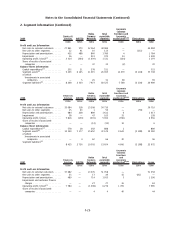
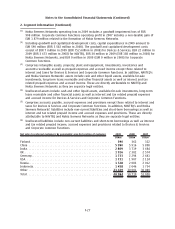
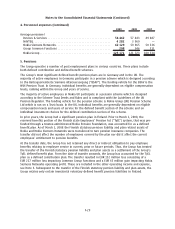
Nokia 2009 Annual Report Download - page 197
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 197 of the 2009 Nokia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.1. Accounting principles (Continued)
feasibility, have been met. Should a product fail to substantiate its estimated feasibility or life cycle,
material development costs may be required to be writtenoff in future periods.
Business combinations
The Group applies the purchase method of accounting to account for acquisitions of businesses. The
cost of an acquisition is measured as the aggregate of the fair values at the date of exchange of the
assets given, liabilities incurred, equity instruments issued and costs directly attributable to the
acquisition. Identifiable assets, liabilities and contingent liabilities acquired or assumed are measured
separately at their fair value as of the acquisition date. The excess of the cost of the acquisition over
our interest in the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired is recorded as goodwill.
The allocation of fair values to the identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed is based on
various valuation assumptions requiring management judgment. Actual results may differ from the
forecasted amounts and the difference could be material. See also Note 8.
Assessment of the recoverability of longlived assets, intangible assets and goodwill
The recoverable amounts for longlived assets, intangible assets and goodwill have been determined
based on the expected future cash flows attributable to the asset or cashgenerating unit discounted
to present value. The key assumptions applied in the determination of recoverable amount include
the discount rate, length of the explicit forecast period and estimated growth rates, profit margins
and level of operational and capital investment. Amounts estimated could differ materially from what
will actually occur in the future. See also Note 7.
Fair value of derivatives and other financial instruments
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market (for example, unlisted
equities, currency options and embedded derivatives) are determined using various valuation
techniques. The Group uses judgment to select an appropriate valuation methodology as well as
underlying assumptions based on existing market practice and conditions. Changes in these
assumptions may cause the Group to recognize impairments or losses in future periods.
Income taxes
Management judgment is required in determining income tax expense, tax provisions, deferred tax
assets and liabilities and the extent to which deferred tax assets can be recognized. When
circumstances indicate it is no longer probable that deferred tax assets will be utilized they are
assessed for realizability and adjusted as necessary. If the final outcome of these matters differs from
the amounts initially recorded, differences may impact the income tax expense in the period in which
such determination is made.
Pensions
The determination of pension benefit obligation and expense for defined benefit pension plans is
dependent on the selection of certain assumptions used by actuaries in calculating such amounts.
Those assumptions include, among others, the discount rate, expected longterm rate of return on
plan assets and annual rate of increase in future compensation levels. A portion of plan assets is
invested in equity securities which are subject to equity market volatility. Changes in assumptions
and actuarial conditions may materially affect the pension obligation and future expense. See also
Note 5.
Sharebased compensation
The Group operates various types of equity settled sharebased compensation schemes for employees.
Fair value of stock options is based on certain assumptions, including, among others, expected
F23
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)