Wells Fargo 2013 Annual Report Download - page 190
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 190 of the 2013 Wells Fargo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.investors. Generally, CLOs are structured on behalf of a third
party asset manager that typically selects and manages the assets
for the term of the CLO. Typically, the asset manager has the
power over the significant decisions of the VIE through its
discretion to manage the assets of the CLO. We assess whether
we are the primary beneficiary of CLOs based on our role in
them and the variable interests we hold. In most cases, we are
not the primary beneficiary because we do not have the power to
manage the collateral in the VIE.
In addition to our role as arranger, we may have other forms
of involvement with these CLOs. Such involvement may include
acting as underwriter, derivative counterparty, secondary market
maker or investor. For certain CLOs, we may also act as the
servicer, for which we receive fees in connection with that role.
We also earn fees for arranging these CLOs and distributing the
securities.
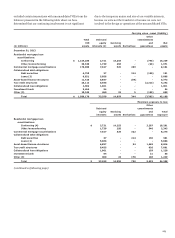
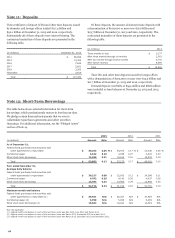
ASSET-BASED FINANCE STRUCTURES We engage in various
forms of structured finance arrangements with VIEs that are
collateralized by various asset classes including energy contracts,
auto and other transportation leases, intellectual property,
equipment and general corporate credit. We typically provide
senior financing, and may act as an interest rate swap or
commodity derivative counterparty when necessary. In most
cases, we are not the primary beneficiary of these structures
because we do not have power over the significant activities of
the VIEs involved in them.
For example, we have investments in asset-backed securities
that are collateralized by auto leases or loans and cash reserves.
These fixed-rate and variable-rate securities have been
structured as single-tranche, fully amortizing, unrated bonds
that are equivalent to investment-grade securities due to their
significant overcollateralization. The securities are issued by
VIEs that have been formed by third party auto financing
institutions primarily because they require a source of liquidity
to fund ongoing vehicle sales operations. The third party auto
financing institutions manage the collateral in the VIEs, which is
indicative of power in them and we therefore do not consolidate
these VIEs.
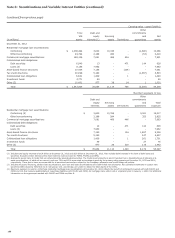
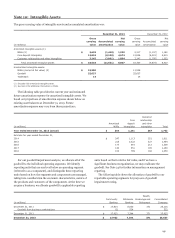
TAX CREDIT STRUCTURES We co-sponsor and make
investments in affordable housing and sustainable energy
projects that are designed to generate a return primarily through
the realization of federal tax credits. In some instances, our
investments in these structures may require that we fund future
capital commitments at the discretion of the project sponsors.
While the size of our investment in a single entity may at times
exceed 50% of the outstanding equity interests, we do not
consolidate these structures due to the project sponsor’s ability
to manage the projects, which is indicative of power in them.
INVESTMENT FUNDS We do not consolidate the investment
funds because we do not absorb the majority of the expected
future variability associated with the funds’ assets, including
variability associated with credit, interest rate and liquidity risks.
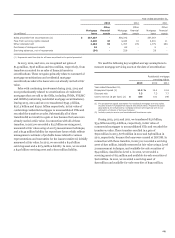
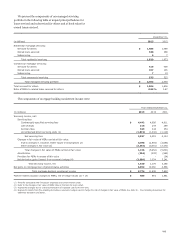
OTHER TRANSACTIONS WITH VIEs Auction rate securities
(ARS) are debt instruments with long-term maturities, but
which re-price more frequently, and preferred equities with no
maturity. At December 31, 2013, we held in our securities
available-for-sale portfolio $653 million of ARS issued by VIEs
redeemed pursuant to agreements entered into in 2008 and
2009, compared with $686 million at December 31, 2012.
We do not consolidate the VIEs that issued the ARS because
we do not have power over the activities of the VIEs.
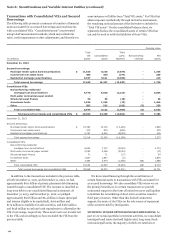
TRUST PREFERRED SECURITIES VIEs that we wholly own
issue debt securities or preferred equity to third party investors.
All of the proceeds of the issuance are invested in debt securities
or preferred equity that we issue to the VIEs. The VIEs’
operations and cash flows relate only to the issuance,
administration and repayment of the securities held by third
parties. We do not consolidate these VIEs because the sole assets
of the VIEs are receivables from us, even though we own all of
the voting equity shares of the VIEs, have fully guaranteed the
obligations of the VIEs and may have the right to redeem the
third party securities under certain circumstances. In our
consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2013 and
December 31, 2012, we reported the debt securities issued to the
VIEs as long-term junior subordinated debt with a carrying
value of $1.9 billion and $4.9 billion, respectively, and the
preferred equity securities issued to the VIEs as preferred stock
with a carrying value of $2.5 billion at both dates. These
amounts are in addition to the involvements in these VIEs
included in the preceding table.
In 2013, we redeemed $2.8 billion of trust preferred
securities that will no longer count as Tier 1 capital under the
Dodd-Frank Act and the Basel Committee recommendations
known as the Basel III standards.
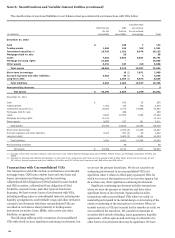
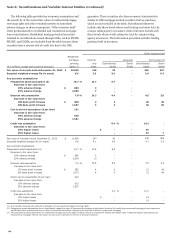
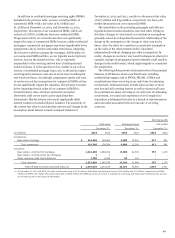
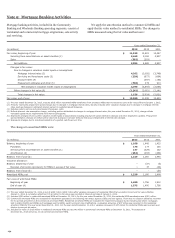
Securitization Activity Related to Unconsolidated
VIEs
We use VIEs to securitize consumer and CRE loans and other
types of financial assets, including student loans and auto loans.
We typically retain the servicing rights from these sales and may
continue to hold other beneficial interests in the VIEs. We may
also provide liquidity to investors in the beneficial interests and
credit enhancements in the form of standby letters of credit.
Through these securitizations we may be exposed to liability
under limited amounts of recourse as well as standard
representations and warranties we make to purchasers and
issuers. The following table presents the cash flows with our
securitization trusts that were involved in transfers accounted
for as sales.
Note 8: Securitizations and Variable Interest Entities (continued)
188