Vodafone 2007 Annual Report Download - page 142
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 142 of the 2007 Vodafone annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
140 Vodafone Group Plc Annual Report 2007
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
continued
38. US GAAP information continued
d. Goodwill and other intangible assets
The differences related to goodwill and other intangible assets included in
the reconciliations of net loss and shareholders’ equity relate to acquisitions
prior to the Group’s adoption of SEC guidance issued on 29 September 2004.
In determining the value of licences purchased in business combinations
prior to 29 September 2004, the Group allocated the portion of the purchase
price in excess of the fair value attributed to the share of net assets acquired
to licences. The Group had previously concluded that the nature of the
licences and the related goodwill acquired in business combinations was
fundamentally indistinguishable.
Following the adoption of the SEC guidance issued on 29 September 2004,
the Group’s US GAAP accounting policy for initial and subsequent
measurement of goodwill and other intangible assets, other than
determination of impairment of goodwill and finite lived intangible assets, is
substantially aligned to that of IFRS described in note 2. However, there are
substantial adjustments arising prior to 29 September 2004 from different
methods of transition to current IFRS and US GAAP as discussed below.
Goodwill arising before the date of transition to IFRS has been retained under
IFRS at the previous UK GAAP amounts for acquisitions prior to 1 April 2004.
The Group has assigned amounts to licences and customer bases under US
GAAP as they meet the criteria for recognition separately from goodwill, while
these had not been recognised separately from goodwill under UK GAAP
because they did not meet the recognition criteria. Under US GAAP, goodwill
and other intangible assets with indefinite lives are capitalised and not
amortised, but tested for impairment at least annually. Intangible assets with
finite lives are capitalised and amortised over their useful economic lives.
Under IFRS and US GAAP, the purchase price of a transaction accounted for as
an acquisition is based on the fair value of the consideration. In the case of
share consideration, under IFRS the fair value of such consideration is based
on the share price on the date of exchange. Under US GAAP, the fair value of
the share consideration is based on the average share price over a reasonable
period of time before and after the proposed acquisition is agreed to and
announced. This has resulted in a difference in the fair value of the
consideration for certain acquisitions and consequently in the amount of
goodwill capitalised under IFRS and US GAAP.
The Group’s accounting policy for testing goodwill and finite lived intangible
assets for impairment under IFRS is discussed in note 2. For the purpose of
goodwill impairment testing under US GAAP, the fair value of a reporting unit
including goodwill is compared to its carrying value. If the fair value of a
reporting unit is lower than its carrying value, the fair value of the goodwill
within that reporting unit is compared to its respective carrying value, with
any excess carrying value written off as an impairment loss. The fair value of
the goodwill is the difference between the fair value of the reporting unit and
the fair value of the identifiable net assets of the reporting unit. Intangible
assets with finite lives are subject to periodic impairment tests when
circumstances indicate that an impairment loss may exist. Where an asset’s
(or asset group’s) carrying amount exceeds its sum of undiscounted future
cash flows, an impairment loss is recognised in an amount equal to the
amount by which the asset’s (or asset group’s) carrying amount exceeds its
fair value, which is generally based on discounted cash flows.
As a result of the above, there are significant amounts reported as goodwill
and not amortised under IFRS which are reported as licences, customers
and deferred tax liabilities under US GAAP.
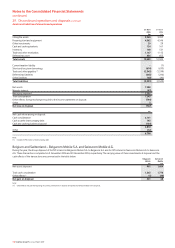
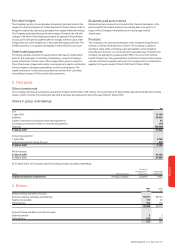
Finite-lived intangible assets
2007 2006
Licences £m £m
Gross carrying value 152,358 154,135
Accumulated amortisation (88,541) (75,170)
63,817 78,965
Customer bases
Gross carrying value 493 1,663
Accumulated amortisation (168) (1,071)
325 592
The total amortisation charge for the year ended 31 March 2007, under US
GAAP, was £15,207 million (2006: £15,011 million; 2005: £15,400 million).
During the year ended 31 March 2007, the Group revised the estimated
useful life of certain customer bases. As a result, an additional £113 million of
amortisation expense has been recorded during the year.
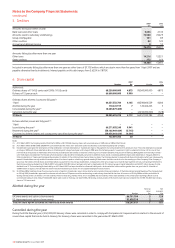
The estimated future amortisation charge on finite-lived intangible assets for
each of the next five years is set out in the following table. The estimate is
based on finite-lived intangible assets recognised at 31 March 2007 using
foreign exchange rates on that date. It is probable that future amortisation
charges will vary from the figures below, as the estimate does not include the
impact of any future investments, disposals, capital expenditures or
fluctuations in foreign exchange rates.
Year ending 31 March £m
2008 14,966
2009 14,959
2010 12,114
2011 3,623
2012 3,355
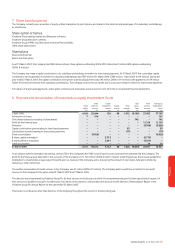
e. Impairment losses
As discussed in note 10, during the year ended 31 March 2007, the Group
recorded impairment losses of £11,600 million (2006: £23,000 million) in
relation to the goodwill of Vodafone Germany and Vodafone Italy under IFRS.
Under US GAAP, the Group evaluated the recoverability of the long-lived
assets, comprised primarily of licences, in Vodafone Germany and Vodafone
Italy using undiscounted cash flows and determined that the carrying
amount of these assets was recoverable. As a result, the IFRS impairment
losses of £11,600 million related to Vodafone Germany and Vodafone Italy
were not recognised under US GAAP.
During the year ended 31 March 2006, the Group also recorded an
impairment loss under IFRS of £515 million and £4,900 million in relation to
the goodwill of Vodafone Sweden and Vodafone Japan, respectively. Under
US GAAP, the Group recognised impairment losses of licences of £883 million
and £8,556 million in Vodafone Sweden and in Vodafone Japan. As a result of
these impairment losses, the Group released related deferred tax liabilities of
£247 million and £3,508 million, which have been included in the
adjustment for income taxes for the period. The impairment losses on
Vodafone Sweden’s and Vodafone Japan’s licences have been included in
discontinued operations under US GAAP.
Cumulative foreign currency gains and losses arising on the translation of the
assets and liabilities into sterling have been included in the carrying value of
a discontinued operation when assessing that carrying value for impairment.
f. Capitalised interest
Under IFRS, the Group has adopted the benchmark accounting treatment for
borrowing costs and, as a result, the Group does not capitalise interest costs
on borrowings in respect of the acquisition or construction of tangible and
intangible fixed assets. Under US GAAP, the interest costs of financing the
acquisition or construction of network assets and other fixed assets is
capitalised during the period of construction until the date that the asset is
placed in service. Interest costs of financing the acquisition of licences are
also capitalised until the date that the related network service is launched.
Capitalised interest costs are amortised over the estimated useful lives of the
related assets.
g. Other
Financial instruments
Under IFRS, equity put rights and similar arrangements are classified as
financial liabilities. The liabilities are measured as the present value of the
estimated exercise prices of the equity put rights and similar arrangements,
which is the fair value of the underlying shares on the date of exercise, with
any changes in this estimate recognised in the consolidated income
statement each period. Under US GAAP, the redemption amount under these
arrangements is credited to the minority interest and changes in the
redemption amount are reflected as a charge or credit to retained earnings.