Wells Fargo 2012 Annual Report Download - page 52
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 52 of the 2012 Wells Fargo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Risk Management
All financial institutions must manage and control a variety of
business risks that can significantly affect their financial
performance. Among the key risks that we must manage are
credit risks, asset/liability interest rate and market risks, and
operational risks. Our Board of Directors (Board) and executive
management have overall and ultimate responsibility for
management of these risks, which they carry out through
committees with specific and well-defined risk management
functions. For example, the Board’s Credit Committee oversees
the annual credit quality plan and lending policies, credit
trends, the allowance for credit loss policy, and high risk
portfolios and concentrations. The Finance Committee
oversees the Company’s major financial risks, including
market, interest rate, and liquidity and funding risks, as well as
equity exposure and fixed income investments, and also
oversees the Company’s capital management and planning
processes. The Audit and Examination Committee oversees
operational, legal and compliance risk, in addition to the
policies and management activities relating to the Company’s
financial reporting. The Risk Committee oversees the
Company’s enterprise-wide risk management framework,
including the strategies, policies, processes and systems used to
identify, assess, measure and manage the major risks facing the
Company. The Risk Committee does not duplicate the risk
oversight of the Board’s other committees, but rather helps
ensure end-to-end ownership of oversight of all risk issues in
one Board committee and enhances the Board’s and
management’s understanding of the Company’s aggregate
enterprise-wide risk appetite.
The Board and its committees work closely with
management in overseeing risk. Each Board committee
receives reports and information regarding risk issues directly
from management and, in some cases, management
committees have been established to inform the risk
management framework and provide governance and advice
regarding risk management functions. These management
committees include the Company’s Operating Committee,
which consists of the Company’s senior executives who report
to the CEO and who meet weekly to, among other things,
discuss strategic, operational and risk issues at the enterprise
level, and the Enterprise Risk Management Committee, which
is chaired by the Company’s Chief Risk Officer and includes
other senior executives responsible for managing risk across
the Company. Management’s corporate risk organization is
headed by the Chief Risk Officer who, among other things,
oversees the Company’s credit, market and operational risks.
The Chief Risk Officer and the Chief Credit, Market and
Operational Risk Officers, who report to the Chief Risk Officer,
work closely with the Board’s Risk, Credit and Audit and
Examination Committees and frequently provide reports to
these and other Board committees and update the committee
chairs and other Board members on risk issues outside of
regular committee meetings, as appropriate. The full Board
receives reports at each of its meetings from the committee
chairs about committee activities, including risk oversight
matters, and receives a quarterly report from the Enterprise
Risk Management Committee regarding current or emerging
risk issues.
Operating Risk Management
Effective management of operational risks, which include risks
relating to management information systems, security systems,
and information security, is also an important focus for
financial institutions such as Wells Fargo. Wells Fargo and
reportedly other financial institutions have been the target of
various denial-of-service or other cyber attacks as part of what
appears to be a coordinated effort to disrupt the operations of
financial institutions and potentially test their cybersecurity in
advance of future and more advanced cyber attacks. To date
Wells Fargo has not experienced any material losses relating to
these or other cyber attacks. Cybersecurity and the continued
development and enhancement of our controls, processes and
systems to protect our networks, computers, software, and data
from attack, damage or unauthorized access remain a priority
for Wells Fargo. See the “Risk Factors” section of this Report
for additional information regarding the risks associated with a
failure or breach of our operational or security systems or
infrastructure, including as a result of cyber attacks.
Credit Risk Management
Loans represent the largest component of assets on our balance
sheet and their related credit risk is among the most significant
risks we manage. We define credit risk as the risk of loss
associated with a borrower or counterparty default (failure to
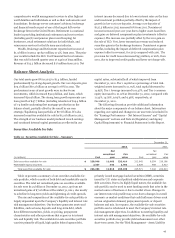
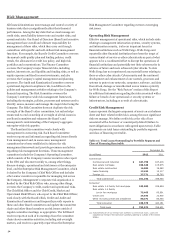
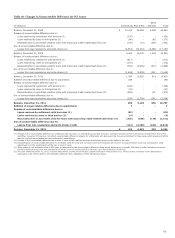
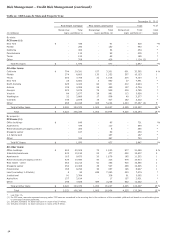
meet obligations in accordance with agreed upon terms). Table
16 presents our total loans outstanding by portfolio segment
and class of financing receivable.
Table 16: Total Loans Outstanding by Portfolio Segment and
Class of Financing Receivable
December 31,
(in millions) 2012 2011
Commercial:
Commercial and industrial $ 187,759 167,216
Real estate mortgage 106,340 105,975
Real estate construction 16,904 19,382
Lease financing 12,424 13,117
Foreign (1) 37,771 39,760
Total commercial 361,198 345,450
Consumer:
Real estate 1-4 family first mortgage 249,900 228,894
Real estate 1-4 family
junior lien mortgage 75,465 85,991
Credit card 24,640 22,836
Other revolving credit and installment 88,371 86,460
Total consumer 438,376 424,181
Total loans $ 799,574 769,631
(1)
Substantially all of our foreign loan portfolio is commercial loans. Loans are
classified as foreign if the borrower’s primary address is outside of the United
States.
50