Lenovo 2010 Annual Report Download - page 93
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 93 of the 2010 Lenovo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
2009/10 Annual Report Lenovo Group Limited
91
2009/10 Annual Report Lenovo Group Limited
91
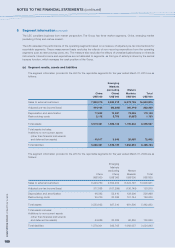
2 Significant accounting policies (continued)
(z) Segment reporting
Operating segments are reported in a manner consistent with the internal reporting provided to the chief operating
decision-maker. The chief operating decision-maker, who is responsible for allocating resources and assessing
performance of the operating segments, has been identified as the steering committee that makes strategic
decisions.
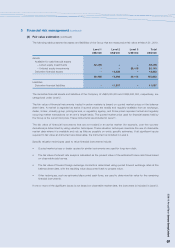
3 Financial risk management
The Group’s activities expose it to a variety of financial risks, such as market risk (including foreign currency risk, price
risk, cash flow interest rate risk and fair value interest rate risk), credit risk, and liquidity risk. The Group’s overall risk
management program focuses on the unpredictability of financial markets and seeks to minimize potential adverse effects
on the Group’s financial performance. The Group uses derivative financial instruments to hedge certain risk exposures.
Risk management is carried out by a central treasury department (“Group Treasury”) under approved policies. Group
Treasury identifies, evaluates and hedges financial risks in close co-operation with the Group’s operating units. The Group
has the overall risk management such as foreign exchange risk, credit risk, interest rate risk, price risk, use of derivative
financial instruments and investing excess liquidity.
(a) Financial risk factors
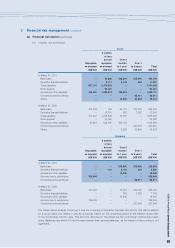
(i) Foreign currency risk
The Group operates internationally and is exposed to foreign exchange risk arising from various currency
exposures, primarily with respect to Australian dollar, Canadian dollar, Euro, Japanese Yen, Pound Sterling and
Renminbi. Foreign currency risk arises from future commercial transactions, recognized assets and liabilities
and net investment in foreign operations.
Management has set up a policy to require group companies to manage their foreign currency risk against their
functional currency. The Group’s forward foreign currency contracts are either used to hedge a percentage of
anticipated cash flows (mainly export sales and purchase of inventories) which are highly probable, or used as
fair value hedges for the identified assets and liabilities.
For segment reporting purposes, external hedge contracts on assets, liabilities or future transactions are
designated to each operating segment, as appropriate.
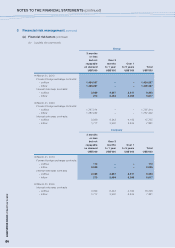
(ii) Cash flow and fair value interest rate risk
The Group’s substantial long-term borrowings are denominated in United States dollar. Borrowings
denominated in other currencies are insignificant. It is the Group’s policy to mitigate interest rate risk through
the use of appropriate interest rate hedging instruments. Generally, the Group manages its cash flow interest
rate risk by using floating-to-fixed interest rate swaps. Such interest rate swaps have the economic effect of
converting borrowings from floating rates to fixed rates. Under the interest rate swaps, the Group agrees with
other parties to exchange, at specified intervals (primarily quarterly), the difference between fixed contract rates
and floating-rate interest amounts calculated by reference to the agreed notional amounts.
The Group exposes to fair value interest rate risk arising from borrowings at fixed interest rate; however, fair
value interest rate risk is considered not significant to the Group and therefore not hedged.
The Group operates a global channel financing program. The Group is exposed to fluctuation of interest rates
of all the currencies covered by the global channel financing program.