ICICI Bank 2006 Annual Report Download - page 111
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 111 of the 2006 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F52
During the year ended March 31, 2005, the Bank issued 115,920,758 equity shares (including 6,992,187 equity shares issued by
exercise of green shoe option) of Rs. 10 each at a premium of Rs. 270 per share aggregating Rs. 32,457.8 million under the
prospectus dated April 12, 2004. The expenses of the issue have been charged to the share premium account.
During the year ended March 31, 2005, ICICI Bank had sponsored American Depository Shares (ADSs) Offering, which opened
for participation on March 7, 2005 and closed on March 11, 2005. In terms of the Offering, 20,685,750 ADSs representing
41,371,500 equity shares had been sold at a price of US$ 21.1 per ADS. The gross proceeds from the ADS Offering were
approximately US$ 436.7million (Rs. 19,099.6 million). Pursuant to this offering, existing outstanding equity shares were exchanged
for newly issued ADSs and accordingly the offering did not result in an increase in share capital of the Bank.
A. SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
1. Foreign currency transactions
The consolidated financial statements are reported in Indian rupees (Rs.), the national currency of India. Foreign currency
income and expenditure items are translated as follows:
a. For domestic operations at the exchange rates prevailing on the date of the transaction with the resultant gain or loss
accounted for in the profit and loss account;
b. For integral foreign operations (representative offices), at weekly average closing rate with the resultant gain or loss
accounted for in the profit and loss account. AS 11 (revised) on “The effects of changes in foreign exchange rates”
issued by the ICAI defines an integral foreign operation as a subsidiary, associate, joint venture or branch of the reporting
enterprise, the activities of which are based or conducted in a country other than the country of the reporting enterprise
but are an integral part of the reporting enterprise;
c. For non-integral foreign operations (foreign branches and off-shore banking units), at quarterly average closing rate with
the resultant gains or losses accounted for as foreign currency translation reserve.
Monetary foreign currency assets and liabilities of domestic and integral foreign operations are translated at closing exchange
rates notified by Foreign Exchange Dealers’ Association of India (“FEDAI”) at the balance sheet date and the resulting
profits/losses are included in the profit and loss account.
Both monetary and non-monetary foreign currency assets and liabilities of non- integral foreign operations are translated at
closing exchange rates notified by FEDAI at the balance sheet date and the resulting profit/loss on exchange differences
are accumulated in the foreign currency translation reserve until the disposal of the net investment in the non-integral
foreign operations.
Outstanding forward exchange contracts are revalued at the exchange rates notified by FEDAI for specified maturities and
at interpolated rates for contracts of in-between maturities. The resultant gains or losses are recognised in the profit and
loss account.
Contingent liabilities on account of guarantees, endorsements and other obligations are stated at the exchange rates
notified by FEDAI at the balance sheet date.
2. Revenue recognition
Interest income on loans and advances is accounted on an accrual basis except in the case of loan exposures classified as
non-performing assets (“NPAs”) or bad and doubtful loans where it is recognised, on a cash basis, as per the prudential
norms of RBI.
Commissions paid to direct marketing agents (“DMAs”) for auto loans, is recorded upfront in the profit and loss account net
of subvention income received from them.
Income from hire purchase operations is accrued by applying the interest rate implicit on outstanding balances.
Income from leases is calculated by applying the interest rate implicit in the lease to the net investment outstanding on the
lease over the primary lease period. Leases effective from April 1, 2001 are accounted as advances at an amount equal to
the net investment in the lease. The lease rentals are apportioned between principal and finance income based on a pattern
reflecting a constant periodic return on the net investment outstanding in respect of finance lease. The principal amount is
recognised as repayment of advances and the finance income is reported as interest income. Income on discounted
instruments is recognised over the tenure of the instrument on a constant yield basis.
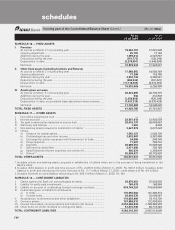
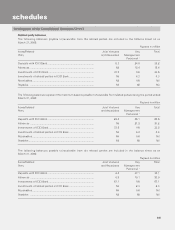
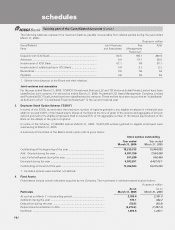
schedules
forming part of the Consolidated Accounts (Contd.)