Blackberry 2014 Annual Report Download - page 73
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 73 of the 2014 Blackberry annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
65
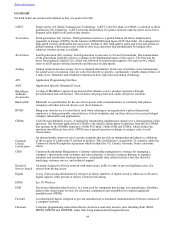
GPRS
General Packet Radio Service. An enhancement to the GSM (see below) mobile communications system
that supports data packets. GPRS enables continuous flows of IP data packets over the system for such
applications as Web browsing and data access. GPRS differs from GSM’s short messaging service, which is
limited to messages of 160 bytes in length.
GPS Global Positioning System.
GSM
Global System for Mobile Communications. A digital cellular phone technology based on TDMA that is the
predominant system in Europe, but is also used around the world. Operating in the 900MHz and 1.8GHz
bands in Europe and the 1.9GHz PCS band in the U.S., GSM defines the entire cellular system, not just the
air interface (i.e. TDMA, CDMA). GSM phones use a Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) smart card that
contains user account information.
HSPA
High-Speed Packet Access. A family of radio interface standards that will improve the speed and accuracy
of traffic over cellular networks. HSPA builds on the existing WCDMA technology that has already been
deployed to allow carriers to offer better speeds and larger bandwidth intensive services like streaming
audio and video.
iDEN
Integrated Digital Enhanced Network. A wireless communications technology from Motorola that provides
support for voice, data, short messages (SMS) and dispatch radio (two-way radio) in one phone. Operating
in the 800MHz and 1.5GHz bands and based on TDMA, iDEN uses Motorola’s VSELP (Vector Sum
Excited Linear Predictors) vocoder for voice compression and QAM modulation to deliver 64 Kbps over a
25 kHz channel. Each 25 kHz channel can be divided six times to transmit any mix of voice, data, dispatch
or text message. Used by various carriers around the globe, Nextel Communications provides nationwide
coverage in the U.S.
IM
Instant Messaging. A medium which enables two or more people to communicate in real time utilizing
typed text over an electronic network.
IP
Intellectual Property. Intangible property that is the result of creativity (such as patents or trademarks or
copyrights).
IPSec
Internet Protocol Security. Allows for the securing of IP communications by authenticating and encrypting
IP packet of a communication exchange from host-to-host.
Java
An object-oriented programming language developed by Sun Microsystems, Inc. Java was designed to be
secure and platform-neutral such that it can be run on any type of platform, making Java a useful language
for programming Internet applications.
LTE
Long Term Evolution is a wireless communication standard of high-speed data for smartphones and data
terminals
NFC
Near Field Communication. Technology that allows smartphones and similar devices to link together
through radio communication, when tapping them together, or bringing them into close proximity.
NOC
Network Operations Centre. A central location for network management. It functions as a control centre for
network monitoring, analysis and accounting.
PBX
Private Branch Exchange. A private telephone network used within an enterprise. Users share a fixed
number of outside lines instead of being provided with one outside line for each individual user. This allows
for use of extensions as opposed to direct dial numbers.
PDA Personal digital assistant. A hand held portable microcomputer.
PIM Personal Information Management.
QWERTY
The modern-day keyboard layout on English-language computer and typewriter keyboards. It takes its name
from the first six characters seen in the far left of the keyboard’s top row of letters.
ROM
Read Only Memory. A class of storage media used in computers and other electronic devices. Once data has
been written to a ROM chip, it cannot be removed and can only be read.
SDK
Software Developers Kit. A set of software routines and utilities used to help programmers write an
application.
Table of Contents