Rogers 2010 Annual Report Download - page 21
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 21 of the 2010 Rogers annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
ROGERS COMMUNICATIONS INC. 2010 ANNUAL REPORT 25
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
WIRELESS STRATEGY
Wireless’ objective is to drive profitable growth within the Canadian
wireless communications industry, and its strategy is designed to
maximize subscriber share, cash flow and return on invested capital.
The key elements of its strategy are as follows:
• Continually enhancing its scale and competitive position in the
Canadian wireless communications market;
• Focusingonofferinginnovativevoiceandwirelessdataservices
into the targeted youth, family, and small and medium-sized
business segments, and specifically to drive increased penetration of
smartphones and other advanced wireless devices;
• Enhancing the customer experience through ongoing focus
principally in the areas of wireless devices, network quality and
customer service in order to maximize service revenue and minimize
customer deactivations, or churn;
• Increasingrevenuefromexistingcustomersbycrosssellingandup
selling wireless data and other enhanced and converged services to
wireless voice customers;
• Enhancingandexpandingownedandthirdpartysalesdistribution
channels to deliver products, services and support to customers;
• Maintainingthemosttechnologicallyadvanced,high-qualityand
national wireless network possible with global coverage enabled by
widely adopted global standard network technologies; and
• Leveraging relationships across the Rogers group of companies
to provide bundled product and service offerings at attractive
prices to common customers, in addition to implementing cross-
selling, distribution and branding initiatives as well as leveraging
infrastructure sharing opportunities.
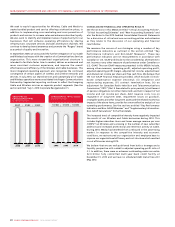
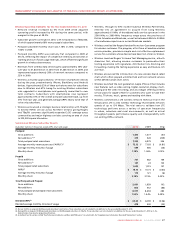
20102009
2008
2009
200
8
201
0
$73.12$73.93$75.41
WIRELESS POSTPAID
MONTHLY ARPU
20102009
2008
2009
200
8
201
0
1.18%1.06%1.10%
WIRELESS POSTPAID
MONTHLY CHURN
RECENT WIRELESS INDUSTRY TRENDS
Focus on Customer Retention
The wireless communications industry’s current market penetration in
Canada is estimated to be 74% of the population, compared to
approximately96%intheU.S.andapproximately121%intheUnited
Kingdom, and Wireless expects the Canadian wireless industry to
continue to grow by approximately 4 to 5 percentage points of
penetration each year for the next several years. As penetration
deepens, it requires an increasing focus on customer satisfaction, the
promotion of new data and voice services to existing customers, and
customer retention.
Demand for Sophisticated Data Applications
The ongoing development of wireless data transmission technologies
has led wireless device developers, such as handsets and portable
computing devices, to develop more sophisticated smartphone type
devices with increasingly advanced capabilities, including access to
e-mail and other corporate information technology platforms, news,
sports, financial information and services, shopping services, photos,
music, applications, and streaming video clips, mobile television and
other functions. Wireless believes that the introduction of such new
devices and applications will drive continued growth of wireless data
services. Along with the acceleration of smartphone penetration comes
the higher costs of equipment subsidies.
Increased Competition from Other Wireless Operators
Wireless faces increased competition from incumbent wireless
operators as well as new entrants, which is fully described in the section
of this MD&A entitled “Competition in our Businesses”. Some new
entrants are introducing new unlimited pricing plans which have
resulted in downward price adjustments and lower ARPU.
Migration to Next Generation Wireless Technology
The ongoing development of wireless data transmission technologies
and the increased demand for sophisticated wireless services, especially
data communications services, have led wireless providers to migrate
towards the next generation of digital voice and data broadband
wireless networks such as HSPA+ and LTE. These networks are intended
to provide wireless communications with wireline quality sound, far
higher data transmission speeds with increased efficiency, and
enhanced streaming video capabilities. These networks support a
variety of increasingly advanced data applications, including broadband
Internet access, multimedia services and seamless access to corporate
information systems, including desktop, client and server-based
applications that can be accessed on a local, national or international
basis. Wireless has been progressing towards next generation
technology with LTE technical trials being conducted in the Ottawa
area. Capital intensity is expected to increase with continuing network
investments.
Development of Additional Technologies
In addition to the two main technology paths of the mobile/broadband
wireless industry, namely GSM/HSPA and Code Division Multiple Access/
Evolution Data Optimized (“CDMA/EVDO”), three other significant
broadband wireless technologies are in the process of development:
WiFi, WiMAX and LTE. These technologies may accelerate the
widespread adoption of digital voice and broadband wireless data
networks.
WiFi (the IEEE 802.11 industry standard) allows suitably equipped
devices, such as laptop computers and personal digital assistants, to
connect to a local area wireless access point. These access points utilize
unlicenced spectrum and the wireless connection is only effective
within a local area radius of approximately 50–100 metres of the access
point, and provide speeds similar to a wired local area network (“LAN”)
environment (most recently the version designated as 802.11n). As the
technology is primarily designed for in-building wireless access, many
access points must be deployed to cover the selected local geographic
area, and must also be interconnected with a broadband network to
supply the connectivity to the Internet. Future enhancements to the
range of WiFi service and the networking of WiFi access points may
provide additional opportunities for wireless operators or municipal
WiFi network operators, each providing capacity and coverage under
the appropriate circumstances.
LTE, the worldwide GSM community’s new fourth generation (“4G”)
broadband wireless technology evolution path, is being deployed in
certain parts of the world. LTE is planned to be an all IP-based wireless
data technology based on a new modulation scheme (orthogonal
frequency-division multiplexing) that is specifically designed to improve