Asus 2014 Annual Report Download - page 169
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 169 of the 2014 Asus annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
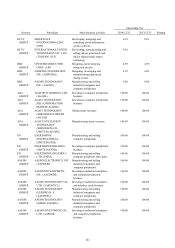 165
165 -
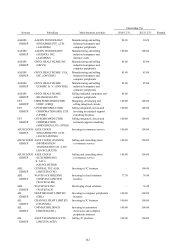 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268
 |
 |

165
(A) Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies at the period end are
re-translated at the exchange rates prevailing at the end of the financial reporting period.
Exchange differences arising upon re-translation at the end of the financial reporting period
are recognized in profit or loss.
(B) Non-monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies at fair value through
profit or loss are re-translated at the exchange rates prevailing at the end of the financial
reporting period. The translation differences are recognized in profit or loss as part of the
fair value gain or loss. Non-monetary assets and liabilities at fair value through other
comprehensive income are re-translated at the exchange rates prevailing at the end of the
financial reporting period. The translation differences are recognized in other
comprehensive income. However, non-monetary assets and liabilities denominated in
foreign currencies that are not measured at fair value are translated using the historical
exchange rates at the dates of the initial transactions.
(C) All other foreign exchange gains and losses based on the nature of those transactions are
presented in the statement of comprehensive income within “other gains (losses)”.
B. Translation of foreign operations
(A) The operating results and financial position of all the group entities and associates that
have a functional currency different from the presentation currency are translated into the
presentation currency as follows:
a. Assets and liabilities for each balance sheet presented are translated at the closing
exchange rate at the end of the financial reporting period;
b. Income and expenses for each statement of comprehensive income are translated at
average exchange rates of that period; and
c. All resulting exchange differences are recognized in other comprehensive income.
(B) When the foreign operation partially disposed of or sold is an associate, exchange
differences that were recorded in other comprehensive income are proportionately
reclassified to profit or loss as part of the gain or loss on sale. In addition, if the Group
retains partial interests in the former foreign associate after losing significant influence over
the former foreign associate, such transactions should be accounted for as disposal of all
interest in these foreign operations.
(C) When the foreign operation partially disposed of or sold is a subsidiary, cumulative
exchange differences that were recorded in other comprehensive income are
proportionately transferred to the non-controlling interest in this foreign operation. In
addition, if the Group retains partial interests in the former foreign subsidiary after losing
control of the former foreign subsidiary, such transactions should be accounted for as
disposal of all interest in these foreign operations.
(5) Classification of current and non-current items
A. Assets that meet one of the following criteria are classified as current assets:
(A) Assets arising from operating activities that are expected to be realized, or are intended to
be sold or consumed within the normal operating cycle;
(B) Assets held mainly for trading purposes;
