Rogers 2010 Annual Report Download - page 82
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 82 of the 2010 Rogers annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
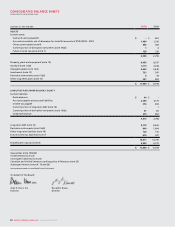
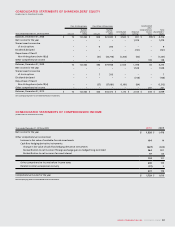
86 ROGERS COMMUNICATIONS INC. 2010 ANNUAL REPORT
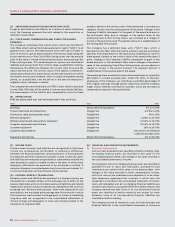
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(C) SUBSCRIBER ACQUISITION AND RETENTION COSTS:
Except as described in note 2(b)(iv), as it relates to cable installation
costs, the Company expenses the costs related to the acquisition or
retention of subscribers.
(D) STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION AND OTHER STOCK-BASED
PAYMENTS:
The Company’s employee stock option plans, which are described in
note 19(a), attach cash-settled share appreciation rights (“SARs”) to all
granted stock options. The SARs feature allows the option holder to
elect to receive in cash an amount equal to the intrinsic value, being the
excess market price of the Class B Non-Voting share over the exercise
price of the option, instead of exercising the option and acquiring Class
B Non-Voting shares. All outstanding stock options are classified as
liabilities and are carried at their intrinsic value, as adjusted for vesting,
measured as the difference between the current stock price and the
option exercise price. The intrinsic value of the liability is marked-to-
market each period and is amortized to income over the period in which
the related services are rendered, which is usually the graded vesting
period, or, as applicable, over the period to the date an employee is
eligible to retire, whichever is shorter.
The Company has a restricted share unit (“RSU”) plan, which is described
in note 19(b). RSUs that will be settled in cash are recorded as liabilities.
The measurement of the liability and compensation costs for these
awards is based on the intrinsic value of the award and is recorded as a
charge to income over the vesting period of the award. Changes in the
Company’s liability subsequent to the grant of the award and prior to
the settlement date, due to changes in the market value of the
underlying Class B Non-Voting shares, are recorded as a charge to
income in the period incurred. The payment amount is established as of
the vesting date of the award.
The Company has a deferred share units (“DSU”) plan, which is
described in note 19(c). DSUs that will be settled in cash are recorded as
liabilities. The measurement of the liability and compensation costs for
these awards is based on the intrinsic value of the award at the date of
grant. Changes in the Company’s liability subsequent to grant of the
award and prior to the settlement date, due to changes in the market
value of the underlying Class B Non-Voting shares, are recorded as a
charge to income in the period incurred. The payment amount is
established as of the exercise date of the award.
The employee share accumulation plan allows employees to voluntarily
participate in a share purchase plan. Under the terms of the plan,
employees of the Company can contribute a specified percentage of
their regular earnings through payroll deductions and the Company
makes certain defined contribution matches, which are recorded as
compensation expense in the period made.
(F) INCOME TAXES:
Future income tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future
income tax consequences attributable to temporary differences
between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets
and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Future income tax assets
and liabilities are measured using enacted or substantively enacted tax
rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those
temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. A
valuation allowance is recorded against any future income tax asset if it
is not more likely than not that the asset will be realized.
(G) FOREIGN CURRENCY TRANSLATION:
Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in a foreign currency are
translated into Canadian dollars at the exchange rate in effect at the
balance sheet dates and non-monetary assets and liabilities and related
depreciation and amortization expenses are translated at the historical
exchange rate. Revenue and expenses, other than depreciation and
amortization, are translated at the average rate for the month in which
the transaction was recorded. Exchange gains or losses on translating
long-term debt are recognized in the consolidated statements of
income. Foreign exchange gains or losses are primarily related to the
translation of long-term debt.
(H) FINANCIAL AND DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS:
(i) Financial instruments:
Cash and cash equivalents are classified as held-for-trading. Held-
for-trading financial assets are recorded at fair value on the
consolidated balance sheets with changes in fair value recorded in
the consolidated statements of income.
The Company’s other non-hedging financial assets are classified as
available-for-sale or loans and receivables. Available-for-sale
investments are carried at fair value on the balance sheet, with
changes in fair value recorded in other comprehensive income,
until such time as the investments are disposed of or an other-
than-temporary impairment has occurred, in which case, the
impairment is recorded in the consolidated statements of income.
Loans and receivables and all non-hedging financial liabilities are
carried at amortized cost using the effective interest method. The
Company determined that none of its non-derivative financial
assets are classified as held-to-maturity and except for bank
advances, none of its non-derivative financial liabilities are
classified as held-for-trading.
The Company records all transaction costs for financial assets and
financial liabilities in the consolidated statements of income as
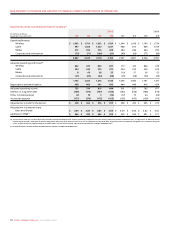
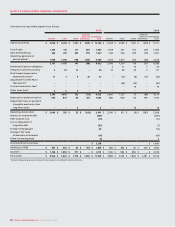
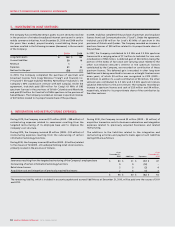
Asset Basis Rate
Buildings Mainly diminishing balance 5% to 6-2/3%
Towers, head-ends and transmitters Straight line 6-2/3% to 25%
Distribution cable and subscriber drops Straight line 5% to 20%
Network equipment Straight line 6-2/3% to 33-1/3%
Wireless network radio base station equipment Straight line 12-1/2% to 14-1/3%
Computer equipment and software Straight line 14-1/3% to 33-1/3%
Customer equipment Straight line 20% to 33-1/3%
Leasehold improvements Straight line Over shorter of estimated
useful life and lease term
Equipment and vehicles Mainly diminishing balance 5% to 33-1/3%
(E) DEPRECIATION:
PP&E are depreciated over their estimated useful lives as follows: