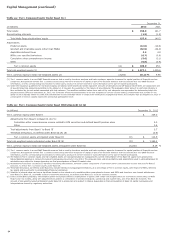
Wells Fargo 2012 Annual Report Download - page 102
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 102 of the 2012 Wells Fargo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Critical Accounting Policies (continued)
x Level 1 – Valuation is based upon quoted prices for identical
instruments traded in active markets. Level 1 instruments
include securities traded on active exchange markets, such
as the New York Stock Exchange, as well as U.S. Treasury
and other U.S. government securities that are traded by
dealers or brokers in active OTC markets.
x Level 2 – Valuation is based upon quoted prices for similar
instruments in active markets, quoted prices for identical or
similar instruments in markets that are not active, and
model-based valuation techniques, such as matrix pricing,
for which all significant assumptions are observable in the
market. Level 2 instruments include securities traded in
functioning dealer or broker markets, plain-vanilla interest
rate derivatives and MHFS that are valued based on prices
for other mortgage whole loans with similar characteristics.
x Level 3 – Valuation is generated primarily from techniques
that use significant assumptions not observable in the
market. These unobservable assumptions reflect our own
estimates of assumptions market participants would use in
pricing the asset or liability. Valuation techniques include
use of option pricing models, discounted cash flow models
and similar techniques.
When developing fair value measurements, we maximize the
use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable
inputs. When available, we use quoted prices in active markets to
measure fair value. If quoted prices in active markets are not
available, fair value measurement is based upon models that use
primarily market-based or independently sourced market
parameters, including interest rate yield curves, prepayment
speeds, option volatilities and currency rates. However, in
certain cases, when market observable inputs for model-based
valuation techniques are not readily available, we are required to
make judgments about assumptions market participants would
use to estimate fair value.
The degree of management judgment involved in
determining the fair value of a financial instrument is dependent
upon the availability of quoted prices in active markets or
observable market parameters. For financial instruments with
quoted market prices or observable market parameters in active
markets, there is minimal subjectivity involved in measuring fair
value. When quoted prices and observable data in active markets
are not fully available, management judgment is necessary to
estimate fair value. Changes in the market conditions, such as
reduced liquidity in the capital markets or changes in secondary
market activities, may reduce the availability and reliability of
quoted prices or observable data used to determine fair value.
When significant adjustments are required to price quotes or
inputs, it may be appropriate to utilize an estimate based
primarily on unobservable inputs. When an active market for a
financial instrument does not exist, the use of management
estimates that incorporate current market participant
expectations of future cash flows, adjusted for an appropriate
risk premium, is acceptable.
When markets for our financial assets and liabilities become
inactive because the level and volume of activity has declined
significantly relative to normal conditions, it may be appropriate
to adjust quoted prices. The methodology we use to adjust the
quoted prices generally involves weighting the quoted prices and
results of internal pricing techniques, such as the net present
value of future expected cash flows (with observable inputs,
where available) discounted at a rate of return market
participants require to arrive at the fair value. The more active
and orderly markets for particular security classes are
determined to be, the more weighting we assign to quoted prices.
The less active and orderly markets are determined to be, the less
weighting we assign to quoted prices.
We may use third party pricing services and brokers
(collectively, “pricing vendors”) to obtain fair values (“vendor
prices”) which are used to either record the price of an
instrument or to corroborate internally developed prices. We
have processes in place to approve such vendors to ensure
information obtained and valuation techniques used are
appropriate. Once these vendors are approved to provide pricing
information, we monitor and review the results to ensure the fair
values are reasonable and in line with market experience with
similar asset classes. For certain securities, we may use internal
traders to price instruments. Where vendor prices are utilized for
recording the price of an instrument, we determine the most
appropriate and relevant pricing vendor for each security class
and obtain a price from that particular pricing vendor for each
security.
Determination of the fair value of financial instruments using
either vendor prices or internally developed prices are subject to
our internal price validation procedures, which include, but are
not limited to, one or a combination of the following procedures:
x comparison to pricing vendors (for internally developed
prices) or to other pricing vendors (for vendor developed
prices);
x variance analysis of prices;
x corroboration of pricing by reference to other independent
market data such as secondary broker quotes and relevant
benchmark indices;
x review of pricing by Company personnel familiar with
market liquidity and other market-related conditions; and
x investigation of prices on a specific instrument-by-
instrument basis.
For instruments where we utilize vendor prices to record the
price of an instrument, we perform additional procedures. We
evaluate pricing vendors by comparing prices from one vendor to
prices of other vendors for identical or similar instruments and
evaluate the consistency of prices to known market transactions
when determining the level of reliance to be placed on a
particular pricing vendor. Methodologies employed and inputs
used by third party pricing vendors are subject to additional
review when such services are provided. This review may consist
of, in part, obtaining and evaluating control reports issued and
pricing methodology materials distributed.
Significant judgment is required to determine whether
certain assets measured at fair value are included in Level 2 or
Level 3. When making this judgment, we consider available
information, including observable market data, indications of
market liquidity and orderliness, and our understanding of the
valuation techniques and significant inputs used. For securities
in inactive markets, we use a predetermined percentage to
evaluate the impact of fair value adjustments derived from
100