Capital One 2004 Annual Report Download - page 74
Download and view the complete annual report
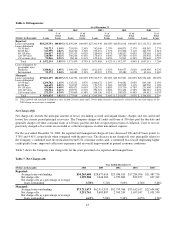
Please find page 74 of the 2004 Capital One annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.cash equivalents at December 31, 2003. As of December 31, 2004, the weighted average life of the investment
securities was approximately 3.6 years. These investment securities, along with cash and cash equivalents,
provide increased liquidity and flexibility to support the Company’s funding requirements.
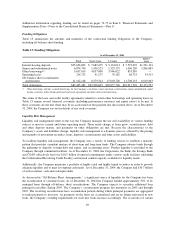
The Company has a $750.0 million credit facility committed through June 2007. The Company may take
advances under the facility subject to covenants and conditions customary in a transaction of this nature. This
facility may be used for general corporate purposes and was not drawn upon at December 31, 2004.
Derivative Instruments
The Company enters into interest rate swap agreements in order to manage interest rate exposure. In most cases,
this exposure is related to the funding of fixed rate assets with floating rate obligations, including off-balance
sheet securitizations. The Company also enters into forward foreign currency exchange contracts and cross
currency swaps to reduce sensitivity to changing foreign currency exchange rates. The hedging of foreign
currency exchange rates is limited to certain intercompany obligations related to international operations. These
derivatives expose the Company to certain credit risks. The Company has established policies and limits, as well
as collateral agreements, to manage credit risk related to derivative instruments.
Additional information regarding derivative instruments can be found on pages 89-91 in Item 8 “Financial
Statements and Supplementary Data—Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements—Note 19”.
Market Risk Management
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk refers to changes in earnings or the net present value of assets and off-balance sheet positions
less liabilities (termed “economic value of equity”) due to interest rate changes. To the extent that managed
interest income and expense do not respond equally to changes in interest rates, or that all rates do not change
uniformly, earnings and economic value of equity could be affected. The Company’s managed net interest
income is affected primarily by changes in short-term interest rates, as variable rate card receivables,
securitization bonds and corporate debts are repriced. The Company manages and mitigates its interest rate
sensitivity through several techniques, which include, but are not limited to, changing the maturity and repricing
characteristics of various balance sheet categories and by entering into interest rate swaps.
The Company’s measurement of interest rate risk considers both earnings and market value exposures. The
consolidated balance sheet and all off-balance sheet positions are included in the analysis. When available,
contractual maturities related to balance sheet and off-balance sheet positions are assumed. Balance sheet
positions lacking contractual maturities and those with a likelihood of maturing prior to their contractual term are
assumed to mature consistent with business line expectations or, when available in the case of marketable
securities, market expectations. The Company’s Asset/Liability Management Policy limits the change in
projected 12-month net interest income due to instantaneous parallel rate shocks of up to 300 basis points to less
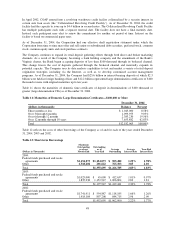
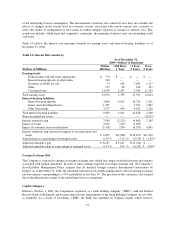
than 3% of base net interest income. As of December 31, 2004 the Company estimated a 2.6% increase in 12
month net interest income for an immediate 300 basis point rate increase and a 2.9% decline in 12 month net
interest income for an immediate 300 basis point rate decline. The impacts to net interest income resulting from
the rate shocks do not consider the impact of loan convexity.
In addition to limits related to possible changes in 12-month net interest income, the Asset/Liability Management
Policy limits the pre-tax change in economic value of equity due to instantaneous parallel rate shocks of 100
basis points to less than 6%. As of December 31, 2004, the estimated reduction in economic value of equity due
to an adverse 100 basis point rate shock is 2.1%.
As of December 31, 2004, the Company was in compliance with all of its interest rate risk management related
policies. The precision of the measures used to manage interest rate risk is limited due to the inherent uncertainty
51