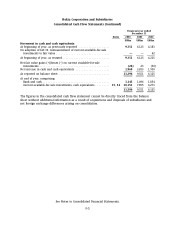
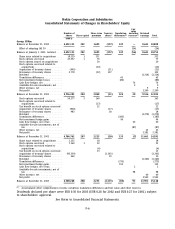
Nokia 2003 Annual Report Download - page 108
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 108 of the 2003 Nokia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.DVB (Digital Video Broadcasting):
A standard for digital satellite, cable and terrestrial video
broadcasting.
EDGE (Enhanced Data Rates for Global Evolution):
A technology to boost cellular network
capacity and increase data rates of existing GSM networks to as high as 473 kbit/s.
ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) Standards:
Standards produced by
the ETSI that contain technical specifications laying down the characteristics required for a
telecommunications product.
GPRS (General Packet Radio Services):
A service that provides packet switched data, primarily
for second generation GSM networks.
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications):
A digital cellular network that operates in
the 900 MHz frequency band, the frequency adopted for use in most European and Asian
countries, as well as the 1800 MHz band.
GSM 1900 system:
A GSM-based cellular system that operates in the 1900 MHz frequency band
(also referred to as PCS 1900 or DCS 1900).
IP (Internet Protocol):
A network layer protocol that offers a connectionless Internetwork
service and forms part of the TCP/IP protocol.
ISP (Internet Service Provider):
A company that provides access to the Internet and World Wide
Web via a fixed or mobile network.
Iu Interface:
An interface standardized by the Third Generation Partnership Program. It enables
multi-vendor interconnection between a core network and a radio network.
LAN (Local Area Network):
A computer network that spans a small area. Most LANs are confined
to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected to other LANs over
any distance via telephone lines and radio waves. A system of LANs connected in this way is
called a wide-area network (WAN).
MMS (Multimedia Messaging Services):
Enables mobile phone users to send and receive
messages with rich content, such as images, polyphonic ring tones, audio clips and even short
videos. MMS is an open standard defined by the Open Mobile Alliance (OMA).
Mobile Phone Engine:
The mobile phone engine is the generic, internal part of a mobile phone.
It does not include the phone cover, key mat or other version-specific mechanical parts, and is free
of customer- or language-specific software.
MSP (Managed Service Provider):
A company that manages information technology services for
other companies by delivering outsourced IT management and problem resolution for e-business
and mission-critical systems. MSPs ordinarily provide and manage their services remotely using an
interactive Web page as the user interface.
OMA (Open Mobile Alliance):
Delivers open standards for the mobile industry, helping to create
interoperable services which work across countries, operators and mobile terminals and are
driven by users’ needs. To expand the mobile market, companies supporting the Open Mobile
Alliance will work to stimulate the fast and wide adoption of a variety of new, enhanced mobile
information, communication and entertainment services. The Open Mobile Alliance includes all key
elements of the wireless value chain, and contributes to the timely and efficient introduction of
services and applications.
Packet:
Part of a message transmitted over a packet switched network.
107