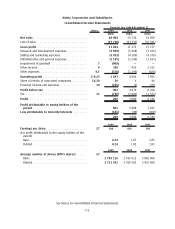
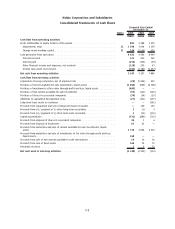
Nokia 2009 Annual Report Download - page 171
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 171 of the 2009 Nokia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Engine:
Hardware and software that perform essential core functions for telecommunication or
application tasks. A mobile device engine includes, for example, the printed circuit boards, radio
frequency components, basic electronics and basic software.
Ethernet:
A type of local area network (LAN).
ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute):
Standards produced by the ETSI
contain technical specifications laying down the characteristics required for a telecommunications
product.
FTTB (
Fiber to the building
): refers to a telecommunications system in which fiber optic cable is
run directly to a specific building such as a business or apartment house.
FTTC (
Fiber to the curb):
refers to a telecommunications system based on the use of optical fiber
cable directly to the curbs near homes or any business environment.
GPRS (General Packet Radio Services):
A service that provides packet switched data, primarily for
second generation GSM networks.
GPS (Global Positioning System):
Satellitebased positioning system that is used for reading
geographical position and as a source of the accurate coordinated universal time.
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications):
A digital system for mobile communications
that is based on a widely accepted standard and typically operates in the 900 MHz, 1800 MHz and
1900 MHz frequency bands.
HSPA (HighSpeed Packet Access):
A wideband code division multiple access feature that refers to
both 3GPP highspeed downlink packet access and highspeed uplink packet access (see also HSDPA
and HSUPA).
HSDPA (HighSpeed Downlink Packet Access):
A wideband code division multiple access feature
that provides high data rate transmission in a WCDMA downlink to support multimedia services.
IHSPA (InternetHSPA):
A 3GPP standardsbased simplified network architecture innovation from
Nokia implemented as a data overlay radio access layer that can be built with already deployed
WCDMA base stations.
IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem):
A subsystem providing IP multimedia services that complement
the services provided by the circuit switched core network domain.
IP (Internet Protocol):
A network layer protocol that offers a connectionless Internet work service
and forms part of the TCP/IP protocol.
IPR (Intellectual Property Right):
Legal right protecting the economic exploitation of intellectual
property, a generic term used to describe products of human intellect, for example, patents, that have
an economic value.
IPTV (Internet Protocol television):
Television services delivered over internet protocol
infrastructure through a telephone or cable network using a broadband access line.
Java:
An objectoriented programming language that is intended to be hardware and software
independent.
LTE (LongTerm Evolution):
3GPP radio technology evolution architecture.
Maemo:
A Linuxbased software platform that powers the Nokia N900 mobile computer, as well as
Nokia Internet Tablets. We are merging Maemo with Intel’s Moblin software platform to create
MeeGo. (See
MeeGo
).
MeeGo:
A Linuxbased, open source software platform that is being formed from the merger of
Maemo and Intel’s Moblin software platform, for use in a wide range of computing devices, including
169