Kodak 2010 Annual Report Download - page 84
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 84 of the 2010 Kodak annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
82
Plan Asset Investment Strategy
The investment strategy underlying the asset allocation for the pension assets is to achieve an optimal return on assets with an
acceptable level of risk while providing for the long-term liabilities, and maintaining sufficient liquidity to pay current benefits and
other cash obligations of the plans. This is primarily achieved by investing in a broad portfolio constructed of various asset classes
including equity and equity-like investments, debt and debt-like investments, real estate, private equity and other assets and
instruments. Long duration bonds are used to partially match the long-term nature of plan liabilities. Other investment objectives
include maintaining broad diversification between and within asset classes and fund managers, and managing asset volatility relative
to plan liabilities.
Every three years, or when market conditions have changed materially, each of the Company’s major pension plans will undertake
an asset allocation or asset and liability modeling study. The asset allocation and expected return on the plans’ assets are
individually set to provide for benefits and other cash obligations and within each country’s legal investment constraints.
Actual allocations may vary from the target asset allocations due to market value fluctuations, the length of time it takes to implement
changes in strategy, and the timing of cash contributions and cash requirements of the plans. The asset allocations are monitored,
and are rebalanced in accordance with the policy set forth for each plan.
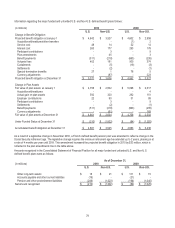
Of the total plan assets attributable to the major U.S. defined benefit plans at December 31, 2010 and 2009, 97% relate to KRIP. The
expected long-term rate of return on plan assets assumption (“EROA”) is based on a combination of formal asset and liability studies
that include forward-looking return expectations given the current asset allocation. During 2009, an asset and liability study was
completed and resulted in an 8.75% EROA for KRIP. A review of the EROA as of December 2010 based upon the current asset
allocation and forward-looking expected returns for the various asset classes in which KRIP invests resulted in an EROA of 8.50%.
The annual expected return on plan assets for the major non-U.S. pension plans range from 3.64% to 8.75% for 2010. EROA
assumptions for 2009 for those plans were based on their respective asset allocations as of the end of the year. As with the KRIP,
the EROA assumptions for certain of the Company’s other pension plans were reassessed as of December 2010. EROA
assumptions for those plans were updated accordingly.
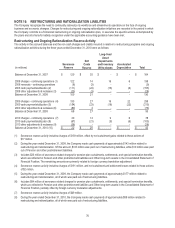
Plan Asset Risk Management
The Company evaluates its defined benefit plans’ asset portfolios for the existence of significant concentrations of risk. Types of
concentrations that are evaluated include, but are not limited to, investment concentrations in a single entity, type of industry, foreign
country, and individual fund. As of December 31, 2010 and 2009, there were no significant concentrations (defined as greater than
10 percent of plan assets) of risk in the Company’s defined benefit plan assets.
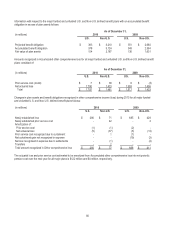
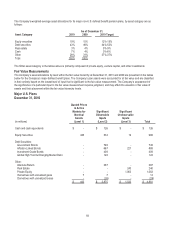
The Company's weighted-average asset allocations for its major U.S. defined benefit pension plans, by asset category, are as
follows:
As of December 31,
Asset Category
2010
2009
2010 Target
Equity securities
20%
21%
18%-27%
Debt securities
45%
45%
41%-47%
Real estate
5%
6%
4%-10%
Cash
3%
2%
0%-3%
Other
27%
26%
24%-30%
Total
100%
100%