MetLife 2004 Annual Report Download - page 69
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 69 of the 2004 MetLife annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
METLIFE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
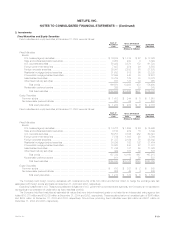
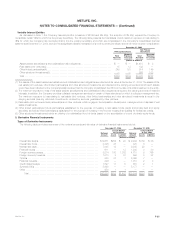
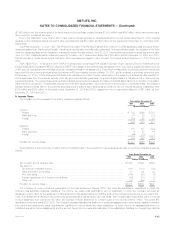
The following table provides a summary of the notional amounts of derivative financial instruments by maturity at December 31, 2004:
Remaining Life
After After
One Year Five Years
One Year Through Five Through Ten After
or Less Years Years Ten Years Total
(Dollars in millions)
Interest rate swaps*************************************************** $1,878 $ 6,846 $ 2,098 $1,859 $12,681
Interest rate floors**************************************************** — — 3,325 — 3,325
Interest rate caps **************************************************** 2,025 5,020 — — 7,045
Financial futures ***************************************************** 611 — — — 611
Foreign currency swaps ********************************************** 277 3,425 3,155 1,357 8,214
Foreign currency forwards********************************************* 1,013 — — — 1,013
Options ************************************************************ 6 — 256 563 825
Financial forwards**************************************************** 326 — — — 326
Credit default swaps ************************************************* 301 1,217 379 — 1,897
Synthetic GICs ****************************************************** 1,000 1,000 3,869 — 5,869
Other ************************************************************** 450 — — — 450
Total*********************************************************** $7,887 $17,508 $13,082 $3,779 $42,256
Interest rate swaps are used by the Company primarily to reduce market risks from changes in interest rates and to alter interest rate exposure
arising from mismatches between assets and liabilities (duration mismatches). In an interest rate swap, the Company agrees with another party to
exchange, at specified intervals, the difference between fixed rate and floating rate interest amounts as calculated by reference to an agreed notional
principal amount. These transactions are entered into pursuant to master agreements that provide for a single net payment to be made by the
counterparty at each due date.
Interest rate caps and floors are used by the Company primarily to protect its floating rate liabilities against rises in interest rates above a specified
level, and to protect its minimum rate guarantee liabilities against declines in interest rates below a specified level, respectively.
In exchange-traded Treasury and equity futures transactions, the Company agrees to purchase or sell a specified number of contracts, the value of
which is determined by the different classes of Treasury and equity securities, and to post variation margin on a daily basis in an amount equal to the
difference in the daily market values of those contracts. The Company enters into exchange-traded futures with regulated futures commission merchants
that are members of the exchanges.
Exchange-traded Treasury futures are used primarily to hedge mismatches between the duration of assets in a portfolio and the duration of liabilities
supported by those assets, to hedge against changes in value of securities the Company owns or anticipates acquiring, and to hedge against changes
in interest rates on anticipated liability issuances by replicating Treasury performance. The value of Treasury futures is substantially impacted by changes
in interest rates and they can be used to modify or hedge existing interest rate risk.
Exchange-traded equity futures are used primarily to hedge liabilities embedded in certain variable annuity products offered by the Company.
Foreign currency derivatives, including foreign currency swaps and foreign currency forwards, are used by the Company to reduce the risk from
fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates associated with its assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies. The Company also uses
foreign currency forwards to hedge the foreign currency risk associated with certain of its net investments in foreign operations.
In a foreign currency forward transaction, the Company agrees with another party to deliver a specified amount of an identified currency at a
specified future date. The price is agreed upon at the time of the contract and payment for such a contract is made in a different currency at the specified
future date.
In a foreign currency swap transaction, the Company agrees with another party to exchange, at specified intervals, the difference between one
currency and another at a forward exchange rate calculated by reference to an agreed upon principal amount. The principal amount of each currency is
exchanged at the inception and termination of the currency swap by each party.
Swaptions are used by the Company primarily to sell, or monetize, embedded call options in its fixed rate liabilities. A swaption is an option to enter
into a swap with an effective date equal to the exercise date of the embedded call and a maturity date equal to the maturity date of the underlying liability.
The Company receives a premium for entering into the swaption.
Equity options are used by the Company primarily to hedge liabilities embedded in certain variable annuity products offered by the Company.
The Company enters into financial forwards, primarily ‘‘to-be-announced’’ (‘‘TBA’’) securities, to gain exposure to the investment risk and return of
securities not yet available. The price is agreed upon at the time of the contract and payment for such a contract is made at a specified future date.
Certain credit default swaps are used by the Company to hedge against credit-related changes in the value of its investments. In a credit default
swap transaction, the Company agrees with another party, at specified intervals, to pay a premium to insure credit risk. If a credit event, as defined by the
contract, occurs, generally the contract will require the swap to be settled gross by the delivery of par quantities of the referenced investment equal to the
specified swap notional in exchange for the payment of cash amounts by the counterparty equal to the par value of the investment surrendered.
Credit default swaps are also used in replication synthetic asset transactions (‘‘RSATs’’) to synthetically create investments that are either more
expensive to acquire or otherwise unavailable in the cash markets. RSATs are a combination of a derivative and usually a U.S. Treasury or Agency
security. RSATs that involve the use of credit default swaps are included in such classification in the preceding table.
Total rate of return swaps (‘‘TRRs’’) are swaps whereby the Company agrees with another party to exchange, at specified intervals, the difference
between the economic risk and reward of an asset or a market index and LIBOR, calculated by reference to an agreed notional principal amount. No
cash is exchanged at the outset of the contract. Cash is paid and received over the life of the contract based on the terms of the swap. These
transactions are entered into pursuant to master agreements that provide for a single net payment to be made by the counterparty at each due date.
TRRs can be used as hedges or RSATs and are included in the other classification in the preceding table.
MetLife, Inc.
F-26