Kroger 2015 Annual Report Download - page 127
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 127 of the 2015 Kroger annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
A-53
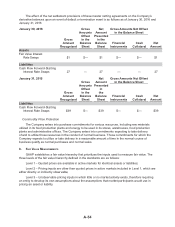
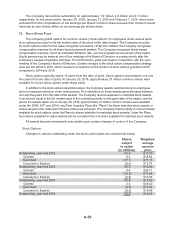
As of January 31, 2015, the Company had four forward-starting interest rate swap agreements with
maturity dates of October 2015 with an aggregate notional amount totaling $300 and seven forward-
starting interest rate swap agreements with maturity dates of August 2017 with an aggregate notional
amount totaling $400. The Company entered into these forward-starting interest rate swaps in order
to lock in fixed interest rates on its forecasted issuances of debt in October 2015 and August 2017.
Accordingly, the forward-starting interest rate swaps were designated as cash-flow hedges as defined by
GAAP. As of January 31, 2015, the fair value of the interest rate swaps was recorded in other long-term
liabilities for $39 and accumulated other comprehensive loss for $25 net of tax.
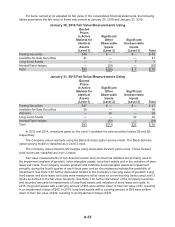
During 2015, the Company terminated eight forward-starting interest rate swap agreements with
maturity dates of October 2015 and January 2016 with an aggregate notional amount totaling $600. Four
of these forward-starting interest rate swap agreements, with an aggregate notional amount totaling
$300, were entered into and terminated in 2015. These forward-starting interest rate swap agreements
were hedging the variability in future benchmark interest payments attributable to changing interest rates
on the forecasted issuance of fixed-rate debt issued in 2015. As discussed in Note 6, the Company
issued $1,100 of senior notes in 2015. Since these forward-starting interest rate swap agreements were
classified as cash flow hedges, the unamortized loss of $17, $11 net of tax, has been deferred in AOCI
and will be amortized to earnings as the interest payments are made.
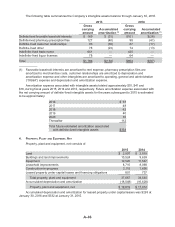
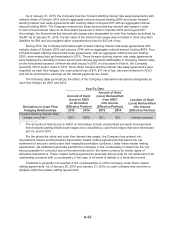
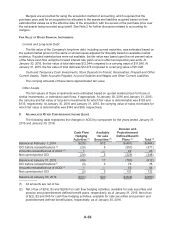
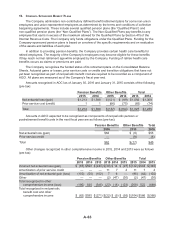
The following table summarizes the effect of the Company’s derivative instruments designated as
cash flow hedges for 2015 and 2014:
Year-To-Date
Derivatives in Cash Flow
Hedging Relationships
Amount of Gain/
(Loss) in AOCI
on Derivative
(Effective Portion)
Amount of Gain/
(Loss) Reclassified
from AOCI
into Income
(Effective Portion)
Location of Gain/
(Loss) Reclassified
into Income
(Effective Portion)2015 2014 2015 2014
Forward-Starting Interest Rate
Swaps, net of tax* $(51) $(49) $(1) $(1) Interest expense
* The amounts of Gain/(Loss) in AOCI on derivatives include unamortized proceeds and payments
from forward-starting interest rate swaps once classified as cash flow hedges that were terminated
prior to end of 2015.
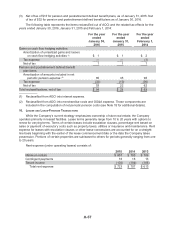
For the above fair value and cash flow interest rate swaps, the Company has entered into
International Swaps and Derivatives Association master netting agreements that permit the net
settlement of amounts owed under their respective derivative contracts. Under these master netting
agreements, net settlement generally permits the Company or the counterparty to determine the net
amount payable for contracts due on the same date and in the same currency for similar types of
derivative transactions. These master netting agreements generally also provide for net settlement of all
outstanding contracts with a counterparty in the case of an event of default or a termination event.
Collateral is generally not required of the counterparties or of the Company under these master
netting agreements. As of January 30, 2016 and January 31, 2015, no cash collateral was received or
pledged under the master netting agreements.