vodafone annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Vodafone Group Plc Annual Report 2007 19
Our Technology and Resources
Vodafone’s key technologies and resources encompass
the telecommunication licences it holds, the related
mobile network infrastructure and the approximately
66,000 people Vodafone employs worldwide. These
key technologies and resources enable the Group to
operate mobile networks in 21 controlled and jointly
controlled markets around the world.
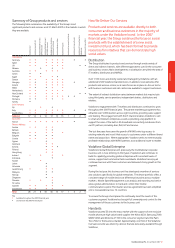
Licences
The Group is dependent on the licences it holds to operate mobile
telecommunications services. Further detail on the issue and regulation of
licences can be found in “Business – Regulation”. The table below
summarises the significant licences held by the Group’s mobile operating
subsidiaries and the Group’s joint venture in Italy at 31 March 2007.
Country by Licence Licence expiry Date of commencement
region type(1) date of commercial service
Europe
Germany 2G December 2009(2) June 1992
3G December 2020 February 2004
Italy 2G January 2015 December 1995
3G December 2021 February 2004
Spain 2G July 2023(3) October 1995
3G April 2020 February 2004
UK 2G See note(4) December 1991
3G December 2021 February 2004
Albania 2G June 2016 August 2001
Greece 2G September 2012 July 1993
3G August 2021 July 2004
Ireland 2G May 2011(5) March 1993
3G October 2022 May 2003
Malta 2G September 2010 July 1997
3G August 2020 August 2006
Netherlands 2G March 2013 September 1995
3G December 2016 February 2004
Portugal 2G October 2021 October 1992
3G January 2016 February 2004(6)
EMAPA
Australia 2G See note(7) September 1993
3G October 2017 October 2005
Czech 2G January 2021 March 2000
Republic 3G February 2025 See note(8)
Egypt 2G January 2022(9) November 1998
3G January 2022 May 2007
Hungary 2G July 2014(10) November 1999
3G December 2019 December 2005
New Zealand 2G See note(11) July 1993
3G March 2021(11) August 2005
Romania 2G December 2011 April 1997
3G March 2020 April 2005
Turkey 2G April 2023 April 1998
Notes:
(1) All 2G networks are of a GSM/GPRS network type. All 3G networks are of a W-CDMA network type.
(2) On 15 May 2007, the Group secured a seven year extension of its GSM licence in Germany to
December 2016.
(3) Date relates to 1800MHz spectrum licence. Vodafone Spain also has a separate 900MHz
spectrum licence which expires in February 2020.
(4) Indefinite licence with a one year notice of revocation.
(5) Date refers to 900MHz licence. Vodafone Ireland also has a separate 1800MHz spectrum
licence which expires in December 2015.
(6) Portugal launched the Vodafone Mobile Connect 3G/GPRS data card in February 2004 and
the launch of 3G voice services took place in May 2005.
(7) Refers to a 900MHz spectrum rolling five year licence. Various licences are held for 1800MHz
licences, which are issued by specific regional regulators. The earliest expires in June 2013
and the latest in March 2015.
(8) Launch date to be determined.
(9) Egypt extended its 2G licence for a further nine years in January 2007.
(10) There is an option to extend this licence for seven years.
(11) Vodafone New Zealand owns three GSM 900 licences (2x21MHz) and one GSM1800 licence
(2x15MHz). The GSM900 licences expire in November 2011, July 2012 and September 2021.
The GSM1800 licence expires in March 2022.
Mobile network infrastructure
Network infrastructure is fundamental to the Group being able to provide
mobile services. The mobile network enables the Group’s customers to
place and receive voice calls and allows the Group to provide other services,
such as text messaging.
When a voice call or data transmission is made on a mobile device, voice or
data is sent from the device and transmitted by low powered radio signals to
the nearest base station, which in turn is connected to the Group’s network.
Each base station provides coverage over a given geographic area, often
referred to as a cell. Cells can be as small as an individual building or as
large as 20 miles across. Each cell is equipped with its own radio transmitter
and receiver antenna. This network of cells provides, within certain
limitations, coverage over the service area. When a customer using a mobile
device approaches the boundary of one cell, the mobile network senses
that the signal is becoming weak and automatically hands over the call to
the transmission unit in the next cell into which the device is moving.
If the voice call or data transmission is intended for delivery to another
device which is not on the Vodafone network, the information is delivered
through a public or private fixed line telephone network or the internet.
In a second generation (“2G”) network, each cell contains a base station
using a number of radio frequencies or channels. A group of base stations is
connected to a base station controller, which in turn is connected to a
mobile switching centre and then via a gateway support node for access to
a fixed line network or the internet.
In a 3G network, voice or data traffic is passed through a node B, being
similar to a base station in a 2G network, to a radio network controller which
is then connected to a mobile switching centre, similar to a 2G network.
Base stations and node Bs form a critical element of a mobile network and
an insufficient number of base stations can result in loss of service for
customers. In addition, the correct deployment of the right base stations is
instrumental in achieving the network quality and coverage that are crucial
to customer satisfaction.
2G
Vodafone operates 2G networks in all its mobile operating subsidiaries,
through GSM networks, offering customers services such as voice, text
messaging and basic data services. In addition, all of the Group’s controlled
networks operate GPRS, often referred to as 2.5G. GPRS allows mobile
devices to be used for sending and receiving data over an internet protocol
(“IP”) based network, enabling wireless access to data networks like the
internet.
The GPRS data service offering includes internet and e-mail access, allowing
the customer to be always connected at download speeds slightly below a
dial-up modem. Vodafone also offers a great variety of services on its
Vodafone live! portal, such as picture and video messaging, download of
ringtones, news and many other services.
3G
Vodafone’s 3G networks, operating the W-CDMA standard, provide
customers with mobile broadband data access allowing data download
speeds of up to 384 kilobits per second (“kbps”), which is up to seven times
faster than a dial-up modem. Vodafone has expanded its service offering on
3G networks with high speed internet and e-mail access, video telephony,
full track music downloads, mobile TV and other data services, in addition to
existing voice and data services.
The Group has secured 3G licences in all jurisdictions in which it operates
through its subsidiary undertakings and in which such licences have been
awarded to date, as well as in Italy through its joint venture. Vodafone
expects to participate in additional 3G licence allocation procedures in
other jurisdictions in which it operates where this is commercially viable. No
assurances can be given that the Group will be successful in obtaining any
3G licences for which it intends to apply or bid.
Business