Wells Fargo 2013 Annual Report Download - page 55
Download and view the complete annual report
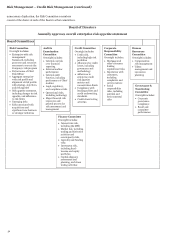
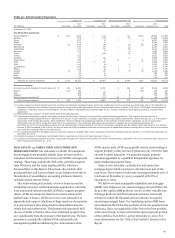
Please find page 55 of the 2013 Wells Fargo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Management’s Oversight of Risk
The Board and its committees work closely with management
in overseeing risk. Each Board committee receives reports and
information regarding risk issues directly from management.
Managers are accountable for managing risks through day-to-
day operations and, in some cases, management committees
have been established to inform the risk management
framework and provide governance and advice regarding
management functions. These committees include:
x The Operating Committee, which meets weekly to,
among other things, discuss strategic, operational and risk
issues at the enterprise level.
x The Enterprise Risk Management Committee
(ERMC), which meets regularly during the year and
reviews significant and emerging risk topics and high-risk
business initiatives, particularly those that may result in
additional regulatory or reputational risk.
x The Asset and Liability Committee (ALCO), which is
responsible for enterprise-wide oversight of the Company's
balance sheet, interest rate exposure, market risks,
liquidity, and capital. The committee provides guidance
and recommendations to management and the Board
related to risk management for these areas.
x The Market Risk Committee, which provides oversight
of the Company’s market risk exposures to ensure
significant market risks throughout the Company are
identified, measured and monitored in accordance with
the Company’s stated risk appetite.
x The Compliance and Operational Risk Committee
(CORC), which provides a forum for senior risk managers
to focus on enterprise-wide compliance and operational
risk issues, and provides leadership and direction in
evaluating management of operational risks, establishing
priorities, and fostering collaboration and coordination of
risk management activities across the Company.
x The Regulatory Compliance Risk Management
Committee (RCRM), which provides a forum for senior
compliance managers to provide leadership, direction, and
assessment of the management of enterprise-wide
regulatory risks, and to escalate such risks to the chief
compliance officer as necessary
x The Corporate Allowance for Credit Losses
Approval Committee, which reviews the process and
supporting analytics for allowance for loan and lease losses
and the allowance for unfunded credit commitments to
help ensure allowances for credit losses are maintained at
adequate levels in conformity with generally accepted
accounting principles and regulatory guidelines.
These committees help management facilitate enterprise-
wide understanding and monitoring of risks and challenges
faced by the Company. Management’s corporate risk
organization, which is part of the second line of defense, is
headed by the Company’s Chief Risk Officer who, among other
things, provides oversight, opines on the performance and
strategy of all risks taken by the businesses, and provides
credible challenge to risks incurred. The Chief Risk Officer, as
well as the Chief Enterprise, Credit, Market, and Operational
Risk Officers as his or her direct reports, work closely with the
Board’s committees and frequently provide reports and
updates to the committees and the committee chairs on risk
issues during and outside of regular committee meetings, as
appropriate. The full Board receives reports at each of its
meetings from the committee chairs about committee
activities, including risk oversight matters, and receives a
quarterly report from the ERMC regarding current or emerging
risk issues.
Further discussion and specific examples of reporting,
measurement and monitoring techniques we use in each risk
area are included within the subsequent sub-sections of the
Risk Management section in this Report.
Operational Risk Management
Operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or
failed internal processes or systems, or resulting from external
events or third parties. Information security is a significant
operational risk for financial institutions such as Wells Fargo,
and includes the risk of losses resulting from cyber attacks.
Wells Fargo and reportedly other financial institutions
continue to be the target of various evolving and adaptive
denial-of-service or other cyber attacks as part of what appears
to be a coordinated effort to disrupt the operations of financial
institutions and potentially test their cybersecurity capabilities.
Wells Fargo has not experienced any material losses relating to
these or other cyber attacks. Cybersecurity and the continued
development and enhancement of our controls, processes and
systems to protect our networks, computers, software, and data
from attack, damage or unauthorized access remain a priority
for Wells Fargo. See the “Risk Factors” section in this Report
for additional information regarding the risks associated with a
failure or breach of our operational or security systems or
infrastructure, including as a result of cyber attacks.
53