MetLife 2002 Annual Report Download - page 42
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 42 of the 2002 MetLife annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
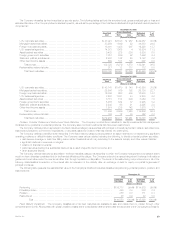
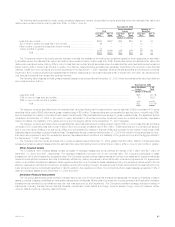
The table below provides a summary of the notional amount and fair value of derivative financial instruments held at:
December 31, 2002 December 31, 2001
Fair Value Fair Value
Notional Notional
Amount Assets Liabilities Amount Assets Liabilities
(Dollars in millions)
Financial futures ******************************************************* $ 4 $— $— $ — $— $—
Interest rate swaps ***************************************************** 3,866 196 126 1,823 73 9
Floors **************************************************************** 325 9 — 325 11 —
Caps **************************************************************** 8,040 — — 7,890 5 —
Financial forwards ****************************************************** 1,945 — 12 — — —
Foreign currency swaps************************************************* 2,371 92 181 1,925 188 26
Options ************************************************************** 78 9 — 1,880 8 12
Foreign currency forwards *********************************************** 54 — 1 67 4 —
Written covered calls *************************************************** —— — 40— —
Credit default swaps *************************************************** 376 2 — 270 — —
Total contractual commitments ***************************************** $17,059 $308 $320 $14,220 $289 $47
Securities Lending
The Company participates in a securities lending program whereby blocks of securities, which are included in investments, are loaned to third
parties, primarily major brokerage firms. The Company requires a minimum of 102% of the fair value of the loaned securities to be separately maintained
as collateral for the loans. Securities with a cost or amortized cost of $14,873 million and $11,416 million and an estimated fair value of $17,625 million
and $12,066 million were on loan under the program at December 31, 2002 and 2001, respectively. The Company was liable for cash collateral under
its control of $17,862 million and $12,661 million at December 31, 2002 and 2001, respectively. Security collateral on deposit from customers may not
be sold or repledged and is not reflected in the consolidated financial statements.
Separate Account Assets
The Company manages each separate account’s assets in accordance with the prescribed investment policy that applies to that specific separate
account. The Company establishes separate accounts on a single client and multi-client commingled basis in conformity with insurance laws. Generally,
separate accounts are not chargeable with liabilities that arise from any other business of the Company. Separate account assets are subject to the
Company’s general account claims only to the extent that the value of such assets exceeds the separate account liabilities, as defined by the account’s
contract. If the Company uses a separate account to support a contract providing guaranteed benefits, the Company must comply with the asset
maintenance requirements stipulated under Regulation 128 of the Department. The Company monitors these requirements at least monthly and, in
addition, performs cash flow analyses, similar to that conducted for the general account, on an annual basis. The Company reports separately as assets
and liabilities investments held in separate accounts and liabilities of the separate accounts. The Company reports substantially all separate account
assets at their fair market value. Investment income and gains or losses on the investments of separate accounts accrue directly to contractholders, and,
accordingly, the Company does not reflect them in its consolidated statements of income and cash flows. The Company reflects in its revenues fees
charged to the separate accounts by the Company, including mortality charges, risk charges, policy administration fees, investment management fees
and surrender charges.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
The Company must effectively manage, measure and monitor the market risk associated with its invested assets and interest rate sensitive
insurance contracts. It has developed an integrated process for managing risk, which it conducts through its Corporate Risk Management Department,
several asset/liability committees and additional specialists at the business segment level. The Company has established and implemented comprehen-
sive policies and procedures at both the corporate and business segment level to minimize the effects of potential market volatility.
Market Risk Exposures
The Company has exposure to market risk through its insurance operations and investment activities. For purposes of this disclosure, ‘‘market risk’’
is defined as the risk of loss resulting from changes in interest rates, equity prices and foreign currency exchange rates.
Interest rates. The Company’s exposure to interest rate changes results from its significant holdings of fixed maturities, as well as its interest rate
sensitive liabilities. The fixed maturities include U.S. and foreign government bonds, securities issued by government agencies, corporate bonds and
mortgage-backed securities, all of which are mainly exposed to changes in medium- and long-term treasury rates. The interest rate sensitive liabilities for
purposes of this disclosure include guaranteed interest contracts and fixed annuities, which have the same interest rate exposure (medium- and long-
term treasury rates) as the fixed maturities. The Company employs product design, pricing and asset/liability management strategies to reduce the
adverse effects of interest rate volatility. Product design and pricing strategies include the use of surrender charges or restrictions on withdrawals in some
products. Asset/liability management strategies include the use of derivatives, the purchase of securities structured to protect against prepayments,
prepayment restrictions and related fees on mortgage loans and consistent monitoring of the pricing of the Company’s products in order to better match
the duration of the assets and the liabilities they support.
Equity prices. The Company’s investments in equity securities expose it to changes in equity prices. It manages this risk on an integrated basis
with other risks through its asset/liability management strategies. The Company also manages equity price risk through industry and issuer diversification
and asset allocation techniques.
Foreign currency exchange rates. The Company’s exposure to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates against the U.S. dollar results from
its holdings in non-U.S. dollar denominated fixed maturity securities and equity securities and through its investments in foreign subsidiaries. The principal
currencies which create foreign currency exchange rate risk in the Company’s investment portfolios are Canadian dollars, Euros, Mexican pesos, Chilean
pesos and British pounds. The Company mitigates the majority of its fixed maturities’ foreign currency exchange rate risk through the utilization of foreign
currency swaps and forward contracts. Through its investments in foreign subsidiaries, the Company is primarily exposed to the Euro, Mexican peso and
South Korean won. The Company has denominated substantially all assets and liabilities of its foreign subsidiaries in their respective local currencies,
thereby minimizing its risk to foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations.
MetLife, Inc.
38