Kroger 2015 Annual Report Download - page 125
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 125 of the 2015 Kroger annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
A-51
Most of the Company’s outstanding public debt is subject to early redemption at varying times
and premiums, at the option of the Company. In addition, subject to certain conditions, some of the
Company’s publicly issued debt will be subject to redemption, in whole or in part, at the option of the
holder upon the occurrence of a redemption event, upon not less than five days’ notice prior to the date
of redemption, at a redemption price equal to the default amount, plus a specified premium. “Redemption
Event” is defined in the indentures as the occurrence of (i) any person or group, together with any affiliate
thereof, beneficially owning 50% or more of the voting power of the Company, (ii) any one person or
group, or affiliate thereof, succeeding in having a majority of its nominees elected to the Company’s
Board of Directors, in each case, without the consent of a majority of the continuing directors of the
Company or (iii) both a change of control and a below investment grade rating.
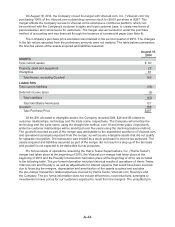
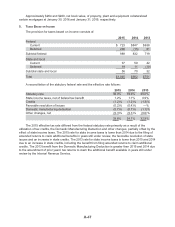
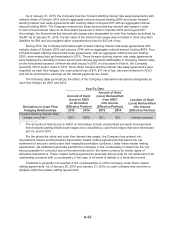
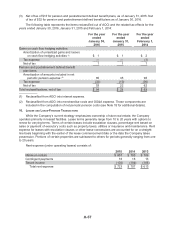
The aggregate annual maturities and scheduled payments of long-term debt, as of year-end 2015,
and for the years subsequent to 2015 are:
2016 $ 2,318
2017 735
2018 1,307
2019 774
2020 724
Thereafter 5,538
Total debt $11,396
7. DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
GAAP defines derivatives, requires that derivatives be carried at fair value on the balance sheet,
and provides for hedge accounting when certain conditions are met. The Company’s derivative financial
instruments are recognized on the balance sheet at fair value. Changes in the fair value of derivative
instruments designated as “cash flow” hedges, to the extent the hedges are highly effective, are recorded
in other comprehensive income, net of tax effects. Ineffective portions of cash flow hedges, if any, are
recognized in current period earnings. Other comprehensive income or loss is reclassified into current
period earnings when the hedged transaction affects earnings. Changes in the fair value of derivative
instruments designated as “fair value” hedges, along with corresponding changes in the fair values of
the hedged assets or liabilities, are recorded in current period earnings. Ineffective portions of fair value
hedges, if any, are recognized in current period earnings.
The Company assesses, both at the inception of the hedge and on an ongoing basis, whether
derivatives used as hedging instruments are highly effective in offsetting the changes in the fair value or
cash flow of the hedged items. If it is determined that a derivative is not highly effective as a hedge or
ceases to be highly effective, the Company discontinues hedge accounting prospectively.
Interest Rate Risk Management
The Company is exposed to market risk from fluctuations in interest rates. The Company manages
its exposure to interest rate fluctuations through the use of a commercial paper program, interest rate
swaps (fair value hedges) and forward-starting interest rate swaps (cash flow hedges). The Company’s
current program relative to interest rate protection contemplates hedging the exposure to changes in
the fair value of fixed-rate debt attributable to changes in interest rates. To do this, the Company uses
the following guidelines: (i) use average daily outstanding borrowings to determine annual debt amounts
subject to interest rate exposure, (ii) limit the average annual amount subject to interest rate reset and the
amount of floating rate debt to a combined total of $2,500 or less, (iii) include no leveraged products, and
(iv) hedge without regard to profit motive or sensitivity to current mark-to-market status.