Cisco 2012 Annual Report Download - page 114
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 114 of the 2012 Cisco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
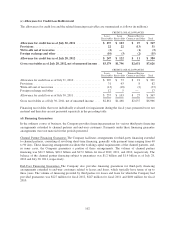
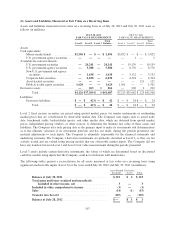
(d) Securities Lending
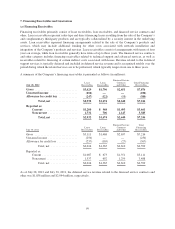
The Company periodically engages in securities lending activities with certain of its available-for-sale
investments. These transactions are accounted for as a secured lending of the securities, and the securities are
typically loaned only on an overnight basis. The average daily balance of securities lending for fiscal 2012 and
2011 was $0.5 billion and $1.6 billion, respectively. The Company requires collateral equal to at least 102% of
the fair market value of the loaned security in the form of cash or liquid, high-quality assets. The Company
engages in these secured lending transactions only with highly creditworthy counterparties, and the associated
portfolio custodian has agreed to indemnify the Company against collateral losses. The Company did not
experience any losses in connection with the secured lending of securities during the periods presented. As of
July 28, 2012 and July 30, 2011, the Company had no outstanding securities lending transactions.
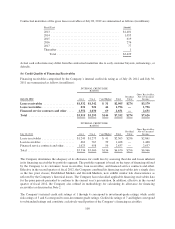
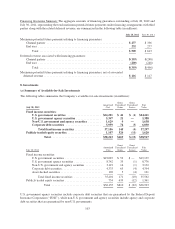
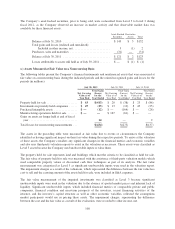
9. Fair Value
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received from selling an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an
orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. When determining the fair value
measurements for assets and liabilities required or permitted to be either recorded or disclosed at fair value, the
Company considers the principal or most advantageous market in which it would transact, and it also considers
assumptions that market participants would use when pricing the asset or liability.
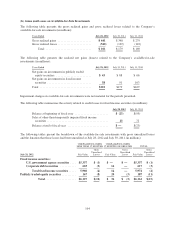
(a) Fair Value Hierarchy
The accounting guidance for fair value measurement requires an entity to maximize the use of observable inputs
and minimize the use of unobservable inputs when measuring fair value. The standard establishes a fair value
hierarchy based on the level of independent, objective evidence surrounding the inputs used to measure fair
value. A financial instrument’s categorization within the fair value hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of
input that is significant to the fair value measurement. The fair value hierarchy is as follows:
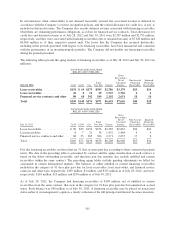
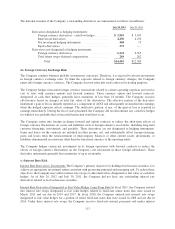
Level 1 applies to assets or liabilities for which there are quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or
liabilities.
Level 2 applies to assets or liabilities for which there are inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for
the asset or liability such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; quoted prices for
identical assets or liabilities in markets with insufficient volume or infrequent transactions (less active markets);
or model-derived valuations in which significant inputs are observable or can be derived principally from, or
corroborated by, observable market data.
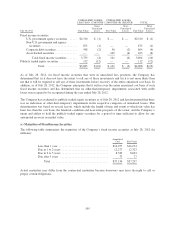
Level 3 applies to assets or liabilities for which there are unobservable inputs to the valuation methodology that
are significant to the measurement of the fair value of the assets or liabilities.
106