Asus 2010 Annual Report Download - page 85
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 85 of the 2010 Asus annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
81
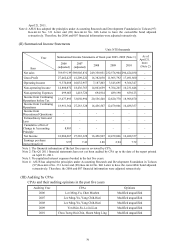
The root causes of the financial ratio change in the last two years:
Ratio of liabilities to assets: It was due to the economic recovery of the year with growing demand of the emerging
markets; therefore, accounts payable for the procurement of raw material went up.
Ratio of long-term capital to fixed assets: It was due to the capital reduction that caused shareholder’s equity to go
down. The change in fixed asses was insignificant; therefore, the ratio of long-term fund to fixed assets went down.
Current ratio: It was due to the economic recovery of the year with growing demand of the emerging markets;
therefore, accounts receivable for the sales of goods went up.
Quick ratio: It was due to the increase of prepayment amount this year; therefore, the quick ratio went down slightly.
Times interest earned ratio: The amortization of CB in the year was decreased (ASUS CB and ECB were without
interest paid; however, CB discount expense was credited to interest expense in accordance with the new notice even
there was no cash actually paid); therefore, Times interest earned ratio was increased.
Account receivable turnover (times): It was due to the growth of purchase order; therefore, revenues went up. The
account receivable turnover (times) was high too.
Inventory turnover (times): It was due to the increase of the cost of goods sold resulted from the growth of sales
revenue; also, the management strived to control inventory; therefore, the inventory turnover (times) went up.
Account payable turnover (times): It was due to the growth of orders; therefore, the accounts payable resulted from
the procurement of materials was high.
Fixed assets turnover (times): It was due to the economic recovery of the year with growing demand of the emerging
markets; therefore, sales revenue went up.
Total assets turnover (times): It was due to the economic recovery of the year with growing demand of the emerging
markets; therefore, sales revenue went up.
Ratio of return on total assets: It was due to the increase of net income and the split of OEM business group;
therefore, long-term investment balance went down and total return on assets went up.
Ratio of return on shareholders’ equity: It was due to the increase of net income and the capital reduction; therefore,
the ratio of return on shareholders’ equity went up.
Ratio of operating income to issued capital stock: It was due to the increase of operating profit and capital
reduction; therefore, the ratio of operating income to issued capital stock went up dramatically.
Cash flow ratio: The economy was poor last year; therefore, the procurement was low relatively. The economy was
recovered this year; therefore, the procurement of raw material was up. The net cash inflow from operating activity
was decreased; therefore, cash flow ratio was down.
Cash flow adequacy ratio: The management strived to control inventory; therefore, the increase of inventory in the
last five years was declining; moreover, the net cash inflow from operating activities in the last five year went up;
therefore, cash flow adequacy ratio was up too.
Cash reinvestment ratio: It was due to split of OEM business group this year; therefore, long-term investment went
down and cash reinvestment ratio was up from the last year.
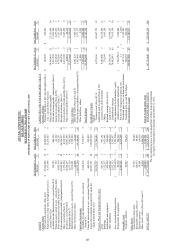
Note 1: ASUS has adopted the principles under Accounting Research and Development Foundation in
Taiwan (97) Kee.mi.tzi No. 331 Letter and (98) Kee.mi.tzi No. 046 Letter to have the convertible
bond adjusted retroactively. Therefore, the 2006 and 007 financial information were adjusted
retroactively.
Note 2: The financial information is reviewed by CPA.
Note 3: Accounts receivable includes the amount of long-term accounts receivable- related party that is in
compliance with trade terms and conditions.
Note 4: The Q1 2011 financial statements have not yet been audited by CPA up to the date of the report
printed on April 21, 2011.
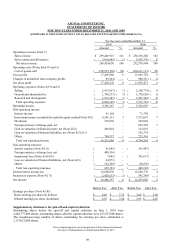
Note 5: Equations:
1. Financial structure
(1) Ratio of liabilities to assets = Total liability/Total assets
(2) Ratio of long-Term capital to fixed assets = (Net shareholders’ equity + Long-term liability)
/ Net fixed assets
2. Solvency
(1) Current ratio = Current assets / current liability
(2) Quick ratio = (Current assets – Inventory – Prepaid expense) / Current liability
(3) Times interest earned ratio = Net income before tax and interest expense / Interest expense
of the year
3. Operating ability