Lenovo 2010 Annual Report Download - page 90
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 90 of the 2010 Lenovo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
2009/10 Annual Report Lenovo Group Limited
88
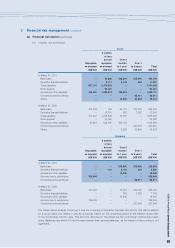
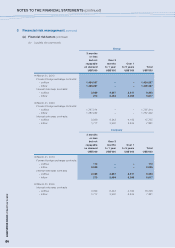
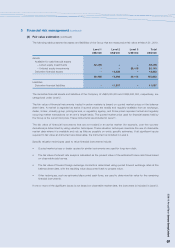
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
2009/10 Annual Report Lenovo Group Limited
88
2 Significant accounting policies (continued)
(r) Current and deferred income tax
The tax expense for the period comprises current and deferred tax.
The current income tax charge is calculated on the basis of the tax laws enacted or substantively enacted at the
balance sheet date in the countries where the Company’s subsidiaries and associated companies operate and
generate taxable income. Management periodically evaluates positions taken in tax returns with respect to situations
in which applicable tax regulation is subject to interpretation. It establishes provisions where appropriate on the basis
of amounts expected to be paid to the tax authorities.
Deferred income tax is provided in full, using the liability method, on temporary differences arising between the tax
bases of assets and liabilities and their carrying amounts in the financial statements. However, deferred income tax
is not accounted for if it arises from initial recognition of an asset or liability in a transaction other than a business
combination that at the time of the transaction affects neither the accounting nor taxable profit or loss. Deferred
income tax is determined using tax rates (and laws) that have been enacted or substantially enacted by the balance
sheet date and are expected to apply when the related deferred income tax asset is realized or the deferred income
tax liability is settled.
Deferred income tax assets are recognized to the extent that it is probable that future taxable profit will be available
against which the temporary differences can be utilized.
Deferred income tax is provided on temporary differences arising on investments in subsidiaries and associated
companies, except where the timing of the reversal of the temporary difference is controlled by the Group and it is
probable that the temporary difference will not reverse in the foreseeable future.
(s) Contingent liabilities
A contingent liability is a possible obligation that arises from past events and whose existence will only be confirmed
by the occurrence or non-occurrence of one or more uncertain future events not wholly within the control of the
Group. It can also be a present obligation arising from past events that is not recognized because it is not probable
that outflow of economic resources will be required or the amount of obligation cannot be measured reliably.
A contingent liability is not recognized but is disclosed in the notes to the financial statements. When a change in the
probability of an outflow occurs so that the outflow is probable, it will then be recognized as a provision.
(t) Financial guarantee contracts
Financial guarantee contracts under which the Group accepts significant risk from a third party by agreeing to
compensate that party on the occurrence of a specified uncertain future event are accounted for in a manner similar
to insurance contracts. Provisions are recognized when it is probable that the Group has obligations under such
guarantees and an outflow of economic resources will be required to settle the obligations.
(u) Revenue
Revenue is measured at the fair value of the consideration received or receivable for the sale of goods and services
in the normal course of the Group’s activities.
(i) Sale of goods and services
Revenue from sale of hardware, software and peripherals, and services and mobile devices, and is recognized,
net of value-added tax, an allowance for estimated returns, rebates and discounts, when both ownership and
risk of loss are effectively transferred to customer, generally when there is a persuasive evidence of a sales
arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, collectability is reasonably assured and delivery has
occurred. Revenue from extended warranty contracts is deferred and amortized as earned over the contract
period, generally of three years. Revenue associated with undelivered elements is deferred and recorded when
delivery occurs. Revenue from provision of systems integration service and information technology technical
service is recognized over the term of contract or when services are rendered.
The Group defers the cost of shipped products awaiting revenue recognition until the goods are delivered and
revenue is recognized. In-transit product shipments to customers of US$48 million as at March 31, 2010 (2009:
US$77 million) are included in deposits, prepayments and other receivables in the balance sheet.