Vodafone 2009 Annual Report Download - page 18
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 18 of the 2009 Vodafone annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
16 Vodafone Group Plc Annual Report 2009
Technology and resources continued
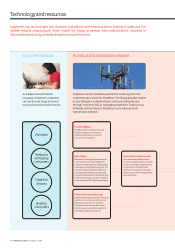
Network infrastructure
Vodafone’s network infrastructure provides the means of delivering
the Group’s mobile and fixed voice, messaging and data services to its
customers. The Group’s customers are linked via the access part of the
network, which connects to the core network that manages the set-up
and routing of calls, transfer of messages and data connections, which
provide a wide variety of other services.
The Group’s mobile network technologies
2G
Vodafone operates 2G networks in all of its mobile operating
subsidiaries, through global system for mobile (‘GSM’) networks,
offering customers services such as voice, text messaging and basic
data services. In addition, all of the Group’s controlled networks
operate general packet radio services (‘GPRS’), often referred to as
2.5G. GPRS allows mobile devices to be used for sending and receiving
data over an IP based network and enabling data service offers such
as internet and email access. In a number of networks, Vodafone also
provides an advanced version of GPRS called enhanced data rates for
GSM evolution (‘EDGE’). These networks provide download speeds of
over 200 kilobits per second (‘kbps’) to Vodafone’s customers.
3G
Vodafone’s 3G networks operating the wideband code division
multiple access (‘W-CDMA’) standard, provide customers with an
optimised data access experience. Vodafone has continued to expand
its service offering on 3G networks, now offering high speed internet
and email access, video telephony, full track music downloads, mobile
TV and other data services in addition to existing voice and basic data
connectivity services.
High speed packet access (‘HSPA’)
HSPA is a 3G wireless technology enhancement enabling significant
increases in data transmission speeds. It provides increased mobile
data traffic capacity and improves the customer experience through
the availability of 3G broadband services and significantly shorter
data transfer times. The Group has now deployed the 3.6 mega bits
per second (‘Mbps’) peak speed evolution of high speed downlink
packet access (‘HSDPA’) across almost all of its 3G networks and also
completed the introduction of the 7.2 Mbps peak speed in key areas.
The figures are theoretical peak rates deliverable by the technology
in ideal radio conditions with no customer contention for resources.
While HSDPA focuses on the downlink (network to mobile), high speed
uplink packet access (‘HSUPA’) focuses on the uplink (mobile to
network) and peak speeds of up to 1.4 Mbps on the uplink have now
been widely introduced across most of the Group’s 3G networks.
Current developments in the infrastructure
As growth in data traffic accelerates with the proliferation in, and
adoption of, web services, Vodafone is evolving its infrastructure
through a range of initiatives.
Access network evolution
Vodafone is actively driving additional 3G data technology
enhancements to further improve the customer’s experience,
including evolutions of HSPA technology to upgrade both the
downlink and uplink speeds. Vodafone has successfully trialled
evolutions of mobile broadband technology achieving actual peak
data download rates of up to 16 Mbps and 21 Mbps, which corresponds
to theoretical peak rates of 21.6 Mbps and 28.8 Mbps, respectively.
Vodafone expects to deploy uplink speeds of around 2 Mbps in a
limited number of areas in Europe during the 2010 financial year.
Vodafone has continued to expand its fixed broadband footprint in
accordance with the Group’s total communications strategy, by
building its own network and/or using wholesale arrangements in
12 countries at 31 March 2009.
Transmission network evolution
Vodafone continues to upgrade its access transmission infrastructure
from the base stations to the core switching network to deal with the
increasing bandwidth demands in the access network and data
dominated traffic mix, driven by HSDPA and fixed broadband. The
Group has continued to pursue a strategy of implementing scaleable
and cost effective self build solutions and is also leveraging its DSL
interests by backhauling data traffic onto more cost effective DSL
transport connections. In the core transmission network, the Group
has continued to expand its high capacity optical fibre infrastructure,
including technology enhancements, which enable the use of cost
effective IP technology to achieve high quality carrier grade transport
of both voice and data traffic.
Core network evolution
The Group has now consolidated ten national IP networks into a single
IP backbone, including the key European markets, centralising IP
operations to avoid duplication and achieve simplicity and flexibility
in the deployment of new services to serve multiple markets. The
Group has continued to expand the deployments of IP multimedia
subsystem (‘IMS’) infrastructure across its markets in order to serve
the increasing demand for advanced internet based services
and applications.
Licences
The licences held across Vodafone’s operating companies enable the
Group to deliver its fixed and mobile communication services. Further
detail on the issue and regulation of licences and a table summarising
the most significant mobile licences held by the Group’s operating
subsidiaries and the Group’s joint ventures in Italy and Vodacom in
South Africa at 31 March 2009 can be found in “Regulation” on page
137. In addition, the Group also has licences to provide fixed line
services in many of the countries in which it operates.
Through its mobile licences, the Group continues to hold sufficient
spectrum in all of its operating subsidiaries and joint ventures to meet
the medium term requirements for Vodafone’s expected voice and
data growth. Re-farming of the Group’s existing spectrum to more
efficient technologies can also increase the voice and data capacity of
Vodafone’s networks. In circumstances where the acquisition of
additional spectrum offers the most cost effective means to increase
capacity, the Group will participate in auctions or other assignment
procedures on a case by case basis.
Cost reduction and innovation
While evolving the Group’s infrastructure, it is also important that the
Group continues to have a tight control over its cost base. Vodafone
has been actively driving a variety of initiatives which enable it to
manage its network investments.
Infrastructure sharing
Significant effort has been placed in reducing the costs of deploying
mobile network infrastructure. During the 2009 financial year,
Vodafone announced a number of significant European agreements,
including those in Germany, Spain, Ireland and the UK, along with the
formation of a joint venture in India, Indus Towers, for the purposes of
network sharing with other operators. The Group is now conducting
network sharing in all but one of its controlled markets.
Power and energy savings
Vodafone has been actively pursuing a number of initiatives to address
energy costs and deliver against its corporate responsibility (‘CR’)
commitment to reduce carbon emissions. During the 2009 financial
year, there has been wide scale adoption of free cooling systems
across the Group’s networks, which remove the need to air condition
base station equipment. In addition, the Group is pursuing the
introduction of sustainable energy sources such as wind and
solar power.