ADT 2010 Annual Report Download - page 174
Download and view the complete annual report
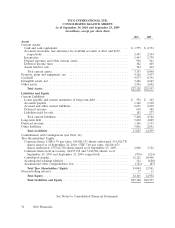
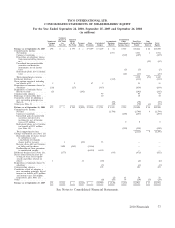
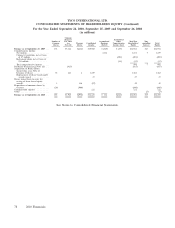
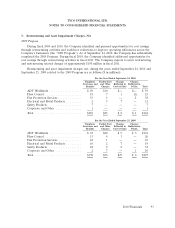
Please find page 174 of the 2010 ADT annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.TYCO INTERNATIONAL LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued)
Environmental Costs—Tyco is subject to laws and regulations relating to protecting the
environment. Tyco provides for expenses associated with environmental remediation obligations when
such amounts are probable and can be reasonably estimated.
Income Taxes—Deferred tax liabilities and assets are recognized for the expected future tax
consequences of events that have been reflected in the Consolidated Financial Statements. Deferred tax
liabilities and assets are determined based on the differences between the book and tax bases of
particular assets and liabilities and operating loss carryforwards, using tax rates in effect for the years in
which the differences are expected to reverse. A valuation allowance is provided to offset deferred tax
assets if, based upon the available evidence, including consideration of tax planning strategies, it is
more-likely-than-not that some or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
Asbestos-Related Contingencies and Insurance Receivables—The Company and certain of its
subsidiaries along with numerous other companies are named as defendants in personal injury lawsuits
based on alleged exposure to asbestos-containing materials. The Company’s estimate of the liability and
corresponding insurance recovery for pending and future claims and defense costs is predominantly
based on claim experience over the past five years, and a projection which covers claims expected to be
filed, including related defense costs, over the next seven years on an undiscounted basis. Due to the
high degree of uncertainty regarding the pattern and length of time over which claims will be made and
then settled or litigated, the Company uses multiple estimation methodologies based on varying
scenarios of potential outcomes to estimate the range of loss. The Company has concluded that
estimating the liability beyond the seven year period will not provide a reasonable estimate, as these
uncertainties increase significantly as the projection period lengthens.
In connection with the recognition of liabilities for asbestos-related matters, the Company records
asbestos-related insurance recoveries that are probable. The Company’s estimate of asbestos-related
insurance recoveries represents estimated amounts due to the Company for previously paid and settled
claims and the probable reimbursements relating to its estimated liability for pending and future claims.
In determining the amount of insurance recoverable, the Company considers a number of factors,
including available insurance, allocation methodologies, solvency and creditworthiness of the insurers.
Insurable Liabilities—The Company records liabilities for its workers’ compensation, product,
general and auto liabilities. The determination of these liabilities and related expenses is dependent on
claims experience. For most of these liabilities, claims incurred but not yet reported are estimated by
utilizing actuarial valuations based upon historical claims experience. Certain insurable liabilities are
discounted using a risk-free rate of return when the pattern and timing of the future obligation is
reliably determinable. The impact of the discount on the Consolidated Balance Sheets as of
September 24, 2010 and September 25, 2009 was to reduce the obligation by $21 million and
$20 million, respectively. The Company maintains captive insurance companies to manage certain of its
insurable liabilities. Additionally, the Company records receivables from third party insurers when
recovery has been determined to be probable.
Financial Instruments—The Company may use interest rate swaps, currency swaps, forward and
option contracts and commodity swaps to manage risks generally associated with interest rate risk,
foreign exchange risk and commodity prices. Derivatives used for hedging purposes are designated and
effective as a hedge of the identified risk exposure at the inception of the contract. Accordingly,
changes in fair value of the derivative contract are highly effective at offsetting the changes in the fair
86 2010 Financials