Experian 2007 Annual Report Download - page 99
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 99 of the 2007 Experian annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Experian Annual Report2007 |97
24. Retirement benefit assets/obligations (continued)
(a) Defined Benefit Schemes (continued)
(viii) The valuations used for IAS 19 have been based on the most recent actuarial funding valuations and have been updated by Watson Wyatt
Limited to take account of the requirements of IAS 19 in order to assess the liabilities of the scheme at 31 March 2007. The principal actuarial
assumptions used to calculate the present value of the defined benefit obligations were as follows:
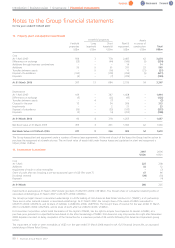
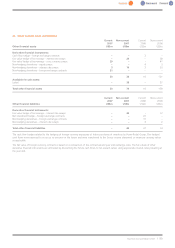
UK schemes 2007 2006
%%
Rate of inflation 3.1 2.9
Rate of increase for salaries 4.9 4.7
Rate of increase for pensions in payment and deferred pensions 3.1 2.9
Rate of increase for medical costs 6.5 6.5
Discount rate 5.4 4.9
Overseas schemes 2006
%
Rate of inflation 2.7
Rate of increase for salaries n/a
Rate of increase for pensions in payment and deferred pensions –
Rate of increase for medical costs 11.5
Discount rate 5.1
The main financial assumption is the real discount rate, i.e. the excess of the discount rate over the rate of inflation. If this assumption
increased/decreased by 0.1%, the UK defined benefit obligation would decrease/increase by approximately US$17m and the annual UK current
service cost would decrease/increase by approximately US$1m. The discount rate is based on the market yields on high quality corporate bonds of
equivalent currency and term to the defined benefit obligations.
The IAS 19 valuation assumes that mortality will be in line with current standard tables for males and females as used at the last actuarial valuation.
An allowance is also made for anticipated future improvements in life expectancy, by assuming that the probability of death occurring at each age
will decrease by 0.25% each year. If this assumption decreased by a further 0.25% per annum then the defined benefit obligation would increase
by US$40m and the annual UK current service cost would increase by approximately US$3m.
Overall, the average expectation of life on retirement in normal health is assumed to be:
–19.1 years at age 65 for a male currently aged 65
–22.2 years at age 65 for a female currently aged 65
–19.8 years at age 65 for a male currently aged 50
–23.1 years at age 65 for a female currently aged 50
The assumptions in respect of discount rate, salaryincreases and mortality all have a significant effect on the IAS 19 accounting valuation. Changes
to these assumptions in the light of prevailing conditions may have a significant impact on future valuations.
The IAS 19 valuation, in respect of post-retirement healthcare insurance benefits provided to certain former Group employees, additionally assumes
arate of increase for medical costs. If this assumption increased/decreased by 1.0% per annum then the obligation would increase/decrease by
US$2m and the annual UK current service cost would remain unchanged.