Vodafone 2009 Annual Report Download - page 19
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 19 of the 2009 Vodafone annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Vodafone Group Plc Annual Report 2009 17
Business
Quality of service for data applications
The Group has been driving the development of innovative
techniques in 3G, which enable it to carefully manage the assignment
of capacity in its networks. With increasing bandwidth demands and
a data dominated traffic mix, driven by faster HSDPA and fixed
broadband, the ability to optimise the allocation of capacity
according to the services and applications being used will be
essential in managing costs.
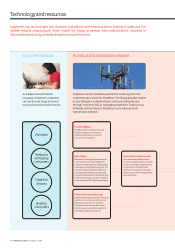
Femtocells
During the 2009 financial year, the Group has been testing femtocells
across a number of markets. Femtocells are based on technology
which consists of a powered booster box connected to a small antenna
that amplifies existing 3G signals from the wide area network to offer
enhanced reception over a range of up to nine metres.
IT
A wide ranging IT transformation programme was initiated in the 2008
financial year to deliver savings, such as the outsourcing of IT
application development and maintenance operations, and identify
new opportunities. The data centre environment continues to be a
major focus area for cost savings, building on the success of the
consolidation programme by driving savings initiatives on server
virtualisation and storage optimisation. Application simplification is
another area of focus as the benefits of reducing the number and
complexity of applications include improving time to market for new
products and services and cost reduction. Significant savings have
been made on Vodafone’s existing IT operations, which have been
reinvested in new products and services.
Supply chain management
Handsets, network equipment, marketing and IT services account for
the majority of Vodafone’s purchases, with the bulk of these purchases
being from global suppliers. The Group’s supply chain management
(‘SCM’) team is responsible for managing the Group’s relationships
with all suppliers, excluding those of handsets, providing cost benefits
to the Group through utilisation of scale and scope.
SCM is a major contributor to the Vodafone cost reduction programme,
achieved through a unified approach using global price books and
framework agreements, a standardised approach to e-auctions, the
introduction of low cost network vendors and achieving best in class
pricing for IT storage and servers. Vodafone’s SCM continues to
transform itself and is operating across all Vodafone’s operating
companies, delivering savings that are measured using a unified
savings methodology, which are reported regularly to the Executive
Committee. Vodafone’s SCM was centralised in Luxembourg during
the 2008 financial year and is delivering further synergies for the
Group through the execution of global material strategies based on
local market expertise. Worldwide independent benchmarking studies
have shown Vodafone SCM as achieving significant cost advantages.
Vodafone also has a China Sourcing Centre, which has achieved
significant trading volumes, further improving the Group’s cost base.
SCM won the “Team of the Year” award and was short listed for the
“Corporate Responsibility and Environment” award in the 2008
European Supply Chain Excellence Awards.
Suppliers to Vodafone are expected to comply with the Group’s Code
of Ethical Purchasing. Further detail on this can be found in “Corporate
responsibility” on page 47.
It is the Group’s policy to agree terms of transactions, including
payment terms, with suppliers and it is the Group’s normal practice
that payment is made accordingly.
Research and development
The Group R&D function comprises an international team for applied
research in mobile and internet communications and their related
applications. It supports the strategic objectives of Vodafone by:
contributing leading edge technical capabilities to Vodafone’s •
consumer offerings in the areas of internet, web and terminal
platforms and by directing the standardisation of relevant cross
platform technologies;
identifying new and emerging business opportunities for fixed and •
mobile services; and
industry leadership in the development of future generation •
network technology through specification of standards,
standardisation and systematic engineering trials.
Group R&D work programme
There have been several significant advances during the 2009
financial year including:
significant progress in long term evolution (‘LTE’) trials, a global •
radio access technology, with key partners Verizon Wireless and
China Mobile, designed to deliver a range of customer benefits
including higher speeds and enhanced throughput performance;
trials conducted to boost backhaul capacity using new ethernet •
microwave technology, which is expected to quadruple backhaul
capacity in channelling voice and data traffic away from base
stations, while enhancing network efficiency and service for
customers and offering cost efficiencies;
launch of the Android powered HTC Magic Pioneer smartphone, •
providing an improved mobile experience and offering scope for
personalisation via the application rich Android market. This follows
Vodafone’s membership of the Open Handset Alliance, established
by Google in 2007 to develop the Android operating system for
mobile phones;
commercial development of near field communications enabled •
mobile phones and SIM cards to reach international standards.
Vodafone and other key players drove the contactless technology
development with the SIM at the centre of the architecture and
have been trialling pre-standard implementations in Germany
and France;
development and roll out of a framework for improving mobile •
access to the internet through small, personalised applications
known as widgets. Vodafone has also played a pivotal role in
driving the standardisation of this technology across the mobile
industry; and
growth and expansion in Vodafone’s developer portal, Betavine, •
which helps developers to transition their applications to operate
on mobile devices. Betavine is also being used as a launch pad for
Vodafone’s engagement with the developer community to bring
innovation to the Group’s customers and to meet needs in emerging
markets through the Betavine social exchange.