Nokia 2009 Annual Report Download - page 253
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 253 of the 2009 Nokia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.33. Risk management (Continued)
Equity price risk
Nokia is exposed to equity price risk as the result of market price fluctuations in the listed equity
instruments held mainly for strategic business reasons.
Nokia has certain strategic minority investments in publicly listed equity shares. The fair value of the
equity investments which are subject to equity price risk at December 31, 2009 was EUR 8 million
(EUR 8 million in 2008). In addition, Nokia invests in private equity through venture funds, which,
from time to time, may have holdings in equity instruments which are listed in stock exchanges.
These investments are classified as availableforsale carried at fair value. See Note 15 for more
details on availableforsale investments.
Due to the insignificant amount of exposure to equity price risk, there are currently no outstanding
derivative financial instruments designated as hedges for these equity investments.
Nokia is exposed to equity price risk on social security costs relating to its equity compensation plans.
Nokia mitigates this risk by entering into cash settled equity option contracts.
ValueatRisk
Nokia uses the ValueatRisk (VaR) methodology to assess the Group exposures to foreign exchange
(FX), interest rate, and equity risks. The VaR gives estimates of potential fair value losses in market
risk sensitive instruments as a result of adverse changes in specified market factors, at a specified
confidence level over a defined holding period.
In Nokia the FX VaR is calculated with the Monte Carlo method which simulates random values for
exchange rates in which the Group has exposures and takes the nonlinear price function of certain FX
derivative instruments into account. The variancecovariance methodology is used to assess and
measure the interest rate risk and equity price risk.
The VaR is determined by using volatilities and correlations of rates and prices estimated from a one
year sample of historical market data, at 95% confidence level, using a onemonth holding period. To
put more weight on recent market conditions, an exponentially weighted moving average is
performed on the data with an appropriate decay factor.
This model implies that within a onemonth period, the potential loss will not exceed the VaR
estimate in 95% of possible outcomes. In the remaining 5% of possible outcomes, the potential loss
will be at minimum equal to the VaR figure, and on average substantially higher.
The VaR methodology relies on a number of assumptions, such as, a) risks are measured under
average market conditions, assuming that market risk factors follow normal distributions; b) future
movements in market risk factors follow estimated historical movements; c) the assessed exposures
do not change during the holding period. Thus it is possible that, for any given month, the potential
losses at 95% confidence level are different and could be substantially higher than the estimated VaR.
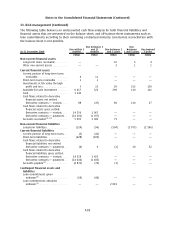
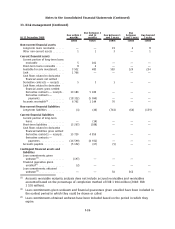
FX Risk
The VaR figures for the Group’s financial instruments which are sensitive to foreign exchange risks are
presented in Table 1 below. As defined under IFRS 7, the financial instruments included in the VaR
calculation are:
• FX exposures from outstanding balance sheet items and other FX derivatives carried at fair value
through profit and loss which are not in a hedge relationship and are mostly used for hedging
balance sheet FX exposure.
F79
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)