PNC Bank 2000 Annual Report Download - page 78
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 78 of the 2000 PNC Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
75
restrictive limitations. Such extensions of credit, with limit-
ed exceptions, must be fully collateralized. The maximum
amount available under statutory limitations for transfer
from subsidiary banks to the parent company in the form of
loans and dividends approximated 18% of consolidated net
assets at December 31, 2000.
Federal Reserve Board regulations require depository
institutions to maintain cash reserves with the Federal
Reserve Bank. During 2000, subsidiary banks maintained
reserves which averaged $113 million.
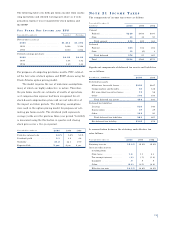
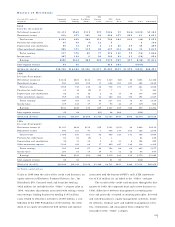
NO T E 1 8 FI N A N C I A L DE R I VAT I V E S
Positive Negative
Notional Fair Notional Fair
In millions Value Value Value Value
December 31, 2000
Interest rate
Swaps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $5,173 $113 $1,814 $(12)
Caps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 308 4
Floors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3,000 1 238 (2)
Total interest rate
risk management . . . . 8,481 118 2,052 (14)
Commercial mortgage
banking risk
management . . . . . . . . . . 121 4 265 (14)
Forward contracts . . . . . . . . 347
Credit default swaps . . . . . . 4,391 (2)
Total . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $8,949 $122 $6,708 $(30)
December 31, 1999
Interest rate
Swaps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $3,666 $46 $5,402 $(108)
Caps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 474 12
Floors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3,000 1 311 (1)
Total interest rate
risk management . . . . 7,140 59 5,713 (109)
Commercial mortgage
banking risk
management . . . . . . . . . . 643 51
Forward contracts . . . . . . . . 681
Credit default swaps . . . . . . 60 4,255 (4)
Total . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $8,524 $110 $9,968 $(113)
The Corporation uses a variety of off-balance-sheet financial
derivatives as part of the overall risk management process
and to manage interest rate, market and credit risk inherent
in the Corporation’s business activities. Financial deriva-
tives involve, to varying degrees, interest rate and credit
risk in excess of the amount recognized on the balance
sheet but less than the notional amount of the contract. For
interest rate swaps and purchased interest rate caps and
floors, only periodic cash payments and, with respect to
such caps and floors, premiums are exchanged. Therefore,
cash requirements and exposure to credit risk are signifi-
cantly less than the notional value. The Corporation man-
ages these risks as part of its asset and liability
management process and through credit policies and proce-
dures. The Corporation seeks to minimize the credit risk by
entering into transactions with only a select number of high-
quality institutions, establishing credit limits, requiring
bilateral-netting agreements, and, in certain instances, seg-
regated collateral.
The Corporation uses interest rate swaps and pur-
chased caps and floors to modify the interest rate character-
istics of designated interest-bearing assets or liabilities from
fixed to variable, variable to fixed, or one variable index to
another. At December 31, 2000, $7.0 billion of interest rate
swaps, caps and floors were designated to loans. At
December 31, 2000, $135 million of financial derivatives
were designated to securities available for sale. During
2000, derivative contracts modified the average effective
yield on interest-earning assets from 7.93% to 7.85% . At
December 31, 2000, $3.5 billion of interest rate swaps were
designated to interest-bearing liabilities. During 2000,
derivative contracts had no impact on the average rate on
interest-bearing liabilities of 5.01% .
PNC also uses interest rate swaps to manage interest
rate risk associated with its commercial mortgage banking
activities.
Forward contracts are used to manage risk positions
associated with student lending activities. Substantially all
forward contracts mature within 90 days of origination.
Forward contracts are traded in over-the-counter markets
and do not have standardized terms. In the event the coun-
terparty is unable to meet its contractual obligations, the
Corporation may be exposed to selling or purchasing stu-
dent loans at prevailing market prices. Unrealized gains or
losses are considered in the lower of cost or market valua-
tion of loans held for sale.
Credit default swaps are used to mitigate credit risk
and lower the required regulatory capital associated with
commercial lending activities.
At December 31, 2000 and 1999, the Corporation’s
exposure to credit losses with respect to financial deriva-
tives was not material.