IBM 2007 Annual Report Download - page 115
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 115 of the 2007 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
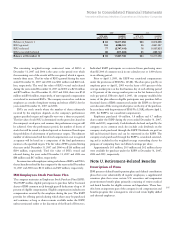
113
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
International Business Machines Corporation and Subsidiary Companies
Healthcare Cost Trend Rate
For nonpension postretirement benefit plan accounting, the com-
pany reviews external data and its own historical trends for healthcare
costs to determine the healthcare cost trend rates. However, the
healthcare cost trend rate has an insignificant effect on plan costs and
obligations as a result of the terms of the plan which limit the com-
pany’s obligation to the participants. The company assumes that the
healthcare cost trend rate for 2008 will be 8 percent. In addition, the
company assumes that the same trend rate will decrease to 5 percent
over the next six years. A one percentage point increase or decrease
in the assumed healthcare cost trend rate would not have a material
effect on the 2007, 2006 and 2005 net periodic cost or the benefit
obligations as of December 31, 2007 and 2006.
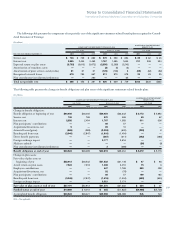
PLAN ASSETS
Defined Benefit Pension Plans
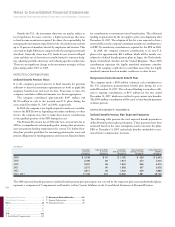
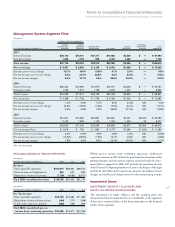
The company’s defined benefit pension plans’ asset allocations at
December 31, 2007 and 2006 and target allocation for 2008, by asset
category, are as follows:
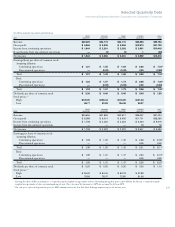
U.S. Plan (Actual Allocations)
PLAN ASSETS 2008
AT DECEMBER 31: TARGET
2007 2006 ALLOCATION
Asset Category:
Equity securities* 46.9% 63.9% 47%
Debt securities 44.6 31.2 43
Real Estate* 5.4 3.9 4
Other 3.1 1.0 6
Total 100.0% 100.0% 100%
* See the following discussion regarding certain private market assets, and future funding
commitments thereof, that are not as liquid as the publicly traded securities.
Material Non-U.S. Plans (Weighted-Average)
PLAN ASSETS 2008
AT DECEMBER 31: TARGET
2007 2006 ALLOCATION
Asset Category:
Equity securities 58.0% 62.7% 57%
Debt securities 37.8 34.8 39
Real estate 1.9 2.1 2
Other 2.3 0.4 2
Total 100.0% 100.0% 100%
The investment objectives of the PPP portfolio are designed to gener-
ate returns that will enable the PPP to meet its future obligations. The
precise amount for which these obligations will be settled depends on
future events, including the retirement dates and life expectancy of the
plans’ participants. The obligations are estimated using actuarial
assumptions, based on the current economic environment. The PPP
portfolio’s investment strategy balances the requirement to generate
returns, using potentially higher yielding assets such as equity securi-
ties, with the need to control risk in the PPP portfolio with less volatile
assets, such as fixed-income securities. Risks include, among others,
inflation, volatility in equity values and changes in interest rates that
could cause the plans to become underfunded, thereby increasing
their dependence on contributions from the company. Within each
asset class, careful consideration is given to balancing the portfolio
among industry sectors, geographies, interest rate sensitivity, depen-
dence on economic growth, currency and other factors that affect
investment returns. During 2007, the company modified the asset
allocation of the PPP portfolio primarily by reducing public equity
securities, by increasing debt securities from 33 percent to 43 percent
of total plan assets, and by increasing the duration of debt securities
and increasing the use of derivatives, including interest rate swaps in
debt securities to further mitigate the effects of future interest rate
changes on the overfunded level of the PPP. These changes were
designed to reduce the potential negative impact that equity markets
or interest rates might have on the funded status of the PPP. These
changes did not impact the expected long-term return on plan assets
assumption, which remained at 8.00 percent for 2008. The effect on
expected long-term return on plan assets of increasing the duration
of debt securities substantially offset the effect of reducing public
equity securities. Derivatives are also used to hedge currency, adjust
portfolio duration and reduce specific market risks.
The assets are managed by professional investment firms, as well
as by investment professionals who are employees of the company.
They are bound by mandates and are measured against specific
benchmarks. Among these managers, consideration is given, but not
limited to, balancing security concentration, issuer concentration,
investment style and reliance on particular active and passive invest-
ment strategies. Market liquidity risks are tightly controlled, with
only a modest percentage of the PPP portfolio invested in private
market assets consisting of private equities and private real estate
investments, which are less liquid than publicly traded securities. The
PPP portfolio included private market assets comprising approxi-
mately 12.0 percent and 10.2 percent of total assets at December 31,
2007 and 2006, respectively. The target allocation for private market
assets in 2008 is 12.0 percent. As of December 31, 2007, the PPP
portfolio had $3,621 million in commitments for future private market
investments to be made over a number of years. These commitments
are expected to be funded from plan assets. Other assets in the PPP
portfolio include commodities and non-traditional investments
designed to further diversify the returns of the PPP portfolio.
Equity securities include IBM common stock of $111 million,
representing 0.2 percent of total PPP plan assets at December 31,
2007 and $159 million, representing 0.3 percent of total PPP plan
assets at December 31, 2006.