National Grid 2014 Annual Report Download - page 142
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 142 of the 2014 National Grid annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
30. Financial risk management continued
(c) Interest rate risk
National Grid’s interest rate risk arises from our long-term borrowings. Borrowings issued at variable rates expose National Grid to cash
flow interest rate risk, partially offset by cash held at variable rates. Borrowings issued at fixed rates expose National Grid to fair value
interest rate risk.
Our interest rate risk management policy is to seek to minimise total financing costs (being interest costs and changes in the market
value of debt) subject to constraints. We do this by using fixed and floating rate debt and derivative financial instruments including
interest rate swaps, swaptions and forward rate agreements.
We hold some borrowings on issue that are inflation linked. We believe that these provide a partial economic offset to the inflation risk
associated with our UK inflation linked revenues.
The table in note 19 sets out the carrying amount, by contractual maturity, of borrowings that are exposed to interest rate risk before
taking into account interest rate swaps.
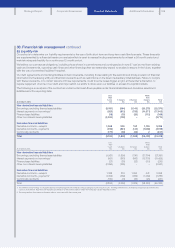
During 2014 and 2013, net debt was managed using derivative instruments to hedge interest rate risk as follows:
2014 2013
Fixed
rate
£m
Floating
rate
£m
Inflation
linked
£m
Other1
£m
Total
£m
Fixed
rate
£m
Floating
rate
£m
Inflation
linked
£m
Other1
£m
Total
£m
Cash and cash equivalents 175 179 – – 354 577 94 – – 671
Financial investments 615 2,979 – 5 3,599 540 4,843 –48 5,431
Borrowings2(15,585) (3,520) (6,836) (9) (25,950) ( 17, 76 7 ) (3,700) (6,617) (11) (28,095)
Pre-derivative position (14,795) (362) (6,836) (4) (21,997) (16,650) 1,237 (6,617) 37 (21,993)
Derivative effect33,359 (2,743) 191 –807 1,555 (1,132) 141 –564
Net debt position (11,436) (3,105) (6,645) (4) (21,190) (15,095) 105 (6,476) 37 (21,429)
1. Represents financial instruments which are not directly affected by interest rate risk, such as investments in equity or other similar financial instruments.
2. Includes bank overdrafts.
3. The impact of 2014/15 (2013: 2013/14) maturing short-dated interest rate derivatives is included.
(d) Currency risk
National Grid operates internationally and is exposed to foreign exchange risk arising from various currency exposures, primarily with
respect to the dollar. Foreign exchange risk arises from future commercial transactions, recognised assets and liabilities, and investments
in foreign operations.
Our policy for managing foreign exchange transaction risk is to hedge contractually committed foreign currency cash flows over a
prescribed minimum size. Where foreign currency cash flow forecasts are less certain, our policy is to hedge a proportion of such cash
flows based on the probability of those cash flows occurring. Instruments used to manage foreign exchange transaction risk include
foreign exchange forward contracts and foreign exchange swaps.
Our policy for managing foreign exchange translation risk relating to our net investment in foreign operations is to maintain a percentage
of net debt and foreign exchange forwards so as to provide an economic offset of our cash flows arising in the foreign currency. The
primary managed foreign exchange exposure arises from the dollar denominated assets and liabilities held by our US operations, with a
further small euro exposure in respect of a joint venture investment.
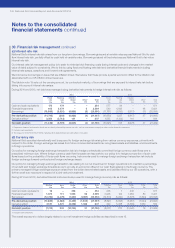
During 2014 and 2013, derivative financial instruments were used to manage foreign currency risk as follows:
2014 2013
Sterling
£m
Euro
£m
Dollar
£m
Other
£m
Total
£m
Sterling
£m
Euro
£m
Dollar
£m
Other
£m
Total
£m
Cash and cash equivalents 16 –338 –354 238 1432 –671
Financial investments 1,879 111 1,553 56 3,599 3,938 124 1,289 80 5,431
Borrowings1(12,780) (4,479) (7,33 0) (1,361) (25,950) (12,573) (5,220) (8,678) (1,624) (28,095)
Pre-derivative position (10,885) (4,368) (5,439) (1,305) (21,997) (8,397) (5,095) (6,957) (1,544) (21,993)
Derivative effect 3,137 4,670 (8,326) 1,326 807 320 5,368 (6,684) 1,560 564
Net debt position (7,74 8) 302 (13,765) 21 (21,190) (8,077) 273 (13,641) 16 (21,429)
1. Includes bank overdrafts.
The overall exposure to dollars largely relates to our net investment hedge activities as described in note 15.
Notes to the consolidated
financial statements continued
140 National Grid Annual Report and Accounts 2013/14