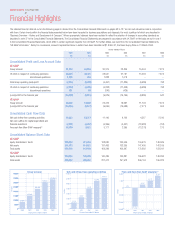
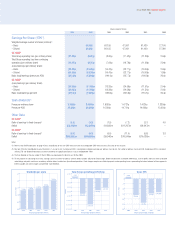
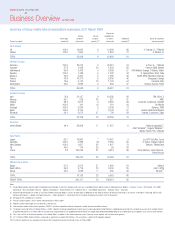
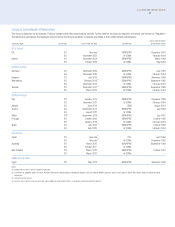
Vodafone 2004 Annual Report Download - page 14
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 14 of the 2004 Vodafone annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Distribution
Distribution is achieved through a wide variety of direct and third party channels, with
different approaches used in the consumer and business sectors.
Products and services are available directly to both consumer and business customers
in the majority of markets. Directly owned stores are becoming increasingly prevalent
in most markets. The look and feel of these stores, particularly in Italy, Greece and the
UK, has focused more on the user experience during the year, with customers invited
to try out service offerings such as Vodafone live!™. Local Internet sites offer
products and services online and local sales forces are in place to discuss terms with
business customers.
The extent of indirect distribution varies between markets but may include using third-
party service providers, independent dealers, agencies and mass marketing.
Marketing to third-party service providers includes maintaining a competitive tariff
structure, providing technical and other training to their staff and providing financial
incentives for service providers, their dealers and sales people. It also entails providing
assistance on advertising campaigns and supporting the development of both
specialist retail outlets and programmes with multiple retailers. Service providers
receive discounts on the Group’s airtime rates for each tariff. Service providers also
receive financial incentives from the Group related to their success in attracting new
customers to the network. These incentives comprise gross connection bonuses,
airtime growth awards and other specific incentives. Independent dealers are used in
the majority of markets, with own-branded stores, business “store-within-stores”and
kiosks becoming increasingly frequent as channels to market. Supermarket chains
and multiple retailers are also used to achieve broad distribution of prepaid products,
with top-up facilities available in a wide selection of outlets such as petrol stations,
newsagents and local stores.
The Group’s leading global customers are served by the International Accounts team,
with a designated executive link.
In the United States, Verizon Wireless sells its service directly to customers through its
own sales force and stores, telemarketing centres and the Internet, and indirectly
through arrangements with independent retailers and agents. Additionally, Verizon
Wireless also sells wireless capacity to resellers, which allows independent companies
to package and resell wireless services to end-users.
Industry initiatives
On 13 October 2003, the Group announced with Microsoft an intention to use
mobile SIM based authentication and billing to help create open Web services
standards that will enable new business opportunities for application developers and
mobile network operators and deliver new integrated services for customers across
fixed and mobile networks.
On 10 March 2004, the Group announced that it had signed a memorandum of
understanding with other leading companies from the mobile industry to apply for
a mobile Top Level Domain (“TLD”) from the Internet Corp. for Assigned Names
and Numbers. A mobile TLD would be a key step in bridging the world of mobility and
the Internet.
Research and development
The Group Research and Development (“R&D”) function was formed in April 2001
from the Vodafone research and development teams in Newbury, Maastricht, Vodafone
Pilotentwicklung in Munich and the Strategic Technology team in Walnut Creek,
California. Since then, centres of excellence in Milan, Madrid and Tokyo have been
added, thereby creating an international and multicultural team for applied research in
mobile telecommunications and its applications.
The work of the Group R&D function is divided broadly into four categories. These
categories are technical leadership and research support for the work of the Group
Vodafone Group Plc Annual Report 2004
12
Business Overview continued
Network strategy is becoming increasingly relevant for mobile operators outside
Europe.
Mobilkom-Group, which operates in Austria, Croatia and Slovenia, will become the first
Partner Network to introduce Vodafone live!™ and is expected to launch services in
June 2004. The Vodafone Mobile Connect 3G/GPRS datacard has been launched in
Austria and the Mobile Connect Card has been introduced in Bahrain, Croatia,
Denmark, Slovenia, Estonia and Finland.
Content standards
In October 2002, a dedicated Content Standards team was established to provide
leadership in mobile content standards in order to protect customers from
inappropriate content, contact and commercialism. Specific emphasis is placed on
protecting young mobile phone users. The Group recognises that, although acceptable
to an older audience, not all content and services are suitable for all ages and it has
committed to exercise responsibility in ways that are consistent with its customer and
public values.
The Content Standards team has actively supported a number of initiatives, such as
the UK mobile operators’ Code of Practice and the Group’s age verification mechanism
currently being piloted in Germany. Looking ahead, the Content Standards team will
work with the operating companies to implement policies and develop an independent
auditing process to ensure they are maintained.
Marketing and distribution
Marketing
Brand
All controlled mobile subsidiary companies operate under the Vodafone brand. Brand
marketing is designed to increase general public awareness of the Vodafone brand, or
other local Group brands, and its values, products and services and embraces
marketing specifically directed at certain distribution channels. Brand communications
include sponsorships and advertising on radio, television, in general circulation
newspapers, in magazines and in specialised publications.
The Group has focused on driving brand preference and usage of Vodafone live!™
services, as well as core voice and text usage. Advertisements used feature the
Group’s key sponsorships: Ferrari, Manchester United, Michael Schumacher, Rubens
Barrichello and David Beckham. Communications materials have been adapted for use
in Partner Network markets. The Vodafone speechmark icon is achieving increasing
recognition as a key visual identity symbol of the brand.
The three year brand migration programme was completed during the year, with Italy
and Japan migrating to the Vodafone brand in May and October 2003, respectively.
Having established the Vodafone brand in the Group’s controlled markets, the focus is
now shifting and more emphasis and resources are aimed at increasing customer
satisfaction and brand preference. In order to do this, Vodafone has put in place a
framework for measuring and improving its performance on every element of
customer experience. In addition, the Group has put in place a segmentation
framework that has been arrived at on a basis of extensive research. All marketing
plans and activities, both global and local, are now built around seven customer
segments identified through the research.
Local marketing
In addition to the Group’s initiatives to establish a global Vodafone brand, funds are
also invested in local marketing activities. Customer database marketing is widely
used to communicate directly with customers and, when linked with customer service,
provides a strong basis for building customer relationships. Loyalty schemes are
beginning to be more widely used as a way of increasing customer satisfaction and
reducing customer churn.
Associated companies are generally marketed under their local brands.