MoneyGram 2013 Annual Report Download - page 80
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 80 of the 2013 MoneyGram annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
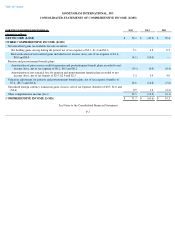
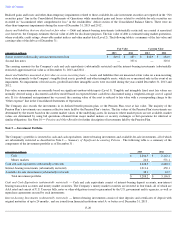
is delinquent and a loss is deemed possible. Receivables are generally written off against the allowance one year after becoming past due. The
following summary details the activity within the allowance for credit losses for the years ended December 31 :
Investments (substantially restricted)
— The Company classifies securities as interest-bearing or available-for-
sale in its Consolidated Balance
Sheets. The Company has no securities classified as trading or held-to-
maturity. Time deposits and certificates of deposits with original
maturities of up to twenty-four months are classified as interest-
bearing investments and recorded at amortized cost. Securities held for indefinite
periods of time, including any securities that may be sold to assist in the clearing of payment service obligations or in the management of the
investment portfolio, are classified as available-for-sale securities. These securities are recorded at fair value, with the net after-
tax unrealized
gain or loss recorded as a separate component of stockholders’ deficit. Realized gains and losses and other-than-
temporary impairments are
recorded in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Interest income on residential mortgage-
backed securities for which risk of credit loss is deemed remote is recorded utilizing the level yield
method. Changes in estimated cash flows, both positive and negative, are accounted for with retrospective changes to the carrying value of
investments in order to maintain a level yield over the life of the investment. Interest income on mortgage-
backed securities for which risk of
credit loss is not deemed remote is recorded under the prospective method as adjustments of yield.
The Company applies the cost recovery method of accounting for interest to its investments categorized as other asset-
backed securities. The
cost recovery method accounts for interest on a cash basis and deems any interest payments received as a recovery of principal, which reduces
the book value of the related security. When the book value of the related security is reduced to zero, interest payments are then recognized as
investment income upon receipt. The Company applies the cost recovery method of accounting as it believes it is probable that the Company will
not recover all, or substantially all, of its principal investment and interest for its other asset-
backed securities given the sustained deterioration in
the investment and securities market, the collapse of many asset-
backed securities and the low levels to which the securities have been written
down.
Securities with gross unrealized losses as of the balance sheet date, are subject to a process for identifying other-than-
temporary impairments.
Securities that the Company deems to be other-than-
temporarily impaired are written down to fair value in the period the impairment occurs. The
assessment of whether such impairment has occurred is based on management’
s evaluation of the underlying reasons for the decline in fair value
on an individual security basis. The Company considers a wide range of factors about the security and uses its best judgment in evaluating the
cause of the decline in the estimated fair value of the security and the prospects for recovery. The Company considers an investment to be other-
than-
temporarily impaired when it is deemed probable that the Company will not receive all of the cash flows contractually stipulated for the
investment. The Company evaluates mortgage-backed and other asset-
backed investments rated A and below for which risk of credit loss is
deemed more than remote for impairment. When an adverse change in expected cash flows occurs, and if the fair value of a security is less than
its carrying value, the investment is written down to fair value through a permanent reduction to its amortized cost. Securities gains and losses
are recognized upon the sale, call or maturity of securities using the specific identification method to determine the cost basis of securities sold.
Any impairment charges and other securities gains and losses are included in the Consolidated Statements of Operations under “
Net securities
gains.”
Payment Service Obligations
—
Payment service obligations primarily consist of: outstanding payment instruments; amounts owed to financial
institutions for funds paid to the Company to cover clearings of official check payment instruments, remittances and clearing adjustments;
amounts owed to agents for funds paid to consumers on behalf of the Company; commissions owed to financial institution customers and agents
for instruments sold; amounts owed to investment brokers for purchased securities; and unclaimed instruments owed to various states. These
obligations are recognized by the Company at the time the underlying transactions occur.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
—
Financial instruments consist of cash and cash equivalents, investments, derivatives, deferred
compensation and debt. The carrying values of cash and cash equivalents and interest-
bearing investments approximate fair value. The carrying
value of debt is stated at amortized cost; however, for disclosure purposes the fair value is estimated. See Note 4 — Fair Value Measurement
for
information regarding the principles and processes used to estimate the fair value of financial instruments.
Derivative Financial Instruments
—
The Company recognizes derivative financial instruments in the Consolidated Balance Sheets at fair value.
The accounting for changes in the fair value is recognized through the “Transaction and operations support” line in
F-12
(Amounts in millions) 2013
2012
2011
Beginning balance
$
11.7
$
10.5
$
20.0
Charged to expense
9.6
7.5
6.6
Write-offs, net of recoveries
(10.6
)
(6.3
)
(16.1
)
Ending balance
$
10.7
$
11.7
$
10.5