Experian 2007 Annual Report Download - page 68
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 68 of the 2007 Experian annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Introduction | Business review | Governance | Financial statements
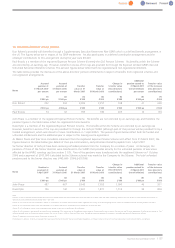
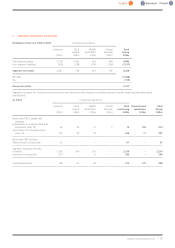
2. Basis of preparation and significant accounting policies (continued)
On consolidation, exchange differences arising from the translation of the net investment in foreign entities, and of borrowings and other currency
instruments, primarily foreign exchange contracts, designated as hedges of such investments, are taken to equity. Tax charges and credits
attributable to those exchange differences are taken directly to equity. When a foreign operation is sold, such exchange differences are recognised
in the Group income statement as part of the gain or loss on sale. Goodwill and fair value adjustments arising on the acquisition of a foreign entity
are treated as assets and liabilities of the foreign entity and are translated at the closing rate.
Share-based payments
IFRS 2 ‘Share-based Payment’ applies to equity instruments, such as share options granted since 7 November 2002. The Group elected to adopt full
retrospective application of the standard on all share options and awards granted to employees before 7 November 2002 but not vested at the date
of transition to IFRS (1 April 2004).
The Group has a number of equity settled, share-based compensation plans. These include awards in respect of shares in Experian Group Limited
made at or after demerger together with awards previously made in respect of shares in GUS plc which were rolled over into awards in respect of
shares in Experian Group Limited at demerger. The fair value of options and shares granted is recognised as an expense in the income statement on
astraight line basis over the vesting period after taking into account the Group’s best estimate of the number of awards expected to vest. The
Group revises the vesting estimate at each balance sheet date. Non-market performance conditions are included in the vesting estimates. Expenses
areincurred over the vesting period. Fair value is measured at the date of grant using whichever of the Black-Scholes, Monte Carlo model and
closing market price is most appropriate to the award. Market based performance conditions are included in the fair value measurement on grant
date and are not revised for actual performance.
Goodwill
Goodwill is the excess of the fair value of the consideration payable for an acquisition over the fair value of the Group’s share of identifiable net
assets of a subsidiary or associate acquired at the date of acquisition. Fair values are attributed to the identifiable assets, liabilities and contingent
liabilities that existed at the date of acquisition, reflecting their condition at that date. Adjustments aremade wherenecessaryto bring the
accounting policies of acquired businesses into alignment with those of the Group.
Goodwill on acquisitions of subsidiaries is separately recognised in the balance sheet. Goodwill on acquisitions of associates is included in the
carrying amount of the investment. Goodwill is stated at cost less any impairment. Goodwill is not amortised but is tested annually for impairment.
An impairment charge is recognised for any amount by which the carrying value of goodwill exceeds its recoverable amount.
Goodwill is allocated to cash generating units (‘CGUs’) and monitored for internal management purposes by geographical segment. The allocation
is made to those CGUs or groups of CGUs that are expected to benefit from the business combination in which the goodwill arose. Where the
recoverable amount of the CGU is less than its carrying amount, including goodwill, an impairment loss is recognised in the Group income
statement.
Gains and losses on the disposal of an entity include the carrying amount of goodwill relating to the entity sold, allocated where necessary on the
basis of relative fair value.
Other intangible assets
Intangible assets acquired as part of an acquisition of a business are capitalised separately from goodwill, if those assets are identifiable, separable
or arising from legal rights and their fair value can be measured reliably. Intangible assets acquired separately from the acquisition of a business are
capitalised at cost. Certain costs incurred in the developmental phase of an internal project arecapitalised as intangible assets provided that a
number of criteria aresatisfied. These include the technical feasibility of completing the asset so that it is available for use or sale, the availability of
adequate resources to complete the development and to use or sell the asset and how the asset will generate probable future economic benefit.
The cost of other intangible assets with finite useful economic or contractual lives is amortised over those lives. The carrying values of intangible
assets are reviewed for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying values may not be recoverable. If impaired
the carrying values are written down to the higher of fair value less costs to sell, and value-in-use. Value-in-use is determined by reference to
projected future income streams using assumptions in respect of profitability and growth.
Research expenditure is charged in the Group income statement in the year in which it is incurred.
Databases and computer software
Databases
Capitalised databases comprise the fair value of databases acquired as partof a business combination or the data purchase and data capture costs
of internally developed databases.
Databases are held at cost and are amortised on a straight line basis over three to seven years.
Computer software
Acquired computer softwarelicences arecapitalised on the basis of the costs incurred to acquireand bring into use the specific software. Computer
software licences are held at cost and are amortised on a straight line basis over three to five years.
Costs that are directly associated with the production of identifiable and unique software products controlled by the Group, and that will generate
economic benefits beyond one year,are recognised as intangible assets. Computer softwaredevelopment costs recognised as assets areamortised
on a straight line basis over three to five years. Other costs associated with developing or maintaining computer softwareprogrammes are
recognised as an expense as incurred.
Notes to the Group financial statements
for the year ended 31 March 2007
66 |Experian Annual Report2007