ICICI Bank 2006 Annual Report Download - page 73
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 73 of the 2006 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
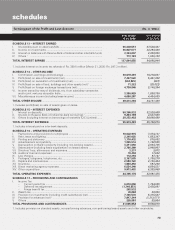
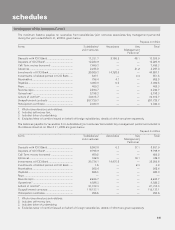
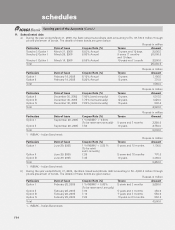
F14
forming part of the Accounts (Contd.)
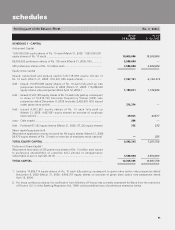
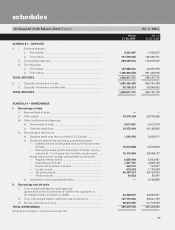
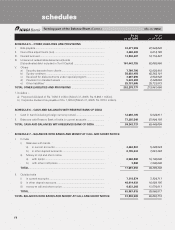
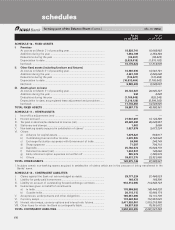
schedules
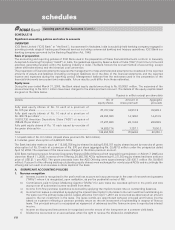
namely insignificant, low, moderate, high, very high, restricted and off-credit and provisioning made on exposures
exceeding 90 days on a graded scale ranging from 0.25% to 100%. For exposures with contractual maturity of less
than 90 days, 25% of the normal provision requirement is held. If the country exposure (net) of the Bank in respect of
each country does not exceed 1% of the total funded assets, no provision is maintained on such country exposure.
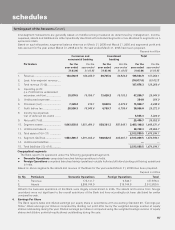
4. Transfer and servicing of financial assets
The Bank transfers commercial and consumer loans through securitisation transactions. The transferred loans are
de-recognised and gains/losses are recorded only if the Bank surrenders the rights to benefits specified in the loan contract.
Recourse and servicing obligations are reduced from proceeds of the sale. Retained beneficial interests in the loans is
measured by allocating the carrying value of the loans between the assets sold and the retained interest, based on the
relative fair value at the date of the securitisation.
During the year RBI has issued guidelines on accounting for securitisation of standard assets. In accordance with these
guidelines, with effect from February 1, 2006, the Bank accounts for any loss arising on sale immediately at the time of sale
and the profit/premium arising on account of sale is amortised over the life of the securities issued or to be issued by the
special purpose vehicle/special purpose entity to which the assets are sold.
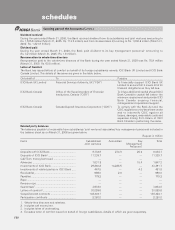
5. Fixed assets and depreciation
a) Premises and other fixed assets are carried at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is charged over the
estimated useful life of a fixed asset on a straight-line basis. The rates of depreciation for fixed assets, which are not
lower than the rates prescribed in schedule XIV of the Companies Act, 1956, are given below.
Asset Depreciation Rate
Premises owned by the Bank ................................................................................... 1.63%
Improvements to leasehold premises ...................................................................... 1.63% or over the lease period,
whichever is higher
ATMs ......................................................................................................................... 12.50%
Plant and machinery like air conditioners, xerox machines, etc. ............................. 10.00%
Computers ................................................................................................................ 33.33%
EDC Terminals ........................................................................................................... 16.67%
Furniture and fixtures ................................................................................................ 15.00%
Motor vehicles .......................................................................................................... 20.00%
Others (including Software and system development expenses) ........................... 25.00%
b) Depreciation on leased assets is made on a straight-line basis at the higher of the rates determined with reference to
the primary period of lease and the rates specified in Schedule XIV to the Companies Act, 1956.
c) Assets purchased/sold during the year are depreciated on the basis of actual number of days the asset has been put
to use.
d) Items costing less than Rs.5,000/- are depreciated fully over a period of 12 months from the date of purchase.
6. Foreign currency transactions
a) Foreign currency income and expenditure items of domestic operations are translated at the exchange rates prevailing
on the date of the transaction, income and expenditure items of integral foreign operations (representative offices) are
translated at weekly average closing rate, and income and expenditure of non-integral foreign operations (foreign
branches and offshore banking units) are translated at quarterly average closing rate.
b) Monetary foreign currency assets and liabilities of domestic and integral foreign operations are translated at closing
exchange rates notified by Foreign Exchange Dealers’ Association of India (“FEDAI”) at the balance sheet date and the
resulting profits/losses are included in the profit and loss account.
c) Both monetary and non-monetary foreign currency assets and liabilities of non-integral foreign operations are translated
at closing exchange rates notified by FEDAI at the balance sheet date and the resulting profits/losses from exchange
differences are accumulated in the foreign currency translation reserve until the disposal of the net investment in the
non-integral foreign operations.
d) Outstanding forward exchange contracts are revalued at the exchange rates notified by FEDAI for specified maturities
and at interpolated rates for contracts of in-between maturities. The resultant gains or losses are recognised in the
profit and loss account.
e) Contingent liabilities on account of guarantees, endorsements and other obligations are stated at the exchange rates
notified by FEDAI at the balance sheet date.
7. Accounting for derivative contracts
The Bank enters into derivative contracts such as foreign currency options, interest rate and currency swaps and cross
currency interest rate swaps to hedge on-balance sheet/off-balance sheet assets and liabilities or for trading purposes.
The swap contracts entered to hedge on-balance sheet assets and liabilities are structured in such a way that they bear an
opposite and offsetting impact with the underlying on-balance sheet items. The impact of such derivative instruments is
correlated with the movement of underlying assets and accounted pursuant to the principles of hedge accounting.
Foreign currency and rupee derivatives, which are entered for trading purposes, are marked to market and the resulting
gain/loss, (net of provisions, if any) is recorded in the profit and loss account.