Asus 2010 Annual Report Download - page 126
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 126 of the 2010 Asus annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211
 |
 |

122
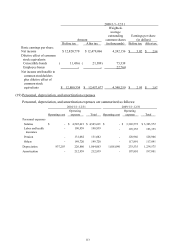
38
resulting from the forward contracts and currency option contracts. Thus, the
market risk of foreign currency exchange rate changes does not have material
impact on the Company.
(B) The open-end funds and stocks of listed companies held by the Company are
classified as financial assets measured at fair value through profit or loss and
available-for-sale financial assets. As these assets are measured at fair value,
the Company has risk exposure related to changes in fair value in an equity
securities market.
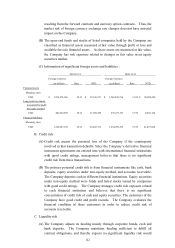
(C) Information of significant foreign assets and liabilities :
2010/12/31 2009/12/31
Foreign Currency
Foreign Currency
(in dollars) Rate NTD (in dollars) Rate NTD
Financial a
ssets
Monetary item
USD
$
1,790,476,186 29.13
$ 52,156,571
$
1,569,530,796 31.99
$ 50,209,290
Long
-term investment
accounted for under
the equity method
USD 401,932,589 29.13 11,708,296 276,277,271 31.99 8,838,110
Financial l
iabilities
Monetary item
USD 1,566,947,170 29.13 45,645,171 1,294,999,513 31.99 41,427,034
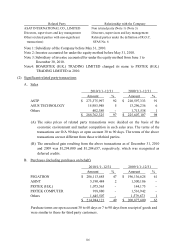
B. Credit risk
(A) Credit risk means the potential loss of the Company if the counterparty
involved in that transaction defaults. Since the Company’s derivative financial
instrument agreements are entered into with international financial institutions
with good credit ratings, management believes that there is no significant
credit risk from these transactions.
(B) The primary potential credit risk is from financial instruments like cash, bank
deposits, equity securities under non-equity method, and accounts receivable.
The Company deposits cash in different financial institutions. Equity securities
under non-equity method were funds and listed stocks issued by companies
with good credit ratings. The Company manages credit risk exposure related
to each financial institution and believes that there is no significant
concentration of credit risk of cash and equity securities. The customers of the
Company have good credit and profit records. The Company evaluates the
financial condition of these customers in order to reduce credit risk of
accounts receivable.
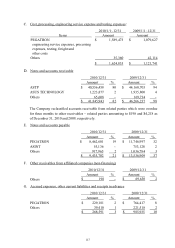
C. Liquidity risk
(A) The Company adjusts its funding mainly through corporate bonds, cash and
bank deposits. The Company maintains funding sufficient to fulfill all
contract obligations, and thereby expects no significant liquidity risk would
