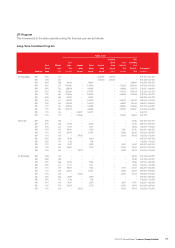
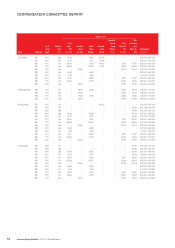
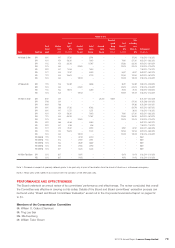
Lenovo 2013 Annual Report Download - page 89
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 89 of the 2013 Lenovo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.2012/13 Annual Report Lenovo Group Limited 87
2. Installing a solar array at the manufacturing plant in
Shanghai, China, which generated 209,835 kWh
of solar energy between July 2012 – March 2013.
This represents between 10-15% of the site’s annual
electricity consumption and is targeted to reduce GHG
emissions by more than 400 MT CO2e yearly.
3. Purchasing carbon offsets (4,000 MT CO2e) and
Renewable Energy Credits (40,303 MWh) from a
carbon offset provider in China and the 2012 U.S. EPA
Green Power supplier of the year in the United States.
For additional details on Lenovo’s GHG emissions inventory
and management, see Lenovo’s Sustainability Reports and
climate change website: http://www.lenovo.com/climate.
We are focusing on the next milestone in our ten-year
initiative to reduce Scope 2 emissions by 16% relative to FY
2009/10 by March 31, 2016. All sites continue to identify
and implement energy efficiency projects and evaluate
opportunities to implement the use of renewable energy.
While we have demonstrated good progress during the
early stages of our ten-year GHG reduction commitment,
we are keenly aware there is still much to be done. In light
of our impressive growth, we realize that accomplishing
our longer term goals will be a significant challenge. With
a continued focus on energy efficiency, Lenovo’s Global
Energy Management Team will work to identify and
implement energy reduction, renewable energy and carbon
offset opportunities that provide the most cost effective
path to meeting our targets.
We are exploring opportunities to take energy efficiency
to the next level through energy efficiency audits in our
Huiyang and Xiamen manufacturing facilities and installing
more renewable energy sources in facilities worldwide.
Moreover we are looking into a carbon fee program and
green revolving funds as a mean for financing energy and
GHG reduction projects and making Lenovo’s business
units accountable for their own emissions and targeted
reductions.
Lenovo’s Global Real Estate team benchmarked energy,
waste and GHG emissions best practices at all sites larger
than 10,000 square feet and is working on developing
management practices for sustainable real estate.
We continue efforts to improve our ability to quantify,
track, and mitigate the impacts of our supply chain and
our products. During FY 2012/13 we continued work with
the Electronics Industry Citizenship Coalition (EICC) on
the development of a carbon system to track the GHG
emissions of our supply chain, engaging our suppliers’
support in helping reduce GHG emissions. Working with
suppliers representing 95% of our procurement spend
we have improved our suppliers’ inventory relative to
GHG emissions. Our efforts with the EICC also continue
to include work on tracking water impacts in our supply
chain. This has allowed us to begin tracking the water
performance of our suppliers and initiate dialogue regarding
opportunities for improved performance and corrective
actions for identified compliance issues.
Lenovo has established a product transportation carbon
emissions baseline for FY 2011/12 and is working on
improving data collection processes and increasing carriers’
coverage in the baseline through the use of a web-based
carbon dashboard. Lenovo participates in U.S. EPA
SmartWay and is committed to support the incorporation
of Green Freight Asia Network for promoting sustainable
logistics practices.
We continue our engagement in the development of
standards and tools to accurately quantify the lifetime
impact of our products. Our China Standards and
Compliance Group is engaged in the Chinese government’s
development of a product category rule for establishing
the product carbon footprint for information and
communications technologies (ICT) products. Lenovo is
planning to participate in an ICT Product LCA Database
project which is anticipated to kick off in May 2013. The
project’s goal is to develop a Chinese product life-cycle
database for ICT products, parts and components. The
initial step is gathering suppliers’ data for carbon emissions
determination. In the future, it is expected that the database
will store information about water, air emissions, hazardous
substances, etc., and provide methodologies, tools and
training for users.