ICICI Bank 2006 Annual Report Download - page 91
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 91 of the 2006 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F32
Dealing in derivatives is carried out by identified groups in the treasury of the Bank based on purpose of transaction.
Derivative transactions are entered into by the treasury front office. Treasury middle office conducts an independent check
of the transactions entered into by the front office and also undertakes activities such as confirmation, settlement, accounting,
risk monitoring and reporting and ensures compliance with various internal and regulatory guidelines.
The market making and the proprietary trading activities in derivatives are governed by the investment policy of the Bank,
which lays down the position limits, stop loss limits as well as other risk limits. The Risk Management Group (“RMG”) lays
down the methodology for computation and monitoring of risk. The Risk Committee of the Board (“RCB”) reviews the
Bank’s risk management policy in relation to various risks (portfolio, liquidity, interest rate, off-balance sheet and operational
risks), investment policies and compliance issues in relation thereto. The RCB comprises of independent directors and the
Managing Director and CEO.
Risk monitoring of the derivatives portfolio is done on a daily basis. The Bank measures and monitors risk using Value at
Risk (“VAR”) approach and the relevant greeks for options. Risk reporting on derivatives forms an integral part of the
management information system and the marked to market position and the VAR of the derivatives portfolio is reported on
a daily basis.
The use of derivatives for hedging purpose is governed by the hedge policy approved by Asset Liability Management
Committee (“ALCO”). Subject to prevailing RBI guidelines, the Bank deals in derivatives for hedging fixed rate, floating rate
or foreign currency assets/ liabilities. Transactions for hedging and market making purposes are recorded separately. For
hedge transactions, the Bank identifies the hedged item (asset or liability) at the inception of the transaction itself. The
effectiveness is assessed at the time of inception of the hedge and periodically thereafter. During the year the Bank changed
its method for testing hedge effectiveness from the price value of basis point (“PVBP”) or duration method to the marked to
market method. Due to this change certain derivative contracts which were hitherto accounted for as hedges, became
ineffective and were accordingly accounted for as trading.
Hedge derivative transactions are accounted for pursuant to the principles of hedge accounting. Derivatives for market
making purpose are marked to market and the resulting gain/loss is recorded in the profit and loss account. Premia on
options are accounted for at the expiry of the options. The Bank makes provisions on the outstanding positions in trading
derivatives for possible adverse movements in underlying. Derivative transactions are covered under International Swap
Dealers Association (‘’ISDA’’) master agreements with the respective counterparties. The credit exposure on account of
derivative transactions is computed as per RBI guidelines and is marked against the credit limits approved for the respective
counterparties.
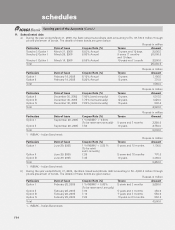
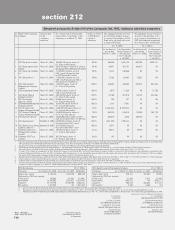
Rupees in million
As on March 31, 2006
Sr. Currency Interest
No. Particular derivatives 1 rate derivatives 2
1. Derivatives (Notional principal amount)
a) For hedging ................................................................................ — 41,252.2
b) For trading .................................................................................. 428,580.4 2,174,510.4
2. Marked to market positions 3
a) Asset (+) .................................................................................... 2,150.3 1,963.2
b) Liability (-) ................................................................................... ——
3. Credit exposure ................................................................................. 21,458.8 28,170.8
4. Likely impact of one percentage change in interest rate (100*PV01)
a) on hedging derivatives 4............................................................ — (1,230.8)
b) on trading derivatives ................................................................ 1,087.0 900.9
5. Maximum and minimum of 100*PV01 observed during the year
a) on hedging4
Maximum ................................................................................... — 838.4
Minimum.................................................................................... (74.4) (1,230.8)
b) on trading
Maximum ................................................................................... 1,119.8 1,097.5
Minimum.................................................................................... 632.8 (1,439.1)
1. Options & Cross Currency Interest Rate Swaps are included in currency derivatives.
2. Foreign currency Interest Rate Swaps, Forward Rate Agreements and swaptions are included in interest rate derivatives.
3. For trading portfolio.
4. The swap contracts entered for hedging purpose would have an opposite and offsetting impact with the underlying
on-balance sheet items.
forming part of the Accounts (Contd.)
schedules