IBM 2003 Annual Report Download - page 99
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 99 of the 2003 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
97
The resulting cost of funds is lower than that which would
have been available if debt with matching characteristics was
issued directly. The weighted-average remaining maturity of
all swaps in the debt risk management program is approxi-
mately four years.
LONG-TERM INVESTMENTS IN FOREIGN SUBSIDIARIES
(NET INVESTMENT)
Asignificant portion of the company’s foreign currency
denominated debt portfolio is designated as a hedge of net
investment to reduce the volatility in stockholders’ equity
caused by changes in foreign currency exchange rates in the
functional currency of major foreign subsidiaries with
respect to the U.S. dollar. The company also uses currency
swaps and foreign exchange forward contracts for this risk
management purpose. The currency effects of these hedges
(approximately $200 million for the current period, net of
tax) are reflected as a loss in the Accumulated gains and
(losses) not affecting retained earnings section of the
Consolidated Statement of Stockholders’ Equity, thereby
offsetting a portion of the translation of the applicable foreign
subsidiaries’ net assets.
ANTICIPATED ROYALTIES AND COST TRANSACTIONS
The company’s operations generate significant nonfunctional
currency, third party vendor payments and intercompany
payments for royalties, and goods and services among the
company’s non-U. S. subsidiaries and with the parent company.
In anticipation of these foreign currency cash flows and in
view of the volatility of the currency markets, the company
selectively employs foreign exchange forward and option
contracts to manage its currency risk. These contracts may
have extended maturities beyond one year and from time to
time that extend to three years. As of December 31, 2003,
the maximum remaining maturity of these derivative instru-
ments was approximately 18 months, commensurate with
the underlying hedged anticipated cash flows.
SUBSIDIARY CASH AND FOREIGN CURRENCY
ASSET/LIABILITY MANAGEMENT
The company uses its Global Treasury Centers to manage the
cash of its subsidiaries. These centers principally use currency
swaps to convert cash flows in a cost-effective manner. In
addition, the company uses foreign exchange forward contracts
to hedge, on a net basis, the foreign currency exposure of a
portion of the company’s nonfunctional currency assets and
liabilities. The terms of these forward and swap contracts
are generally less than one year. The changes in fair value from
these contracts and from the underlying hedged exposures
are generally offsetting and are recorded in Other (income)
and expense in the Consolidated Statement of Earnings.
EQUITY RISK MANAGEMENT
The company is exposed to certain equity price changes
related to certain obligations to employees. These equity
exposures are primarily related to market value movements in
certain broad equity market indices and in the company’s own
stock. Changes in the overall value of this employee com-
pensation obligation are recorded in SG&A expense in the
Consolidated Statement of Earnings. Although not designated
as accounting hedges, the company utilizes equity derivatives,
including equity swaps and futures to economically hedge the
equity exposures relating to this employee compensation
obligation. To match the exposures relating to this employee
compensation obligation, these derivatives are linked to the
total return of certain broad equity market indices and/or the
total return of the company’s common stock. These derivatives
are recorded at fair value with gains or losses also reported in
SG&A expense in the Consolidated Statement of Earnings.
OTHER DERIVATIVES
The company holds warrants in connection with certain
investments that, although not designated as hedging instru-
ments, are deemed derivatives since they contain net share
settlement clauses. During the year, the company recorded
the change in the fair value of these warrants in net income.
The company is exposed to a potential loss if a client fails
to pay amounts due the company under contractual terms
(“credit risk”). The company has established policies and pro-
cedures for mitigating credit risk on principal transactions,
including reviewing and establishing limits for credit expo-
sure, maintaining collateral, and continually assessing the
creditworthiness of counterparties. In 2003, the company
began utilizing credit default swaps to economically hedge
certain credit exposures. These derivatives have terms of two
years. The swaps are not designated as accounting hedges and
are recorded at fair value with gains and losses reported in
SG&A in the Consolidated Statement of Earnings.
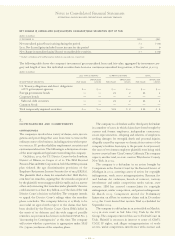
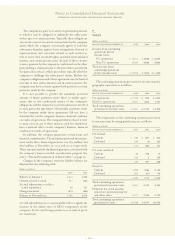
The tables on page 98 summarize the net fair value of the
company’s derivative and other risk management instruments
at December 31, 2003 and 2002 (included in the Consolidated
Statement of Financial Position).
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHINES CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARY COMPANIES