ICICI Bank 2008 Annual Report Download - page 138
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 138 of the 2008 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F64
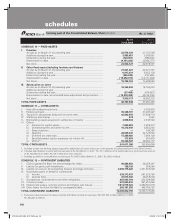
In the consolidated financial statements, deferred tax assets and liabilities are computed at individual entity level and
aggregated for consolidated reporting.
The Group has a comprehensive system of maintenance of information and documents required by transfer pricing legislation
under Section 92-92F of the Income Tax Act, 1961. The management is of the opinion that all international transactions are
at arm’s length so that the above legislation will not have material impact on the financial statements.
5. Claims and benefits paid
In case of general insurance business, claims incurred comprise claims paid, estimated liability for outstanding claims made
following a loss occurrence reported and estimated liability for claims incurred but not reported (‘IBNR’) and claims incurred
but not enough reported (‘IBNER’). Further, claims incurred also include specific claim settlement costs such as survey/legal
fees and other directly attributable costs. Claims (net of amounts receivable from re-insurers/co-insurers) are recognised
on the date of intimation of the loss based on estimates from surveyors/insured. Estimated liability for outstanding claims
at the balance sheet date is recorded net of claims recoverable from/payable to co-insurers/re-insurers and salvage to the
extent there is certainty of realisation. Estimated liability for outstanding claim is determined by the entity on the basis of
ultimate amounts likely to be paid on each claim based on past experience. These estimates are progressively revalidated
on availability of further information. Claims IBNR represent that amount of claims that may have been incurred during the
accounting year but have not been reported or claimed. The claims IBNR provision also includes provision, if any, required
for claims IBNER. Estimated liability for claims IBNR/claims IBNER is based on an actuarial estimate duly certified by the
appointed actuary of the entity. In case of life insurance business, claims other than maturity claims are accounted for on
receipt of intimation. Maturity claims are accounted when due for payment. Re-insurance on such claims is accounted for
in the same period as the related claims. Withdrawals under linked policies are accounted in the respective schemes.
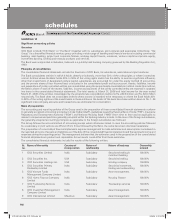
6. Liability for life policies in force
In respect of life insurance business, liability for life policies in force and also policies in respect of which premium has
been discontinued but a liability exists, is determined by the appointed actuary on the basis of an annual review of the life
insurance business, as per the gross premium method in accordance with accepted actuarial practice, requirements of
the IRDA and the Actuarial Society of India. The linked policies sold by the entity carry two types of liabilities – unit liability
representing the fund value of policies and non-unit liability for future expenses, meeting death claims, income taxes and
cost of any guarantees.
7. Reserve for unexpired risk
Reserve for unexpired risk is recognised net of re-insurance ceded and represents premium written that is attributable
and to be allocated to succeeding accounting periods for risks to be borne by the entity under contractual obligations on
contract period basis or risk period basis, whichever is appropriate. It is calculated on a daily pro-rata basis subject to a
minimum of 50% of the premium, written on policies during the twelve months preceding the balance sheet date for fire,
marine, cargo and miscellaneous business and 100% for marine hull business, on all unexpired policies at balance sheet
date, in accordance with the provisions of the Insurance Act, 1938.
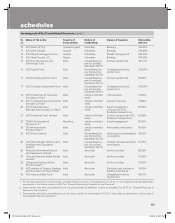
8. Actuarial method and valuation
In case of life insurance business, the actuarial liability on both participating and non-participating policies is calculated using
the gross premium method, using assumptions for interest, mortality, expense and inflation, and in the case of participating
policies, future bonuses together with allowance for taxation and allocation of profits to shareholders. These assumptions
are determined as prudent estimates at the date of valuation with allowances for adverse deviations. No allowance is made
for expected lapses.
The interest rates used for valuing the liabilities are in the range of 4.7% to 10.0% per annum (Previous year – 4.7% to 10%
per annum).
Mortality rates used are based on the published LIC (1994–96) Ultimate Mortality Table for assurances and LIC 96-98 table
for annuities, adjusted to reflect expected experience while morbidity rates used are based on CIBT 93 table, adjusted to
reflect expected experience.
Expenses are provided for at long-term expected renewal expense levels. Per policy renewal expenses are assumed to
inflate at 5.50% per annum.
Unearned premium reserves are held for the unexpired portion of the risk for the general fund liabilities of linked business
and riders there under and one year renewable group term insurance.
The unit liability in respect of linked business has been taken as the value of the units standing to the credit of policyholders,
using the net asset value (NAV) prevailing at the valuation date. The adequacy of charges under unit-linked policies to meet
future expenses has been tested and provision made as appropriate. Provision has also been made for the cost of guarantee
under unit-linked products that carry a guarantee.
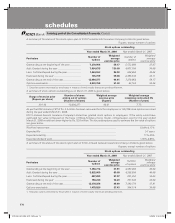
9. Acquisition costs for insurance business
Acquisition costs are those costs that vary with, and are primarily related to the acquisition of new and renewal of insurance
contracts including commissions and policy issue expenses. These costs are expensed in the period in which they are
incurred.
forming part of the Consolidated Accounts (Contd.)
schedules
ICICI_BK_AR_2008_(F47_F92).indd 64ICICI_BK_AR_2008_(F47_F92).indd 64 6/20/08 3:32:11 PM6/20/08 3:32:11 PM