ICICI Bank 2008 Annual Report Download - page 184
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 184 of the 2008 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F110
mitigation of operational risk and help business and operation groups to improve internal controls. The
Bank aims to minimize losses and customer dissatisfaction due to failure in processes. The key elements
in the operational risk management process in the Bank include:
l Identification, assessment and control of key operational risks
l Establishment of key risk indicators
l Monitoring
l Mitigation and
l Reporting.
The operational risk standards facilitate the effective communication of operational risk both within and
across businesses. Information about the businesses’ operational risk, historical losses, and the control
environment is reported by each major business segment and functional area, and summarized for senior
management and the Board of Directors.
In each of the banking subsidiaries, local management is responsible for implementing the Bank’s
operational risk management framework as per the operational risk management policy approved by
respective Boards.
b. Approaches for computation of capital charge for operational risk
As per the mandate from RBI, the Bank has adopted Basic Indicator Approach for computing capital
charge for operational risk. Both quantitative and qualitative steps have been initiated to migrate to
advanced approaches for capital computation.
10. INTEREST RATE RISK IN THE BANKING BOOK (IRRBB)
a. Risk Management Framework for IRRBB
Interest rate risk is the risk of potential variability in earnings and capital value resulting from changes
in market interest rates. The Bank holds assets, liabilities and off balance sheet items across various
markets with different maturity or re-pricing dates and linked to different benchmark rates, thus creating
exposure to unexpected changes in the level of interest rates in such markets. Interest rate risk in the
banking book refers to the risk associated with interest rate sensitive instruments that are not held in
the trading book of the Bank.
Risk management framework
The Asset Liability Committee (ALCO) decides strategies and specifies prudential limits for management
of interest rate risk in the banking book within the broad parameters laid down by Board of Directors
/Risk Committee of the Board (RCB). Structural Rate Risk Management Group (SRMG) in the treasury
and the Asset Liability Management (ALM) groups in overseas branches and overseas business units
(OBUs) are responsible for management of interest rate risk on the domestic and the specific offshore
branch banking book respectively by assuming risks within the interest rate risk limits specified by
ALCO. The policy formulation for management of this interest rate risk is done by the GRMG. TMOG is
responsible for preparing the various reports required for monitoring the interest rate risk in the Bank.
These limits are monitored periodically and the breaches, if any, are reported to ALCO. The ALCOs of
individual banking subsidiaries decide on strategies to optimize the interest rate risk carried within their
respective banking book.
Strategies and processes
The Bank proactively manages impact of interest rate in its banking book as a part of its ALM activities.
ALCO of the Bank decides strategies for managing the IRRBB at the desired level. ALCO periodically
gives direction for management of interest rate risk on the basis of its expectations of future interest
rates and various tools viz. gap statement, DoE, earning at risk (EaR), credit spread risk, simulation for
basis risk etc, used to measure the impact of interest rates in the banking book.
Further, certain ratios are monitored for overseas branches, such as Liquidity ratio, Long Term Asset
ratio among others. These provide an appropriate framework for decision making on interest rate
management.
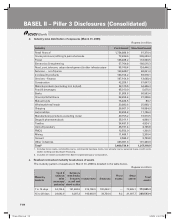
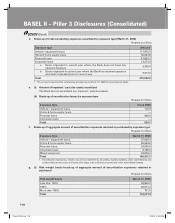
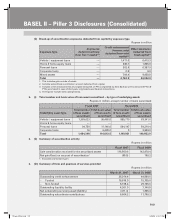
BASEL II – Pillar 3 Disclosures (Consolidated)
1P-less_(Pillar).indd 1101P-less_(Pillar).indd 110 6/20/08 4:53:20 PM6/20/08 4:53:20 PM